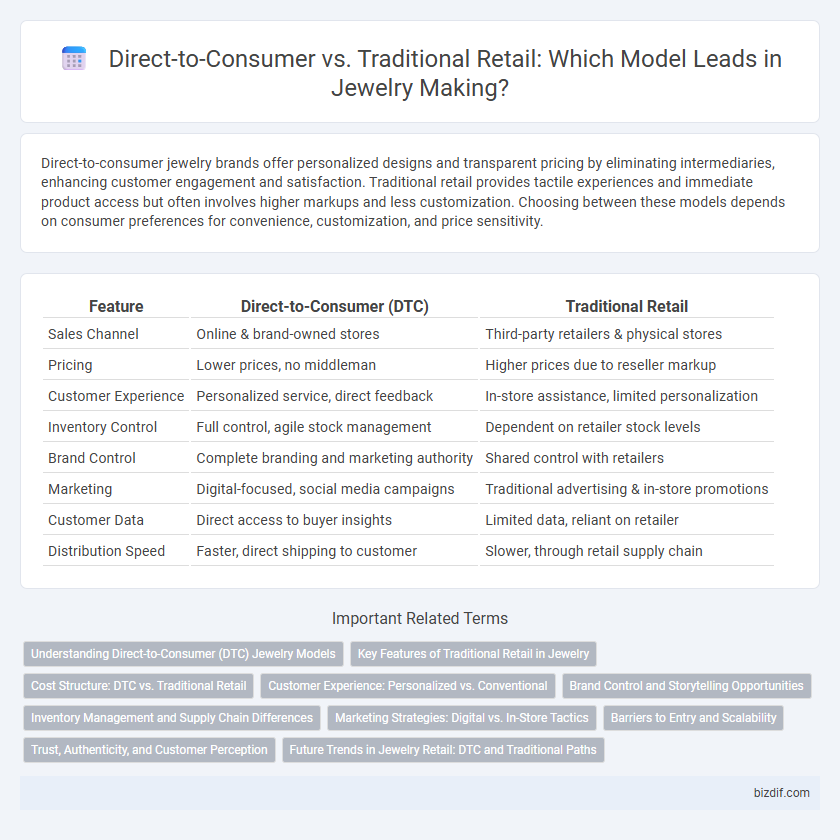
Direct-to-consumer jewelry brands offer personalized designs and transparent pricing by eliminating intermediaries, enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction. Traditional retail provides tactile experiences and immediate product access but often involves higher markups and less customization. Choosing between these models depends on consumer preferences for convenience, customization, and price sensitivity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) | Traditional Retail |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Channel | Online & brand-owned stores | Third-party retailers & physical stores |
| Pricing | Lower prices, no middleman | Higher prices due to reseller markup |
| Customer Experience | Personalized service, direct feedback | In-store assistance, limited personalization |
| Inventory Control | Full control, agile stock management | Dependent on retailer stock levels |
| Brand Control | Complete branding and marketing authority | Shared control with retailers |
| Marketing | Digital-focused, social media campaigns | Traditional advertising & in-store promotions |
| Customer Data | Direct access to buyer insights | Limited data, reliant on retailer |
| Distribution Speed | Faster, direct shipping to customer | Slower, through retail supply chain |
Understanding Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Jewelry Models
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) jewelry models eliminate intermediaries, allowing brands to sell directly to customers through online platforms, which reduces costs and improves pricing transparency. This approach provides greater control over branding, customer experience, and inventory management compared to traditional retail methods reliant on third-party stores. DTC leverages digital marketing and personalized service, enhancing customer engagement and enabling data-driven decisions in product development and sales strategies.
Key Features of Traditional Retail in Jewelry
Traditional retail in jewelry offers hands-on, personalized customer service with in-store consultations and immediate product availability. Physical stores showcase a wide variety of designs and allow customers to evaluate gemstone quality, metal finishes, and craftsmanship up close. Established jewelry retailers often provide certified appraisals, after-sale servicing, and trusted brand reputation, enhancing buyer confidence.
Cost Structure: DTC vs. Traditional Retail
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) jewelry brands eliminate intermediaries, reducing wholesale markups and retail commissions, which lowers overall costs and increases profit margins. Traditional retail jewelry incurs expenses such as distributor fees, brick-and-mortar store rents, and retail staff salaries, leading to higher product prices. DTC models benefit from streamlined supply chains and direct customer engagement, optimizing inventory control and minimizing overhead compared to conventional retail structures.
Customer Experience: Personalized vs. Conventional
Direct-to-consumer jewelry brands leverage personalized customer experiences through customized designs, virtual try-ons, and direct communication, enhancing engagement and satisfaction. Traditional retail often offers a conventional shopping environment with limited customization, relying on in-person service and established brand presence. Personalized experiences in direct-to-consumer models drive higher customer loyalty and unique product appeal compared to standard retail settings.
Brand Control and Storytelling Opportunities
Direct-to-consumer jewelry brands maintain full control over brand image and storytelling, enabling personalized narratives that resonate deeply with customers. Traditional retail often limits this control, as third-party retailers impose restrictions on how products and brand stories are presented. Leveraging direct-to-consumer channels enhances customer engagement through authentic storytelling, fostering stronger brand loyalty and distinct market positioning.
Inventory Management and Supply Chain Differences
Direct-to-consumer jewelry brands streamline inventory management by leveraging real-time sales data to produce pieces on demand, minimizing overstock and reducing storage costs. Traditional retail relies on bulk production and distributor networks, resulting in larger inventory holdings and complex supply chain logistics. This fundamental difference impacts lead times, flexibility in design updates, and overall operational efficiency in the jewelry industry.
Marketing Strategies: Digital vs. In-Store Tactics
Direct-to-consumer jewelry brands leverage targeted digital marketing strategies such as social media advertising, influencer partnerships, and personalized email campaigns to create direct engagement and collect valuable consumer data. Traditional retail relies heavily on in-store experiences, visual merchandising, and local promotions to attract customers and build brand loyalty through face-to-face interactions. Optimizing digital tactics enhances customer reach and data-driven insights, while in-store marketing enriches tactile experiences and trust in jewelry craftsmanship.
Barriers to Entry and Scalability
Direct-to-consumer jewelry brands face lower barriers to entry due to reduced reliance on physical storefronts and third-party retailers, enabling quicker market penetration through e-commerce platforms. Traditional retail demands significant upfront investment in inventory, showroom space, and staff, creating higher entry costs and limiting scalability. Scalability in DTC models benefits from streamlined supply chains and digital marketing, allowing rapid geographic expansion without proportional increases in overhead.
Trust, Authenticity, and Customer Perception
Direct-to-consumer jewelry brands build trust by offering transparent sourcing and customization options, fostering a perception of authenticity and personalized craftsmanship. Traditional retail relies on established reputations and physical storefronts to convey legitimacy, but may face challenges with perceived price markups and less direct brand engagement. Customer perception often favors direct-to-consumer models for their authenticity and value, while traditional retail benefits from tactile experience and immediate product availability.
Future Trends in Jewelry Retail: DTC and Traditional Paths
Future trends in jewelry retail reveal a growing shift toward direct-to-consumer (DTC) models, driven by digital platforms offering personalized customization and immersive online experiences. Traditional retail remains relevant by integrating omnichannel strategies, combining in-store expertise with digital conveniences to enhance customer engagement. Data analytics and augmented reality will further blur lines between DTC and traditional paths, creating hybrid approaches that leverage the strengths of both channels.
Direct-to-consumer vs Traditional retail Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com