Slow craft emphasizes quality, sustainability, and the artisan's personal touch, resulting in unique, durable products that honor traditional techniques. Fast manufacturing prioritizes speed, mass production, and cost efficiency, often sacrificing individuality and environmental impact for rapid market turnaround. Embracing slow craft fosters cultural preservation and mindful consumption, contrasting sharply with the disposable nature typical of fast-manufactured goods.
Table of Comparison
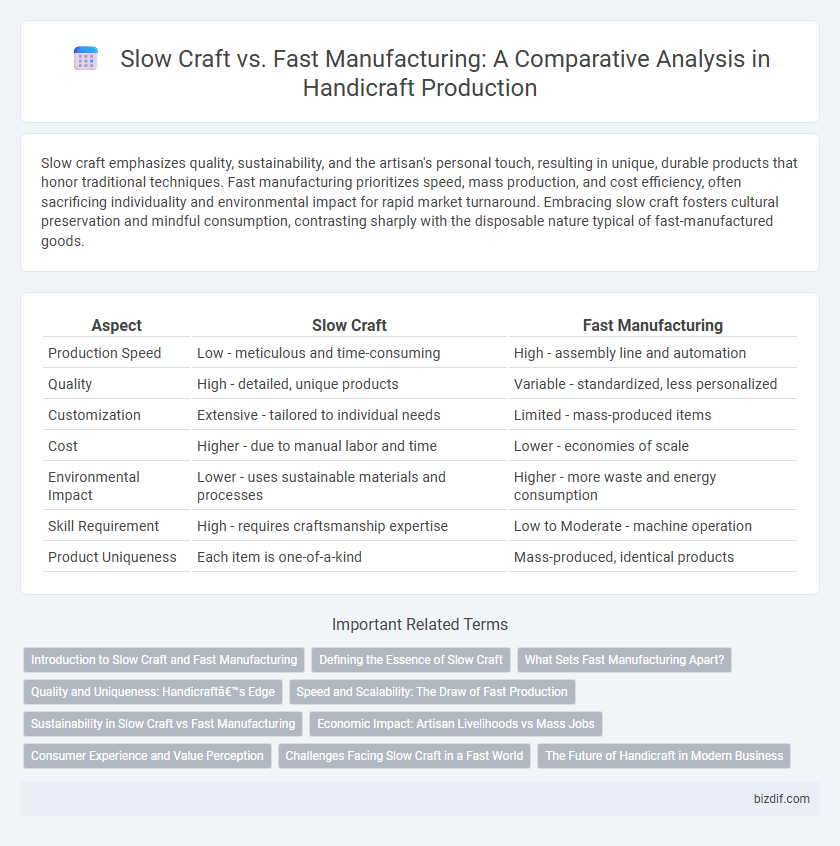
| Aspect | Slow Craft | Fast Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Low - meticulous and time-consuming | High - assembly line and automation |
| Quality | High - detailed, unique products | Variable - standardized, less personalized |
| Customization | Extensive - tailored to individual needs | Limited - mass-produced items |
| Cost | Higher - due to manual labor and time | Lower - economies of scale |
| Environmental Impact | Lower - uses sustainable materials and processes | Higher - more waste and energy consumption |
| Skill Requirement | High - requires craftsmanship expertise | Low to Moderate - machine operation |
| Product Uniqueness | Each item is one-of-a-kind | Mass-produced, identical products |
Introduction to Slow Craft and Fast Manufacturing
Slow craft emphasizes traditional techniques, quality materials, and mindful production, fostering unique, durable products with cultural significance. Fast manufacturing prioritizes speed, cost-efficiency, and mass production, often relying on automation and standardized processes to meet high demand. This contrast highlights the trade-off between artisanal value and industrial scalability in the handicraft industry.
Defining the Essence of Slow Craft
Slow craft embodies the meticulous art of creating handmade products with intentionality, prioritizing quality, tradition, and sustainability over mass production. This approach emphasizes the unique value of each piece, fostering a deep connection between the artisan and their craft. By resisting the pressures of fast manufacturing, slow craft preserves cultural heritage and promotes environmentally conscious practices.
What Sets Fast Manufacturing Apart?
Fast manufacturing distinguishes itself through high-speed production processes powered by advanced machinery and automation, enabling mass output with consistent quality. It leverages standardized designs and materials to minimize production time and reduce costs, meeting large-scale market demands efficiently. Efficiency, scalability, and rapid turnaround are key factors that set fast manufacturing apart from traditional slow craft methods.
Quality and Uniqueness: Handicraft’s Edge
Handicraft products excel in quality and uniqueness by emphasizing meticulous attention to detail and individualized craftsmanship, often resulting in durable and bespoke items. Slow craft methods allow artisans to infuse cultural stories and personal touches into each piece, setting them apart from the uniformity of fast manufacturing. This commitment to originality and superior materials gives handicrafts a distinctive edge in markets saturated with mass-produced goods.
Speed and Scalability: The Draw of Fast Production
Fast manufacturing prioritizes speed and scalability, enabling large-scale production to meet high market demand efficiently. Unlike slow craft processes, which emphasize meticulous handmade quality and limited output, fast production uses automated techniques to reduce time-to-market significantly. This approach appeals to industries requiring rapid product turnover and consistent bulk supply, though it may sacrifice uniqueness and artisanal detail inherent in handicrafts.
Sustainability in Slow Craft vs Fast Manufacturing
Slow craft prioritizes sustainability by using eco-friendly materials and minimizing waste through meticulous, hands-on production processes. Fast manufacturing often relies on mass production techniques that generate significant environmental pollution and resource depletion. Emphasizing slow craft supports circular economy principles and reduces carbon footprints compared to the high energy consumption characteristic of fast manufacturing.
Economic Impact: Artisan Livelihoods vs Mass Jobs
Slow craft sustains artisan livelihoods by preserving traditional skills and generating higher-value, unique products that often command premium prices in niche markets. Fast manufacturing creates mass jobs through large-scale production but frequently leads to lower wages and job insecurity due to automation and cost-cutting measures. The economic impact balances the preservation of cultural heritage and quality with the demand for affordable, widely accessible goods.
Consumer Experience and Value Perception
Slow craft emphasizes artisanal quality and unique, handcrafted details that enhance the consumer experience through emotional connection and authenticity, fostering stronger value perception. Fast manufacturing prioritizes efficiency and mass production, often compromising individuality and craftsmanship, which can lead to a diminished sense of exclusivity and reduced perceived value. Consumers increasingly seek slow-crafted products for their durability and story, valuing the tangible and intangible benefits that fast-manufactured goods rarely provide.
Challenges Facing Slow Craft in a Fast World
Slow craft faces significant challenges in a fast-paced world dominated by mass production, including limited scalability and higher production costs. Artisans struggle with consumer demand for instant gratification, which fast manufacturing meets through rapid, low-cost output. Maintaining quality and authenticity while competing with inexpensive, machine-made alternatives remains a critical hurdle for slow craft practitioners.
The Future of Handicraft in Modern Business
Slow craft emphasizes quality, tradition, and sustainability, contrasting sharply with the speed and mass production of fast manufacturing. The future of handicraft in modern business hinges on integrating artisanal skills with innovative technologies to meet growing consumer demand for unique, eco-friendly products. Embracing this fusion positions handicrafts as valuable assets in differentiating brands and fostering long-term customer loyalty.
Slow Craft vs Fast Manufacturing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com