Peer feedback encourages collaborative learning by allowing students to engage actively and reflect on language use within their social context, fostering critical thinking and communication skills. Teacher feedback provides expert guidance, ensuring accuracy and addressing nuanced grammatical or pronunciation errors that peers might overlook. Balancing both approaches maximizes language development by combining diverse perspectives with professional expertise.
Table of Comparison
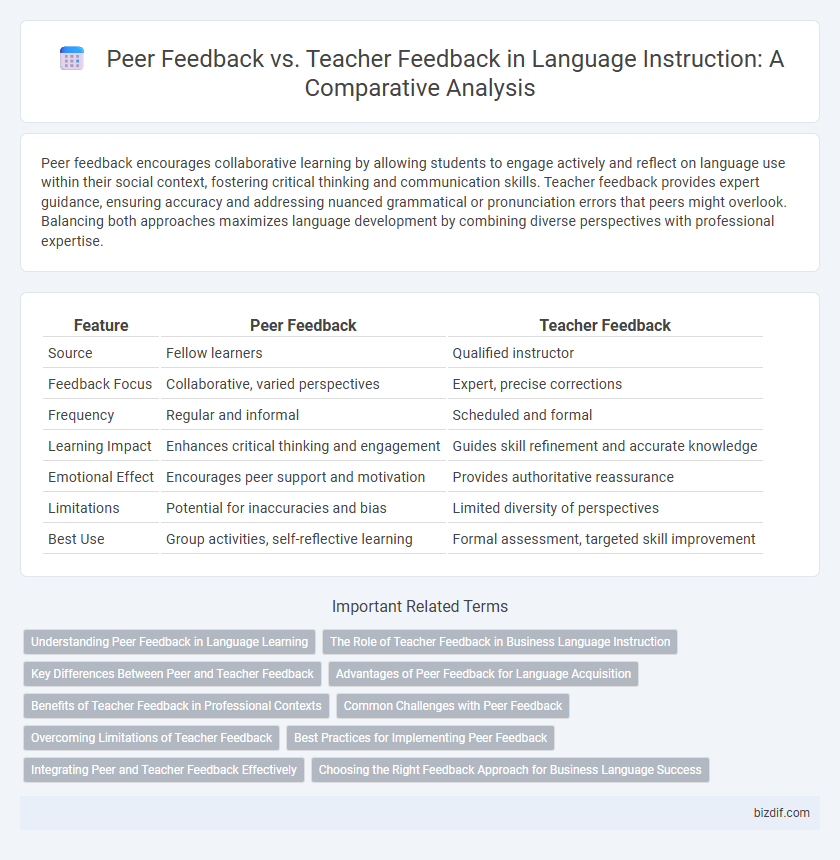
| Feature | Peer Feedback | Teacher Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fellow learners | Qualified instructor |
| Feedback Focus | Collaborative, varied perspectives | Expert, precise corrections |
| Frequency | Regular and informal | Scheduled and formal |
| Learning Impact | Enhances critical thinking and engagement | Guides skill refinement and accurate knowledge |
| Emotional Effect | Encourages peer support and motivation | Provides authoritative reassurance |
| Limitations | Potential for inaccuracies and bias | Limited diversity of perspectives |
| Best Use | Group activities, self-reflective learning | Formal assessment, targeted skill improvement |
Understanding Peer Feedback in Language Learning
Peer feedback in language learning enhances collaborative skills and encourages active engagement by allowing learners to identify and correct errors in real-time. Students develop critical thinking and self-assessment abilities by analyzing peers' language use, leading to deeper comprehension of grammar and vocabulary. Research shows peer feedback fosters a supportive learning environment that complements teacher feedback, promoting greater language proficiency and learner autonomy.
The Role of Teacher Feedback in Business Language Instruction
Teacher feedback in business language instruction plays a critical role in providing expert correction, tailored guidance, and professional communication standards that peer feedback may lack. It enhances learners' proficiency by addressing specific language nuances, industry jargon, and cultural context essential for business interactions. Consistent teacher feedback helps bridge gaps in understanding, ensuring accuracy and clarity in formal business communications.
Key Differences Between Peer and Teacher Feedback
Peer feedback emphasizes collaborative learning and diverse perspectives, encouraging students to develop critical thinking and self-assessment skills, whereas teacher feedback provides expert evaluation, subject-specific insights, and authoritative guidance. Peer feedback often focuses on formative aspects, promoting revision and ongoing improvement, while teacher feedback balances formative and summative assessment, contributing to final grading and curriculum standards. The immediacy and relatability of peer feedback contrast with the depth, accuracy, and structured criteria inherent in teacher feedback, shaping distinct impacts on students' language acquisition and motivation.
Advantages of Peer Feedback for Language Acquisition
Peer feedback enhances language acquisition by promoting active engagement and critical thinking among learners, facilitating deeper cognitive processing of linguistic structures. It creates opportunities for authentic communication in a low-pressure environment, increasing learners' confidence and willingness to experiment with language. Collaborative interaction during peer feedback supports the development of pragmatic skills and cultural awareness, essential components of effective language use.
Benefits of Teacher Feedback in Professional Contexts
Teacher feedback in professional language instruction offers precise, expert guidance that targets individual learning needs and corrects complex language errors effectively. It enhances learners' competence by providing structured, goal-oriented assessments aligned with industry standards, promoting practical language use in workplace scenarios. This form of feedback also supports professional development by fostering critical thinking and encouraging continuous improvement through expert insights.
Common Challenges with Peer Feedback
Common challenges with peer feedback include variability in the accuracy and quality of comments due to differing skill levels among students, which can lead to misunderstandings or unhelpful suggestions. Peers may also hesitate to provide critical feedback to avoid hurting classmates' feelings, resulting in less constructive input. Limited training in giving effective feedback often causes inconsistent or vague responses, reducing the overall benefit of peer assessment in language instruction.
Overcoming Limitations of Teacher Feedback
Peer feedback expands opportunities for formative assessment by increasing the frequency and diversity of responses learners receive, addressing the limited availability of teacher feedback in large classes. It fosters collaborative learning and critical thinking, enabling students to engage actively with language use and error correction. Integrating peer feedback reduces dependence on teacher input alone, helping overcome delays and bottlenecks associated with single-source feedback in language instruction.
Best Practices for Implementing Peer Feedback
Implementing peer feedback in language instruction requires clear guidelines to ensure constructive and specific comments that promote learner autonomy and critical thinking. Structured peer review sessions, combined with training on giving and receiving feedback effectively, enhance the quality of interactions and support language development. Utilizing rubrics and exemplars helps students focus on key language features and content accuracy, maximizing the benefits of peer assessment alongside teacher feedback.
Integrating Peer and Teacher Feedback Effectively
Integrating peer and teacher feedback effectively enhances language instruction by combining diverse perspectives and fostering active learning. Peer feedback encourages collaborative skills and self-reflection, while teacher feedback ensures accuracy and expert guidance critical for language development. Structured integration of both feedback types leverages the strengths of each, resulting in more comprehensive proficiency and improved learner outcomes.
Choosing the Right Feedback Approach for Business Language Success
Peer feedback fosters collaborative learning and enhances communication skills by allowing learners to exchange diverse perspectives on business language use, promoting real-world application. Teacher feedback offers expert guidance and precise correction, essential for mastering complex grammar and specialized vocabulary in professional settings. Selecting the right feedback approach depends on learner goals, language proficiency, and context, with a blended strategy often yielding the most effective business communication outcomes.
Peer feedback vs teacher feedback Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com