Gemstone setting involves securely mounting precious stones into jewelry using metal prongs, bezels, or channels, ensuring durability and enhancing the gem's natural brilliance. Resin casting, by contrast, creates vibrant, customizable pieces by embedding materials or pigments in liquid resin that hardens into a solid form around molds or inclusions. Both techniques offer unique aesthetic and functional qualities, with gemstone setting emphasizing traditional elegance and resin casting enabling innovative, contemporary designs.
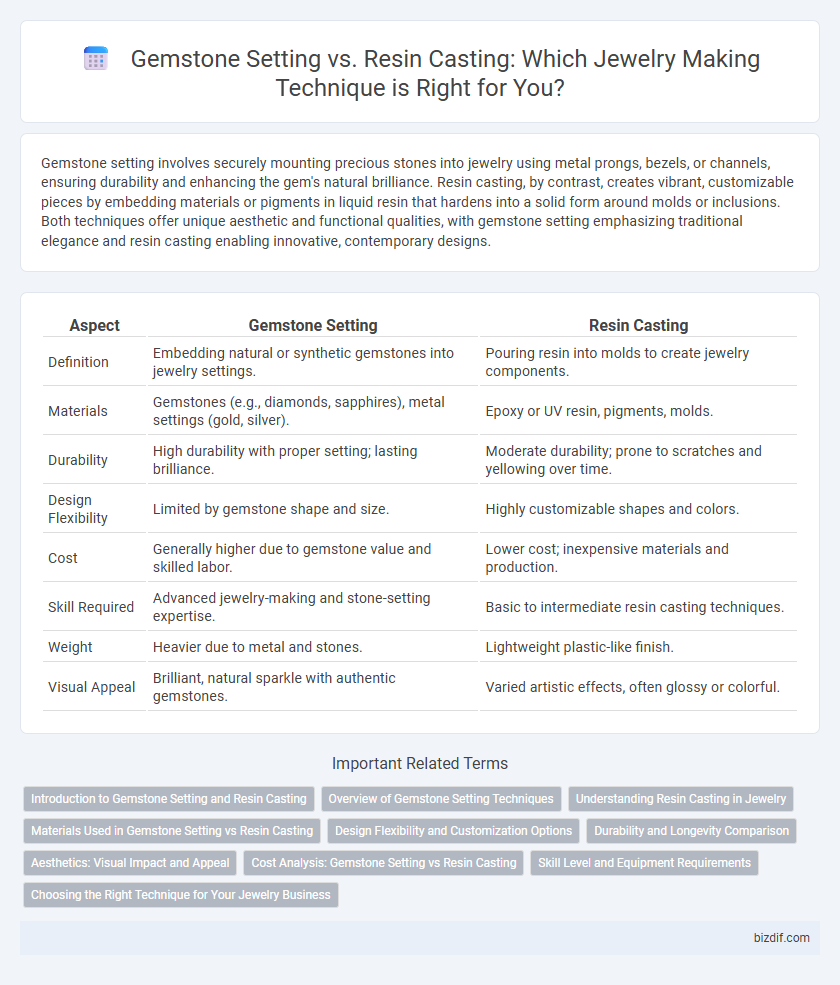
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Gemstone Setting | Resin Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Embedding natural or synthetic gemstones into jewelry settings. | Pouring resin into molds to create jewelry components. |
| Materials | Gemstones (e.g., diamonds, sapphires), metal settings (gold, silver). | Epoxy or UV resin, pigments, molds. |
| Durability | High durability with proper setting; lasting brilliance. | Moderate durability; prone to scratches and yellowing over time. |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by gemstone shape and size. | Highly customizable shapes and colors. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to gemstone value and skilled labor. | Lower cost; inexpensive materials and production. |
| Skill Required | Advanced jewelry-making and stone-setting expertise. | Basic to intermediate resin casting techniques. |
| Weight | Heavier due to metal and stones. | Lightweight plastic-like finish. |
| Visual Appeal | Brilliant, natural sparkle with authentic gemstones. | Varied artistic effects, often glossy or colorful. |
Introduction to Gemstone Setting and Resin Casting
Gemstone setting involves securely embedding precious or semi-precious stones into metal frameworks, enhancing both durability and aesthetic appeal in jewelry pieces. Resin casting utilizes liquid resin poured into molds to create custom shapes that mimic gemstones or incorporate real inclusions for unique designs. These techniques differ in materials, processes, and final appearance, catering to diverse creative expressions in jewelry making.
Overview of Gemstone Setting Techniques
Gemstone setting techniques, essential in jewelry making, include prong, bezel, channel, and pave settings, each offering unique ways to secure and highlight gems. Prong settings elevate the gemstone for maximum light exposure, while bezel settings encircle the stone with metal for enhanced protection. Channel and pave settings integrate multiple stones seamlessly into the design, ensuring both security and visual appeal.
Understanding Resin Casting in Jewelry
Resin casting in jewelry involves pouring liquid resin into molds to create intricate shapes, often incorporating gemstones or decorative elements for added visual appeal. This technique allows for greater versatility and customization compared to traditional gemstone setting, enabling the creation of lightweight, colorful, and complex designs. Understanding the properties of different resins, such as epoxy or UV resin, is crucial for achieving durability and clarity in finished pieces.
Materials Used in Gemstone Setting vs Resin Casting
Gemstone setting typically involves precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum as the primary materials to securely hold natural or synthetic gemstones, emphasizing durability and aesthetic appeal. Resin casting uses liquid polymer resins, often combined with pigments, inclusions, or molds, allowing for creative freedom and versatility in producing lightweight, custom-shaped jewelry components. The choice of materials directly influences the piece's longevity, appearance, and overall value, distinguishing traditional gemstone settings from the modern resin casting technique.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
Gemstone setting offers precise design flexibility by allowing jewelers to incorporate specific gems, shapes, and arrangements tailored to individual preferences, ensuring high craftsmanship and durability. Resin casting provides extensive customization options, enabling the creation of intricate, lightweight designs with vibrant colors and embedded elements, ideal for experimental and contemporary jewelry styles. Both techniques cater to distinct creative needs depending on the desired aesthetic and functional outcome.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Gemstone setting offers superior durability and longevity due to the hardness and natural resilience of precious and semi-precious stones, ensuring long-term wear without significant deterioration. Resin casting, while versatile and customizable, tends to be less durable, as resin can scratch, yellow, or become brittle over time when exposed to UV light and environmental factors. For jewelry pieces intended to last decades, traditional gemstone setting remains the preferred method for maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Aesthetics: Visual Impact and Appeal
Gemstone setting offers a timeless and luxurious appeal through the natural sparkle and depth of precious stones, enhancing the jewelry's visual richness and authenticity. Resin casting allows for vibrant color customization and intricate design details, providing a modern and versatile aesthetic with a smooth, glass-like finish. Both techniques influence the jewelry's overall allure, with gemstone settings emphasizing elegance and resin casting highlighting creativity and boldness.
Cost Analysis: Gemstone Setting vs Resin Casting
Gemstone setting typically involves higher costs due to the price of natural stones and skilled labor required for precise placement and secure mounting. Resin casting offers a more affordable alternative, with lower material expenses and faster production times, making it ideal for budget-conscious jewelry designers. Comparing both methods, resin casting reduces upfront costs and allows for mass production, while gemstone setting commands premium pricing driven by unique, high-value gems and craftsmanship.
Skill Level and Equipment Requirements
Gemstone setting demands advanced skills in precision and steady hand techniques, requiring specialized tools such as prong pushers, bezel rollers, and ultrasonic cleaners. Resin casting is more accessible to beginners, utilizing basic equipment like silicone molds, resin mixers, and UV lamps, with less emphasis on intricate manual dexterity. Both methods offer unique creative possibilities, but gemstone setting often involves higher investment in training and professional-grade tools.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Jewelry Business
Selecting the appropriate technique between gemstone setting and resin casting hinges on factors such as design complexity, durability requirements, and target market preferences. Gemstone setting offers timeless elegance and long-lasting value, ideal for high-end jewelry with precious stones, while resin casting allows for versatile, lightweight, and cost-effective custom designs, perfect for trend-driven or artisanal pieces. Understanding material behaviors and production scalability ensures optimal results tailored to your jewelry business's niche and customer expectations.
Gemstone setting vs Resin casting Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com