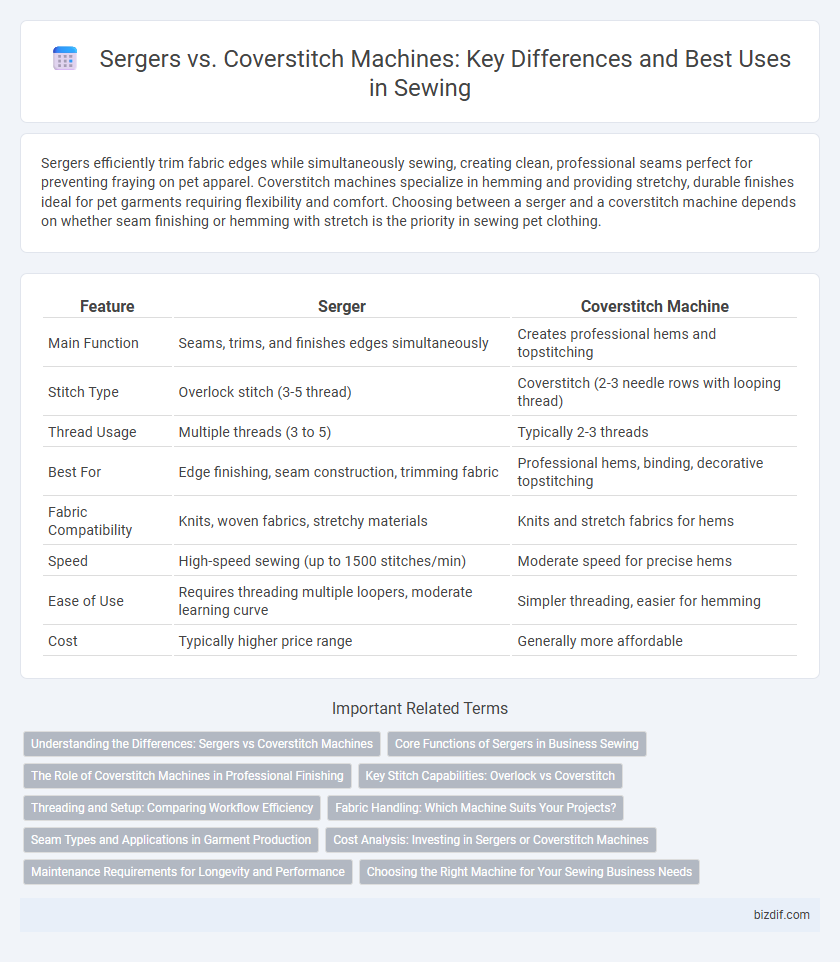
Sergers efficiently trim fabric edges while simultaneously sewing, creating clean, professional seams perfect for preventing fraying on pet apparel. Coverstitch machines specialize in hemming and providing stretchy, durable finishes ideal for pet garments requiring flexibility and comfort. Choosing between a serger and a coverstitch machine depends on whether seam finishing or hemming with stretch is the priority in sewing pet clothing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Serger | Coverstitch Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Seams, trims, and finishes edges simultaneously | Creates professional hems and topstitching |
| Stitch Type | Overlock stitch (3-5 thread) | Coverstitch (2-3 needle rows with looping thread) |
| Thread Usage | Multiple threads (3 to 5) | Typically 2-3 threads |
| Best For | Edge finishing, seam construction, trimming fabric | Professional hems, binding, decorative topstitching |
| Fabric Compatibility | Knits, woven fabrics, stretchy materials | Knits and stretch fabrics for hems |
| Speed | High-speed sewing (up to 1500 stitches/min) | Moderate speed for precise hems |
| Ease of Use | Requires threading multiple loopers, moderate learning curve | Simpler threading, easier for hemming |
| Cost | Typically higher price range | Generally more affordable |
Understanding the Differences: Sergers vs Coverstitch Machines
Sergers expertly trim fabric edges while simultaneously sewing, creating clean, professional seams perfect for knit and woven fabrics, whereas coverstitch machines specialize in producing parallel rows of stitching ideal for hemming and topstitching stretchy materials like activewear. The primary difference lies in the stitch type: sergers use multiple threads to encase edges with an overlock stitch, preventing fraying, while coverstitch machines form durable hems with a distinctive double or triple needle stitch. Understanding these functional distinctions helps sewers choose the right equipment for garment construction and finishing, enhancing fabric durability and appearance.
Core Functions of Sergers in Business Sewing
Sergers excel in business sewing by providing fast, professional seam finishing through overlocking, which trims fabric edges and prevents fraying in a single step. Their ability to sew, trim, and overcast seams simultaneously enhances production efficiency and durability in garment manufacturing. Unlike coverstitch machines that specialize in hemming and topstitching, sergers are indispensable for robust seam construction and edging.
The Role of Coverstitch Machines in Professional Finishing
Coverstitch machines excel in creating durable, stretchable hems and professional topstitching, essential for garment finishing in activewear and knit fabrics. Unlike sergers that primarily trim and overlock seams, coverstitch machines produce clean, flat hems with parallel stitch lines for a polished, high-quality appearance. Their precision in hemming and decorative stitching enhances garment durability and aesthetic appeal, making them indispensable in professional sewing environments.
Key Stitch Capabilities: Overlock vs Coverstitch
Sergers excel in overlock stitching, efficiently trimming seams and securing fabric edges with multiple threads to prevent fraying, ideal for garment construction and finishing. Coverstitch machines specialize in creating professional hems and topstitching with parallel rows of stitching that stretch without breaking, perfect for knit fabrics and activewear. Combining both machines enhances sewing versatility, delivering strong seam finishes and attractive hems on various fabric types.
Threading and Setup: Comparing Workflow Efficiency
Sergers typically offer faster threading with color-coded guides and fewer loopers to manage, streamlining the setup process for edge-finishing tasks. Coverstitch machines require more precise threading of multiple needles and loopers, which can extend setup time but ensures professional hemming and topstitching quality. Workflow efficiency depends on project requirements, with sergers favoring quick overlock seams and coverstitch machines optimized for stretch fabrics and garment hems.
Fabric Handling: Which Machine Suits Your Projects?
Sergers excel in handling stretchy and knit fabrics by efficiently trimming seams while simultaneously sewing, ideal for finishing edges and creating professional-looking seams on garments like activewear. Coverstitch machines specialize in topstitching and hemming, providing strong, flexible stitches perfect for securing hems on heavier or multiple-layered fabrics such as denim or woven textiles. Choosing between a serger and coverstitch machine depends on the fabric type and the specific sewing tasks, with sergers suited for seam construction and coverstitch machines tailored for decorative and functional hemming.
Seam Types and Applications in Garment Production
Sergers specialize in overlock seams, creating strong, stretchable edges ideal for knitwear and activewear, while coverstitch machines produce parallel stitch lines perfect for hemming and decorative topstitching in t-shirts and denim. Overlock seams offer durability and prevent fraying, making them essential for garment assembly, whereas coverstitch seams provide flexibility and professional finishing on hems and cuffs. Understanding the distinction in seam types enhances garment production efficiency by matching machine capabilities to specific fabric characteristics and design requirements.
Cost Analysis: Investing in Sergers or Coverstitch Machines
Sergers generally cost between $300 and $1,200, offering multifunctional stitching capabilities like overlocking, trimming, and seam finishing, which reduces the need for additional machines. Coverstitch machines, priced from $400 to $1,500, specialize in hemming and topstitching, providing professional finishes for knit fabrics but often requiring a serger for seam construction. Investing in a serger yields more versatile stitching options and faster production, making it a cost-effective choice for comprehensive garment construction, whereas coverstitch machines serve as a complementary investment for specialized hemming tasks.
Maintenance Requirements for Longevity and Performance
Sergers require regular cleaning of loopers and knives, along with timely oiling of moving parts to maintain smooth stitching and prevent thread buildup, ensuring optimal longevity and performance. Coverstitch machines need consistent tension adjustments and routine lubrication of the feed dogs and needles to avoid skipped stitches and fabric damage. Proper maintenance for both machines involves periodic checks for wear on key components, which extends their lifespan and ensures professional-quality seams.
Choosing the Right Machine for Your Sewing Business Needs
Sergers provide professional seam finishes and efficient trimming, ideal for garment construction and stretch fabrics, while coverstitch machines excel at hemming and topstitching, enhancing durability and aesthetics. Choosing the right machine depends on your sewing business's primary focus, such as whether you prioritize seam finishing quality or decorative stitching capabilities. Investing in a serger benefits mass production and fast fabric edge finishing, whereas a coverstitch machine suits businesses emphasizing apparel presentation with visible stitching details.
Sergers vs coverstitch machines Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com