Raster graphics consist of pixels and are ideal for detailed images like photographs, offering rich color depth but losing quality when scaled. Vector graphics use mathematical formulas to create shapes, enabling infinite scalability without distortion, perfect for logos and illustrations. Choosing between raster and vector depends on the project's needs for resolution, scalability, and editing flexibility.
Table of Comparison
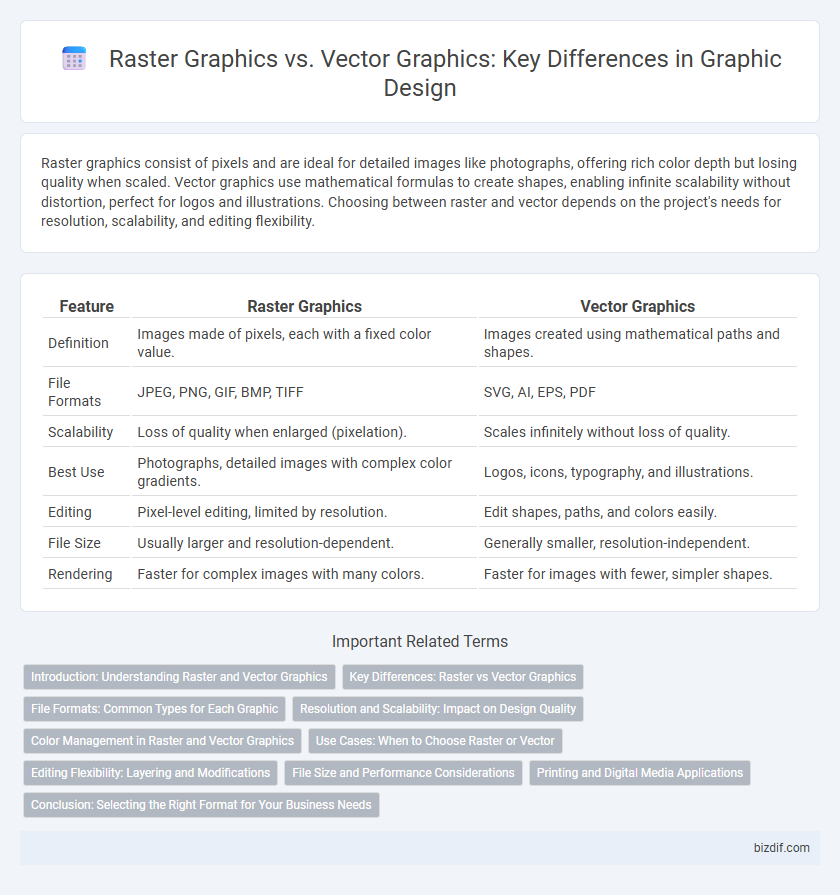
| Feature | Raster Graphics | Vector Graphics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Images made of pixels, each with a fixed color value. | Images created using mathematical paths and shapes. |
| File Formats | JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, TIFF | SVG, AI, EPS, PDF |
| Scalability | Loss of quality when enlarged (pixelation). | Scales infinitely without loss of quality. |
| Best Use | Photographs, detailed images with complex color gradients. | Logos, icons, typography, and illustrations. |
| Editing | Pixel-level editing, limited by resolution. | Edit shapes, paths, and colors easily. |
| File Size | Usually larger and resolution-dependent. | Generally smaller, resolution-independent. |
| Rendering | Faster for complex images with many colors. | Faster for images with fewer, simpler shapes. |
Introduction: Understanding Raster and Vector Graphics
Raster graphics consist of pixel-based images, ideal for detailed and complex color variations, commonly used in photographs and digital paintings. Vector graphics use mathematical equations to create shapes and lines, making them scalable without loss of quality, perfect for logos and illustrations. Understanding the differences between raster and vector formats is essential for selecting the right design approach based on project requirements and output needs.
Key Differences: Raster vs Vector Graphics
Raster graphics are composed of pixels, making them ideal for detailed images like photographs but prone to quality loss when scaled. Vector graphics use mathematical formulas to create shapes and lines, allowing infinite scalability without resolution degradation. Key differences include file size, scalability, and suitability for different design projects, with raster preferred for rich, complex images and vector best for logos and illustrations.
File Formats: Common Types for Each Graphic
Raster graphics commonly use file formats such as JPEG, PNG, GIF, and BMP, which store images as pixels and are ideal for detailed photographs and complex color variations. Vector graphics often utilize formats like SVG, AI, EPS, and PDF, which store images as paths and shapes, allowing for infinite scalability without loss of quality. Choosing between raster and vector formats depends on the project's requirements for resolution, scalability, and editing flexibility.
Resolution and Scalability: Impact on Design Quality
Raster graphics consist of pixels, causing resolution loss and pixelation when scaled beyond their original size, which diminishes design quality. Vector graphics use mathematically defined paths, enabling infinite scalability without compromising resolution or sharpness. This distinction critically affects design quality, especially for projects requiring various output sizes such as logos, posters, and digital illustrations.
Color Management in Raster and Vector Graphics
Raster graphics use pixels to represent images, making color management crucial for maintaining accurate hues and gradients through color profiles such as sRGB and Adobe RGB. Vector graphics utilize mathematical equations to define shapes, allowing for scalable designs without color distortion, often relying on spot colors and ICC profiles for consistent color reproduction. Effective color management in both formats ensures precise color matching across different devices and print outputs, essential for high-quality graphic design projects.
Use Cases: When to Choose Raster or Vector
Raster graphics excel in complex images with rich color gradients, such as photographs and detailed digital paintings, making them ideal for web images and print media requiring high resolution. Vector graphics are best suited for logos, icons, and scalable graphics that need to maintain crisp edges at any size, commonly used in branding, typography, and CAD designs. Choosing between raster and vector depends on the project's need for scalability versus detail and color depth.
Editing Flexibility: Layering and Modifications
Raster graphics rely on pixels, making detailed edits challenging without quality loss, while vector graphics use mathematical paths that allow infinite scaling and precise modifications. Layering in vector graphics offers superior editing flexibility, enabling designers to manipulate individual elements independently. This advantage streamlines complex projects by preserving image clarity and facilitating quick adjustments.
File Size and Performance Considerations
Raster graphics, composed of pixels, often result in larger file sizes compared to vector graphics, which use mathematical equations to define shapes, optimizing storage efficiency. High-resolution raster images can slow down software performance due to increased memory usage, while vector graphics maintain consistent performance regardless of scaling. Choosing vector graphics is ideal for projects requiring frequent resizing without quality loss, whereas raster graphics are suited for detailed images like photographs despite higher file size demands.
Printing and Digital Media Applications
Raster graphics consist of pixels, making them ideal for detailed and photorealistic images in digital media, but they lose quality when scaled for large print formats. Vector graphics use mathematical paths, ensuring sharp, scalable images that are essential for logos and illustrations in both printing and digital media. The choice between raster and vector impacts print resolution, file size, and versatility across platforms.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Format for Your Business Needs
Choosing between raster and vector graphics depends on your business's specific needs: raster images excel in detailed, complex visuals like photographs but lose quality when scaled, making them ideal for digital use and print at fixed sizes. Vector graphics maintain crispness at any size, perfect for logos, icons, and branding materials that require scalability and versatility across various media. Prioritize vector formats for flexible design applications and raster formats when working with intricate, color-rich images.
Raster graphics vs Vector graphics Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com