A bench jeweler specializes in the hands-on crafting and repair of jewelry, using precision tools to shape metals and set stones. Jewelry designers focus on creating original concepts and sketches, bringing artistic vision to life through innovative and aesthetic designs. Both roles are essential in the jewelry making process, combining technical skill with creative artistry.
Table of Comparison
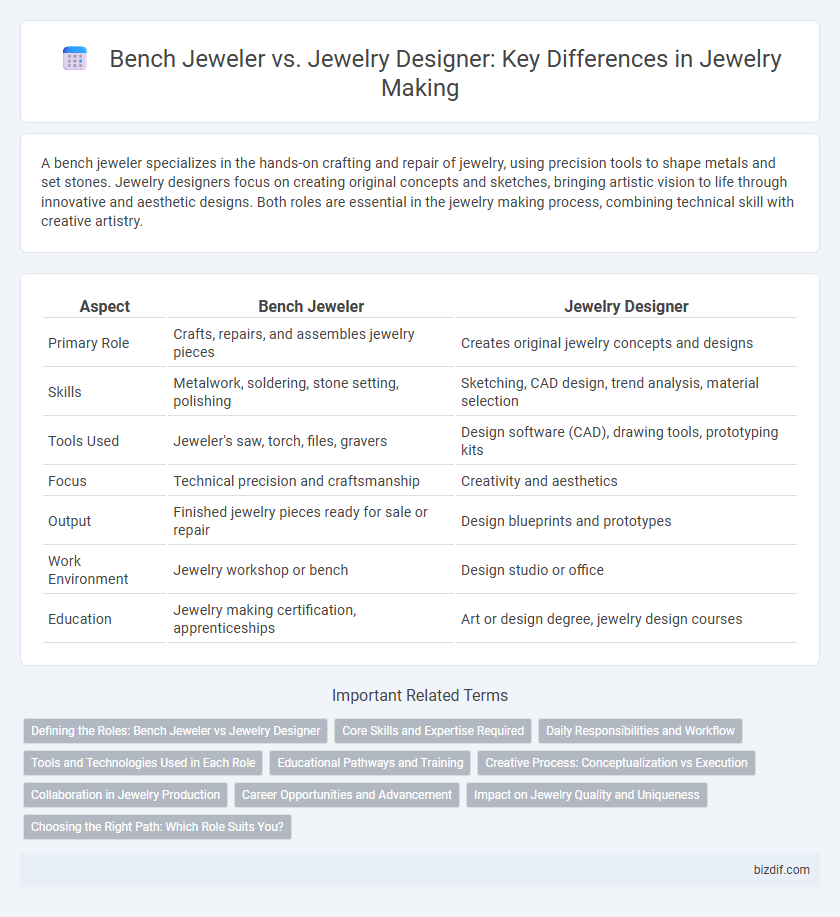
| Aspect | Bench Jeweler | Jewelry Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Crafts, repairs, and assembles jewelry pieces | Creates original jewelry concepts and designs |
| Skills | Metalwork, soldering, stone setting, polishing | Sketching, CAD design, trend analysis, material selection |
| Tools Used | Jeweler's saw, torch, files, gravers | Design software (CAD), drawing tools, prototyping kits |
| Focus | Technical precision and craftsmanship | Creativity and aesthetics |
| Output | Finished jewelry pieces ready for sale or repair | Design blueprints and prototypes |
| Work Environment | Jewelry workshop or bench | Design studio or office |
| Education | Jewelry making certification, apprenticeships | Art or design degree, jewelry design courses |
Defining the Roles: Bench Jeweler vs Jewelry Designer
Bench jewelers specialize in the hands-on crafting, repairing, and assembling of jewelry pieces using various tools and techniques, ensuring precision and durability. Jewelry designers focus on the creative process, conceptualizing unique designs, selecting materials, and producing detailed sketches or computer-aided models for production. While bench jewelers bring designs to life through technical skill, jewelry designers innovate aesthetics and style, making both roles essential in the jewelry making industry.
Core Skills and Expertise Required
Bench jewelers require precision hand skills, expertise in metalworking, stone setting, soldering, and polishing to fabricate and repair jewelry pieces. Jewelry designers focus on creativity, proficiency in design software like CAD, knowledge of gemstones, and an understanding of market trends to create appealing and wearable designs. Both roles demand a strong grasp of materials, attention to detail, and specialized training in their respective disciplines.
Daily Responsibilities and Workflow
Bench jewelers primarily focus on hands-on tasks such as soldering, stone setting, polishing, and repairing jewelry pieces, ensuring each item meets quality and durability standards. Jewelry designers concentrate on conceptualizing and sketching new designs, selecting materials, and collaborating with clients or manufacturers to bring creative visions to life. Both roles require precision and creativity, but bench jewelers emphasize technical craftsmanship, while designers prioritize aesthetic innovation and market trends.
Tools and Technologies Used in Each Role
Bench jewelers primarily use traditional hand tools such as files, saws, soldering torches, and polishing machines to craft and repair jewelry pieces with precision. Jewelry designers rely heavily on digital technologies including CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, 3D printers, and rendering programs to conceptualize and prototype innovative designs before physical production. The integration of these distinct tools defines the hands-on craftsmanship of bench jewelers and the creative technical design process of jewelry designers.
Educational Pathways and Training
Bench jewelers typically undergo vocational training or apprenticeships focusing on hands-on skills like metalworking, stone setting, and repair techniques, often through technical schools or community colleges. Jewelry designers usually pursue formal education in fine arts or design programs, earning degrees in jewelry design or related fields, emphasizing creativity, conceptual development, and digital design tools. Both pathways require mastery of gemology and materials science, but bench jewelers prioritize practical craftsmanship while jewelry designers focus on artistic innovation and market trends.
Creative Process: Conceptualization vs Execution
Bench jewelers specialize in the execution phase of jewelry making, transforming designs into tangible pieces through expert craftsmanship and precision techniques. Jewelry designers focus on the conceptualization stage, developing original ideas, sketches, and design plans that guide the creation process. The synergy between designers' creativity and bench jewelers' technical skills ensures high-quality, unique jewelry pieces that reflect both artistic vision and meticulous construction.
Collaboration in Jewelry Production
Bench jewelers and jewelry designers collaborate closely to transform creative concepts into wearable art, blending technical expertise with artistic vision. Bench jewelers execute precise metalwork, stone setting, and assembly based on designers' sketches, ensuring structural integrity and high-quality craftsmanship. This partnership enhances the jewelry production process by combining innovative design ideas with practical fabrication skills, resulting in unique, meticulously crafted pieces.
Career Opportunities and Advancement
Bench jewelers specialize in hands-on crafting and repair, offering steady career growth through mastery of technical skills and specialization in areas like stone setting or engraving. Jewelry designers focus on creative concept development and marketing, with advancement linked to portfolio expansion, brand recognition, and collaboration with manufacturers or retailers. Both paths offer distinct opportunities: bench jewelers can progress to master craftsman roles, while designers may evolve into brand directors or entrepreneurs.
Impact on Jewelry Quality and Uniqueness
Bench jewelers directly influence jewelry quality through expert craftsmanship, ensuring precision in metalwork, stone setting, and finishing that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal. Jewelry designers contribute to uniqueness by creating original concepts and innovative designs, often incorporating artistic vision and trend awareness. Together, the collaboration between bench jewelers and designers elevates both the technical quality and distinctiveness of each piece, resulting in truly exceptional jewelry.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Role Suits You?
A bench jeweler excels in hands-on craftsmanship, shaping and assembling jewelry pieces with precision using tools and techniques like soldering and stone setting. A jewelry designer focuses on creativity and conceptualization, sketching original designs and selecting materials to bring unique visions to life. Choosing the right path depends on whether you prefer technical skill and physical fabrication or artistic innovation and design development.
Bench jeweler vs jewelry designer Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com