A bench jeweler specializes in the hands-on crafting, repairing, and finishing of jewelry pieces using traditional tools and techniques. A designer jeweler focuses on conceptualizing and creating original jewelry designs, often working with sketches or computer-aided design software to bring artistic visions to life. Both roles require a deep understanding of materials and craftsmanship but differ in their emphasis on creation versus execution.
Table of Comparison
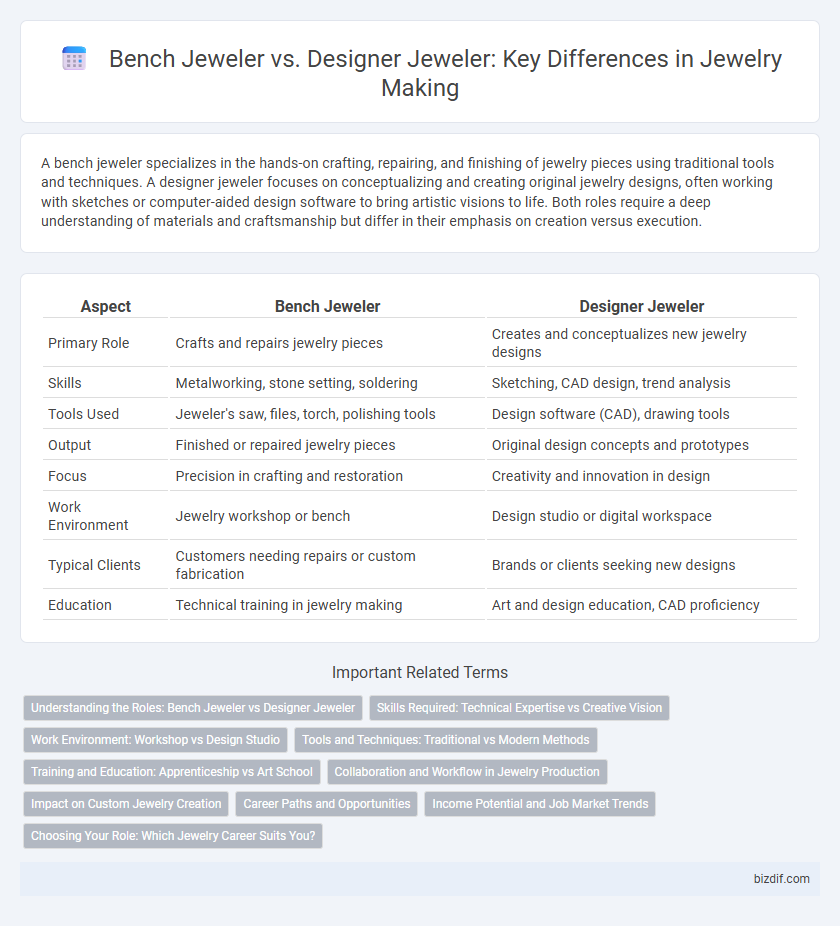
| Aspect | Bench Jeweler | Designer Jeweler |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Crafts and repairs jewelry pieces | Creates and conceptualizes new jewelry designs |
| Skills | Metalworking, stone setting, soldering | Sketching, CAD design, trend analysis |
| Tools Used | Jeweler's saw, files, torch, polishing tools | Design software (CAD), drawing tools |
| Output | Finished or repaired jewelry pieces | Original design concepts and prototypes |
| Focus | Precision in crafting and restoration | Creativity and innovation in design |
| Work Environment | Jewelry workshop or bench | Design studio or digital workspace |
| Typical Clients | Customers needing repairs or custom fabrication | Brands or clients seeking new designs |
| Education | Technical training in jewelry making | Art and design education, CAD proficiency |
Understanding the Roles: Bench Jeweler vs Designer Jeweler
Bench jewelers specialize in the hands-on construction, repair, and finishing of jewelry pieces, utilizing skills such as soldering, stone setting, and polishing. Designer jewelers focus on the creative process, conceptualizing unique jewelry designs, selecting materials, and using CAD software to bring artistic visions to life. Understanding these distinct roles highlights how craftsmanship and creativity intersect to produce both functional and aesthetically stunning jewelry.
Skills Required: Technical Expertise vs Creative Vision
Bench jewelers require precise technical expertise, including skills in metalworking, stone setting, and soldering, to physically craft and repair jewelry pieces with accuracy. Designer jewelers emphasize creative vision, combining artistic design principles and trend awareness to conceptualize unique and aesthetically appealing jewelry. Both roles demand a deep understanding of materials and tools, yet bench jewelers focus on manual craftsmanship while designers prioritize innovation and original design concepts.
Work Environment: Workshop vs Design Studio
A bench jeweler primarily operates in a workshop environment equipped with tools for metalworking, soldering, and stone setting, emphasizing hands-on craftsmanship and precision. In contrast, a designer jeweler works mainly in a design studio, utilizing digital software, sketches, and prototypes to create innovative jewelry concepts before production. The workshop fosters physical fabrication skills, while the studio encourages creativity and technological integration in the jewelry design process.
Tools and Techniques: Traditional vs Modern Methods
Bench jewelers rely heavily on traditional tools such as files, saws, and torches to handcraft intricate pieces with precision and skill, mastering techniques like soldering and stone setting through years of practice. Designer jewelers incorporate modern technology including CAD software, 3D printing, and laser welding to create innovative and customizable designs rapidly while maintaining high accuracy. Both roles demand expertise in detailed workmanship, but the integration of advanced digital methods in design workflows distinguishes designer jewelers from their bench-focused counterparts.
Training and Education: Apprenticeship vs Art School
Bench jewelers often gain expertise through hands-on apprenticeships, mastering practical skills like metalworking and stone setting under experienced mentors. Designer jewelers typically pursue formal education at art schools, focusing on design principles, computer-aided design (CAD), and creative innovation. Both paths emphasize specialized training but differ in balancing technical craftsmanship with artistic design development.
Collaboration and Workflow in Jewelry Production
Bench jewelers and designer jewelers collaborate closely to transform creative concepts into finished pieces, with designers providing detailed sketches and specifications while bench jewelers execute precise metalwork and stone setting. The workflow emphasizes continuous communication to ensure design integrity and technical feasibility, allowing for adjustments during the fabrication process. This dynamic collaboration maximizes craftsmanship quality and accelerates production efficiency in jewelry making.
Impact on Custom Jewelry Creation
Bench jewelers craft custom jewelry by expertly shaping, soldering, and assembling metal components, ensuring precision and structural integrity in each piece. Designer jewelers focus on conceptualizing and sketching unique jewelry designs that reflect client vision and style, often utilizing CAD software for detailed modeling. Collaborative efforts between bench jewelers and designer jewelers significantly enhance the quality and personalization of custom jewelry, combining artistic creativity with technical craftsmanship.
Career Paths and Opportunities
Bench jewelers primarily focus on the hands-on creation, repair, and customization of jewelry, honing skills in metalwork, soldering, and stone setting, which opens career paths in workshops, repair shops, and manufacturing. Designer jewelers blend artistic vision with technical knowledge to create original sketches and concepts, often leading to opportunities in fashion houses, brand design teams, and freelance art studios. Both career paths offer progression through specialization, entrepreneurship, or leadership roles in creative and technical segments of the jewelry industry.
Income Potential and Job Market Trends
Bench jewelers typically earn hourly wages ranging from $15 to $30, with skilled artisans in luxury markets commanding higher rates, while designer jewelers often achieve greater income potential through brand recognition and direct sales of unique pieces. The job market for bench jewelers remains steady due to ongoing demand for repair and customization services, whereas designer jewelers face a more competitive environment driven by trends, requiring strong marketing and client-building skills. Growth in the jewelry sector emphasizes e-commerce and bespoke designs, favoring designer jewelers who can capitalize on online platforms and personalized branding.
Choosing Your Role: Which Jewelry Career Suits You?
Bench jewelers excel in hands-on skills like metal shaping, soldering, and stone setting, making them ideal for those who enjoy craftsmanship and technical precision. Designer jewelers focus on creativity, sketching, CAD design, and concept development, appealing to individuals passionate about artistic innovation and trend forecasting. Selecting the right jewelry career depends on whether you prefer detailed manual work or creative design processes within the jewelry industry.
Bench jeweler vs Designer jeweler Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com