Goldsmithing and silversmithing both involve crafting exquisite jewelry, yet goldsmithing specializes in working with gold, emphasizing its malleability and resistance to tarnish, while silversmithing centers on silver, prized for its bright luster but requiring more frequent polishing. Techniques overlap, including shaping, engraving, and soldering, but the choice of metal influences design durability and maintenance needs. Mastery in either art demands precision and creativity, with gold offering luxury appeal and silver providing affordability and versatility in jewelry crafting.
Table of Comparison
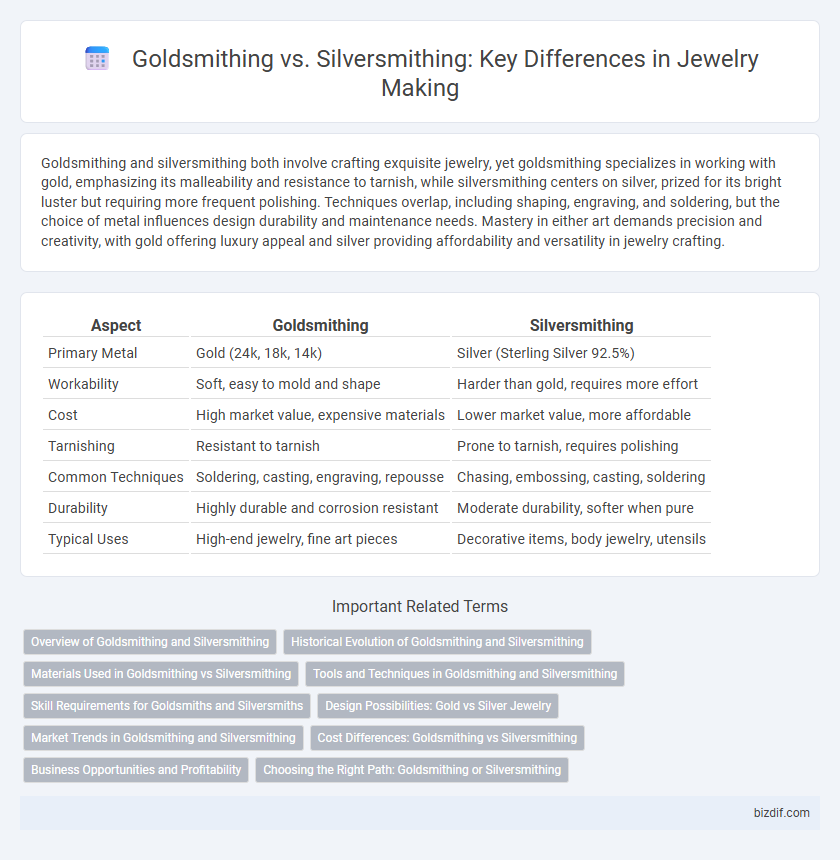
| Aspect | Goldsmithing | Silversmithing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Metal | Gold (24k, 18k, 14k) | Silver (Sterling Silver 92.5%) |
| Workability | Soft, easy to mold and shape | Harder than gold, requires more effort |
| Cost | High market value, expensive materials | Lower market value, more affordable |
| Tarnishing | Resistant to tarnish | Prone to tarnish, requires polishing |
| Common Techniques | Soldering, casting, engraving, repousse | Chasing, embossing, casting, soldering |
| Durability | Highly durable and corrosion resistant | Moderate durability, softer when pure |
| Typical Uses | High-end jewelry, fine art pieces | Decorative items, body jewelry, utensils |
Overview of Goldsmithing and Silversmithing
Goldsmithing involves crafting jewelry primarily from gold, valued for its malleability, durability, and resistance to tarnish, allowing intricate designs and long-lasting pieces. Silversmithing centers on working with silver, prized for its bright luster and affordability but requires protective coatings due to its susceptibility to tarnishing. Both crafts demand specialized skills such as metal alloying, shaping, and finishing techniques, but goldsmithing often caters to luxury markets while silversmithing offers versatile options for decorative and functional items.
Historical Evolution of Goldsmithing and Silversmithing
Goldsmithing and silversmithing have evolved through distinct historical pathways, with goldsmithing dating back to ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt where gold's rarity and malleability symbolized wealth and divine power. Silversmithing gained prominence during the Roman Empire and medieval Europe, valued for its affordability and antimicrobial properties, which made silver a popular choice for both decorative and utilitarian objects. Over centuries, advanced techniques such as filigree in goldsmithing and repousse in silversmithing enhanced craftsmanship, reflecting cultural and technological shifts in jewelry making.
Materials Used in Goldsmithing vs Silversmithing
Goldsmithing primarily utilizes gold alloys such as 14k, 18k, and 24k gold, often mixed with metals like copper and silver to enhance durability and color. Silversmithing focuses on sterling silver, an alloy composed of 92.5% silver and 7.5% other metals, usually copper, to provide strength and resistance to tarnish. The difference in materials affects workability, finish, and the final aesthetic of the crafted jewelry pieces.
Tools and Techniques in Goldsmithing and Silversmithing
Goldsmithing and silversmithing utilize specialized tools such as hammers, anvils, and soldering equipment to shape and join precious metals, with goldsmiths often employing finer tools for intricate detailing on high-karat gold. Techniques in goldsmithing include lost-wax casting, filigree, and granulation, emphasizing precision and delicate artistry, while silversmithing techniques focus on repousse, chasing, and raising to manipulate silver sheets into decorative forms. Both crafts demand mastery of metalworking skills, but the differences in metal properties require tailored approaches in heating, shaping, and finishing processes for optimal results.
Skill Requirements for Goldsmiths and Silversmiths
Goldsmithing demands exceptional precision and a deep understanding of metal properties, given gold's malleability and value, requiring mastery in techniques like soldering, engraving, and stone setting. Silversmithing involves skills tailored to silver's unique characteristics, emphasizing alloy knowledge, oxidation control, and detailed finishing processes to prevent tarnish. Both crafts require refined hand-eye coordination and artistic design capabilities, but goldsmiths often work with higher-value materials necessitating greater attention to detail and durability.
Design Possibilities: Gold vs Silver Jewelry
Goldsmithing offers a rich palette for intricate designs due to gold's malleability and vibrant yellow hue, enabling artisans to create detailed, ornate pieces with enduring luster. Silversmithing provides versatility through silver's reflective surface and affordability, allowing for bold, contemporary designs that can incorporate oxidation or patination techniques to enhance texture and depth. Both metals support diverse styles, but gold lends itself to luxury and classic elegance, while silver favors modern, artistic expressions in jewelry making.
Market Trends in Goldsmithing and Silversmithing
Goldsmithing currently experiences strong market growth driven by high consumer demand for luxury gold jewelry and investment-grade pieces. Silversmithing remains popular due to affordability and trend-driven designs, appealing to younger demographics seeking stylish yet accessible jewelry. Market analysis reveals goldsmithing maintains higher profit margins while silversmithing captures a broader customer base, highlighting distinct opportunities within the jewelry-making industry.
Cost Differences: Goldsmithing vs Silversmithing
Goldsmithing generally incurs higher material costs due to gold's greater market value and density compared to silver, impacting both raw material expenses and tool wear. Silver, being more abundant and affordable, reduces initial investment and is more accessible for entry-level artisans in silversmithing. Labor intensity and finishing processes vary, but the premium for gold craftsmanship primarily stems from gold's intrinsic cost and market demand.
Business Opportunities and Profitability
Goldsmithing often offers higher profit margins due to the intrinsic value and market demand for gold jewelry, appealing to affluent clients seeking luxury items. Silversmithing provides broader business opportunities through affordable product ranges and faster production cycles, attracting a larger customer base. Both crafts require specialized skills, but goldsmithing typically involves higher investment costs and greater returns, while silversmithing allows for more scalable operations in the jewelry market.
Choosing the Right Path: Goldsmithing or Silversmithing
Choosing between goldsmithing and silversmithing depends on the desired aesthetic, material properties, and market demand. Goldsmithing involves working with gold's malleability and intrinsic value, often favored for high-end, intricate jewelry designs. Silversmithing offers affordability and versatility, making it ideal for crafting accessible, stylish pieces with a wide range of finishes and techniques.
Goldsmithing vs Silversmithing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com