Asymmetry in graphic design creates dynamic and engaging compositions by intentionally placing elements unevenly to evoke movement and interest. Symmetry offers balance and harmony, delivering a sense of stability and order that often appeals to a viewer's desire for structure. Choosing between asymmetry and symmetry depends on the message and emotional impact the design aims to convey.
Table of Comparison
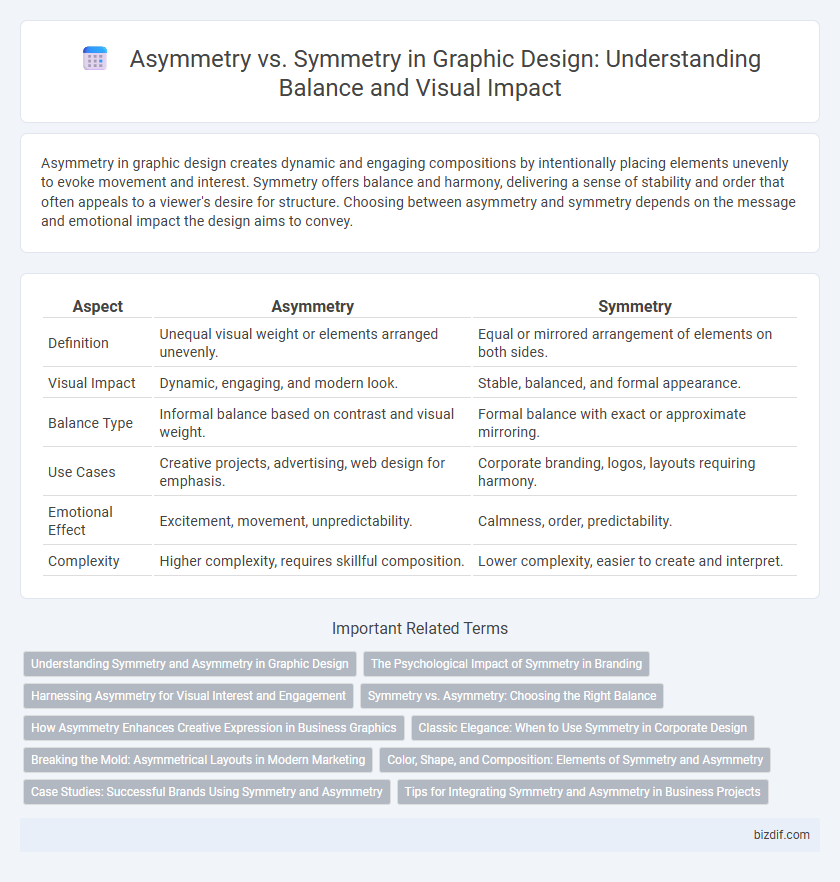
| Aspect | Asymmetry | Symmetry |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unequal visual weight or elements arranged unevenly. | Equal or mirrored arrangement of elements on both sides. |
| Visual Impact | Dynamic, engaging, and modern look. | Stable, balanced, and formal appearance. |
| Balance Type | Informal balance based on contrast and visual weight. | Formal balance with exact or approximate mirroring. |
| Use Cases | Creative projects, advertising, web design for emphasis. | Corporate branding, logos, layouts requiring harmony. |
| Emotional Effect | Excitement, movement, unpredictability. | Calmness, order, predictability. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity, requires skillful composition. | Lower complexity, easier to create and interpret. |
Understanding Symmetry and Asymmetry in Graphic Design
Symmetry in graphic design creates balance and harmony by evenly distributing visual elements, promoting a sense of stability and order that enhances viewer comprehension. Asymmetry, on the other hand, introduces dynamic tension and movement through deliberate imbalance, capturing attention and fostering visual interest. Mastering the interplay between symmetry and asymmetry is essential for designers seeking to evoke specific emotions and guide audience focus effectively.
The Psychological Impact of Symmetry in Branding
Symmetry in branding creates a sense of balance, harmony, and stability, which enhances brand recognition and trustworthiness among consumers. Psychological studies reveal that symmetrical designs are perceived as more attractive and reliable, influencing positive emotional responses and fostering brand loyalty. Brands leveraging symmetry often evoke feelings of professionalism and consistency, crucial for establishing a strong, credible identity in competitive markets.
Harnessing Asymmetry for Visual Interest and Engagement
Harnessing asymmetry in graphic design creates dynamic compositions that capture viewer attention through unexpected balance and visual tension. Unlike symmetry, which offers order and predictability, asymmetrical layouts leverage varying shapes, colors, and negative space to evoke movement and emotional response. Designers strategically use asymmetry to guide the eye, enhance storytelling, and increase engagement by breaking conventional grid patterns and fostering unique aesthetic experiences.
Symmetry vs. Asymmetry: Choosing the Right Balance
Symmetry creates visual harmony and balance by mirroring elements, making designs feel stable and cohesive. Asymmetry, on the other hand, introduces dynamic tension and interest by arranging elements unevenly, encouraging viewers to explore the composition. Choosing the right balance between symmetry and asymmetry depends on the desired emotional impact and the message the graphic design aims to convey.
How Asymmetry Enhances Creative Expression in Business Graphics
Asymmetry in business graphics breaks traditional balance, fostering dynamic visual interest that captures audience attention more effectively than symmetry. By strategically offsetting elements, designers create a sense of movement and innovation, reflecting a brand's unique identity and creativity. This approach enhances user engagement and differentiates marketing materials in competitive markets.
Classic Elegance: When to Use Symmetry in Corporate Design
Symmetry in corporate design conveys classic elegance by creating a balanced, orderly visual structure that enhances brand professionalism and trustworthiness. Utilizing symmetrical layouts in logos, business cards, and website interfaces reinforces stability and reliability, crucial for corporate identity. This approach aligns with established brand values, making it ideal for industries like finance, law, and healthcare where clarity and consistency are paramount.
Breaking the Mold: Asymmetrical Layouts in Modern Marketing
Asymmetrical layouts challenge traditional design conventions by introducing dynamic balance through uneven visual weight, creating eye-catching compositions in modern marketing. This approach enhances brand identity by evoking movement, tension, and creativity, differentiating campaigns from the predictable symmetry-based designs. Companies leveraging asymmetry experience higher engagement rates as their visuals break through clutter and resonate with contemporary audiences seeking originality.
Color, Shape, and Composition: Elements of Symmetry and Asymmetry
Symmetry in graphic design leverages balanced color palettes, uniform shapes, and mirrored compositions to create harmony and visual stability, enhancing user experience through predictability and order. Asymmetry utilizes contrasting colors, varied shapes, and dynamic, unbalanced layouts to evoke emotion, capture attention, and drive interest by breaking traditional visual expectations. Strategic manipulation of these elements enables designers to convey meaning and guide viewer focus effectively within a composition.
Case Studies: Successful Brands Using Symmetry and Asymmetry
Successful brands like Apple leverage symmetry in their logos to communicate balance, professionalism, and reliability, creating a sense of trust and stability in consumers. In contrast, brands like Nike use asymmetry to evoke motion, dynamism, and innovation, which resonates with their focus on athletic performance and energy. These case studies highlight how symmetry and asymmetry strategically influence brand perception and engagement in graphic design.
Tips for Integrating Symmetry and Asymmetry in Business Projects
Balance visual interest and clarity by combining symmetry's structured harmony with asymmetry's dynamic movement in business project designs. Use symmetrical layouts to establish stability and trust, while incorporating asymmetrical elements to highlight key messages and create focal points. Employ grid systems as a flexible foundation that supports both symmetrical alignment and asymmetrical variation, enhancing user engagement and brand impact.
Asymmetry vs Symmetry Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com