Palm oil is commonly used in pet soap for its excellent lathering and moisturizing properties, but concerns about sustainability and potential allergens drive many pet owners to seek palm-free alternatives. Palm-free soaps often rely on ingredients like olive oil, coconut oil, or shea butter, which can provide gentle cleansing and hydration while reducing environmental impact. Choosing palm-free pet soap supports eco-friendly practices and can be beneficial for pets with sensitive skin or allergies.
Table of Comparison
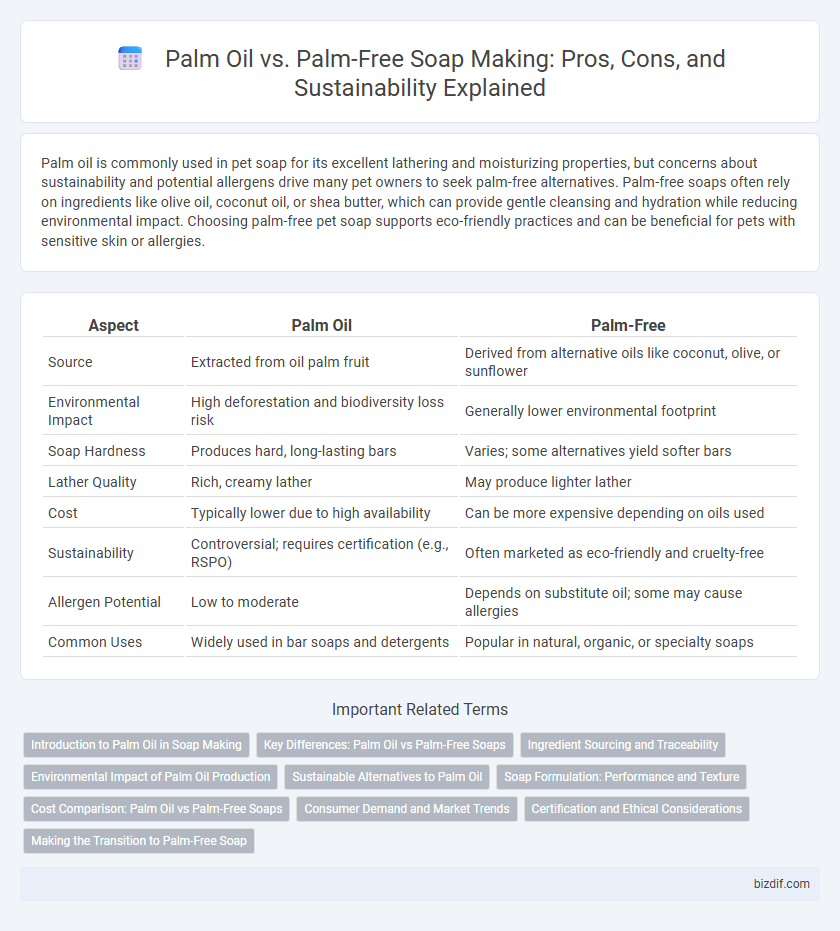
| Aspect | Palm Oil | Palm-Free |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from oil palm fruit | Derived from alternative oils like coconut, olive, or sunflower |
| Environmental Impact | High deforestation and biodiversity loss risk | Generally lower environmental footprint |
| Soap Hardness | Produces hard, long-lasting bars | Varies; some alternatives yield softer bars |
| Lather Quality | Rich, creamy lather | May produce lighter lather |
| Cost | Typically lower due to high availability | Can be more expensive depending on oils used |
| Sustainability | Controversial; requires certification (e.g., RSPO) | Often marketed as eco-friendly and cruelty-free |
| Allergen Potential | Low to moderate | Depends on substitute oil; some may cause allergies |
| Common Uses | Widely used in bar soaps and detergents | Popular in natural, organic, or specialty soaps |
Introduction to Palm Oil in Soap Making
Palm oil is a widely used ingredient in soap making due to its ability to create hard bars with rich lather and moisturizing properties. Extracted from the fruit of the oil palm tree, palm oil contributes to soap's stability and longevity while providing a creamy texture. Some soap makers opt for palm-free alternatives to address environmental concerns related to palm oil production.
Key Differences: Palm Oil vs Palm-Free Soaps
Palm oil soaps contain natural fatty acids that enhance lathering and moisturizing properties, making them popular for their creamy texture and durability. Palm-free soaps use alternative oils like coconut, olive, or shea butter, which offer varied benefits such as gentler cleansing and environmental sustainability. The key differences revolve around ingredient composition, ecological impact, and user preference for skin sensitivity or ethical considerations.
Ingredient Sourcing and Traceability
Palm oil, widely used in soap making, often comes from large-scale plantations with documented supply chains, enabling traceability efforts aimed at reducing environmental impact and ensuring sustainable sourcing. In contrast, palm-free soaps rely on alternative oils like coconut, olive, or sunflower, which may offer simpler traceability due to smaller, localized production but can vary significantly in sustainability credentials. Transparent ingredient sourcing in both palm and palm-free soaps plays a crucial role in verifying ethical practices, minimizing deforestation, and supporting biodiversity conservation.
Environmental Impact of Palm Oil Production
Palm oil production is a major driver of deforestation, habitat loss, and greenhouse gas emissions, significantly impacting biodiversity and contributing to climate change. Palm-free alternatives reduce reliance on unsustainable agricultural practices, helping to preserve tropical rainforests and protect endangered wildlife. Choosing sustainable soap ingredients mitigates environmental harm and supports responsible sourcing initiatives.
Sustainable Alternatives to Palm Oil
Sustainable alternatives to palm oil in soap making include ingredients like coconut oil, shea butter, and olive oil, which offer eco-friendly and biodegradable options. These substitutes reduce the environmental impact linked to deforestation and biodiversity loss caused by unsustainable palm oil production. Utilizing certified sustainable palm oil (CSPO) or fully palm-free formulations supports ethical sourcing while maintaining soap quality and lathering properties.
Soap Formulation: Performance and Texture
Palm oil contributes to a hard, long-lasting bar with stable lather and creamy texture in soap formulation, enhancing soap's durability and moisturization properties. Palm-free alternatives, such as coconut oil, olive oil, or shea butter, offer varied performance with generally softer bars and different lather qualities, often requiring additional formulation adjustments to balance hardness and longevity. The choice between palm oil and palm-free ingredients directly impacts soap texture, firmness, and conditioning, influencing consumer preferences and market positioning.
Cost Comparison: Palm Oil vs Palm-Free Soaps
Palm oil soap is generally more affordable due to the widespread availability and lower production costs of palm oil compared to alternative oils used in palm-free soaps. Palm-free soaps often rely on ingredients like coconut, olive, or shea butter, which tend to be more expensive and can increase the overall cost of the soap. Cost differences impact pricing strategies in soap manufacturing, with palm-free options appealing to eco-conscious consumers despite the higher price point.
Consumer Demand and Market Trends
Consumer demand in soap making is shifting as awareness of environmental and ethical concerns surrounding palm oil production rises. Palm-free soaps are gaining market traction due to their appeal to eco-conscious buyers seeking sustainable and cruelty-free alternatives. Market trends reflect increased innovation in formulations using plant-based oils like coconut, olive, and shea butter to meet the growing preference for palm-free products.
Certification and Ethical Considerations
Palm oil in soap making is often scrutinized for environmental impact, but certified sustainable palm oil (RSPO) ensures traceability and reduced deforestation. Palm-free alternatives appeal to consumers prioritizing ethical sourcing and biodiversity conservation, often using ingredients like coconut or olive oil. Ethical certification and transparency in ingredient sourcing remain crucial for responsible soap production and consumer trust.
Making the Transition to Palm-Free Soap
Transitioning to palm-free soap requires sourcing alternative oils such as coconut, olive, or sunflower, which provide sustainable and eco-friendly options while maintaining lather quality and moisturizing properties. Formulators must adjust saponification values and cure times to accommodate these oils' unique chemical profiles for optimal soap hardness and shelf life. Emphasizing certified organic and fair-trade ingredients ensures ethical production standards and reduces environmental impact associated with palm oil cultivation.
Palm Oil vs Palm-Free Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com