Batch certification ensures each soap batch undergoes rigorous testing by an independent laboratory, guaranteeing consistent quality and safety for pet use. Self-certification allows soap makers to declare their products meet specific standards without third-party verification, offering faster turnaround but potentially less reliability. Choosing between batch certification and self-certification depends on balancing regulatory compliance, consumer trust, and production efficiency in pet soap manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
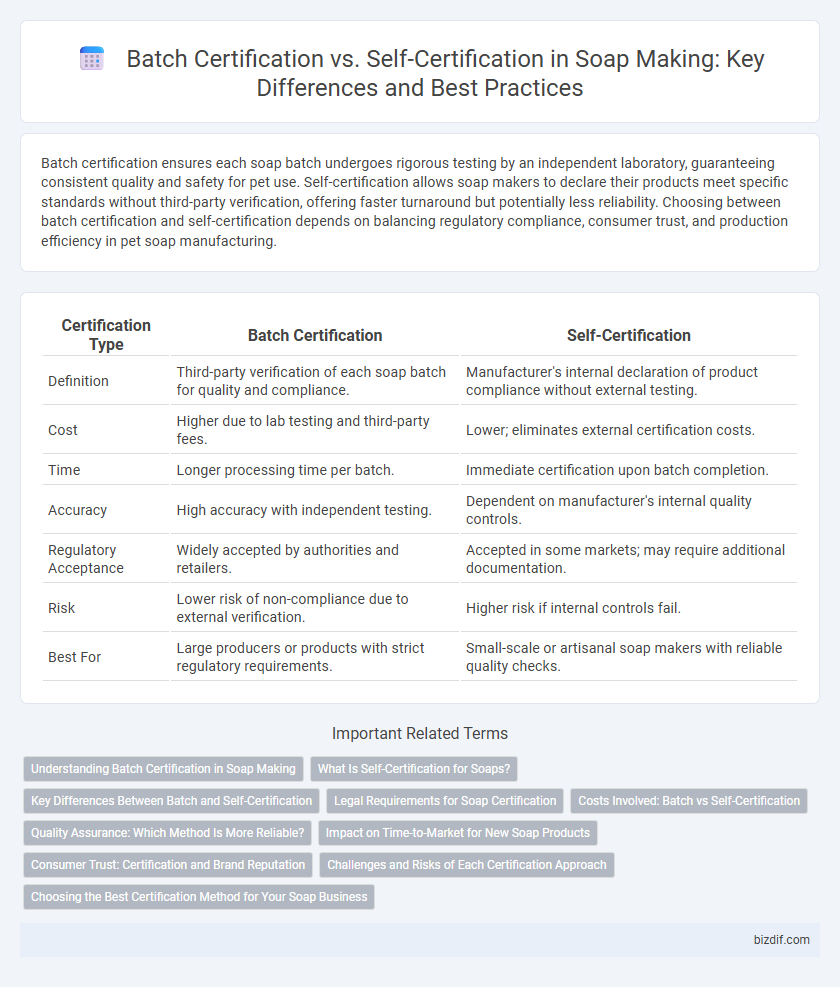
| Certification Type | Batch Certification | Self-Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Third-party verification of each soap batch for quality and compliance. | Manufacturer's internal declaration of product compliance without external testing. |
| Cost | Higher due to lab testing and third-party fees. | Lower; eliminates external certification costs. |
| Time | Longer processing time per batch. | Immediate certification upon batch completion. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with independent testing. | Dependent on manufacturer's internal quality controls. |
| Regulatory Acceptance | Widely accepted by authorities and retailers. | Accepted in some markets; may require additional documentation. |
| Risk | Lower risk of non-compliance due to external verification. | Higher risk if internal controls fail. |
| Best For | Large producers or products with strict regulatory requirements. | Small-scale or artisanal soap makers with reliable quality checks. |
Understanding Batch Certification in Soap Making
Batch certification in soap making involves rigorous testing and documentation to ensure product consistency, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards. This process requires manufacturers to submit samples from each batch for analytical evaluation, verifying factors such as pH levels, moisture content, and ingredient quality before market release. By adhering to batch certification protocols, soap makers can guarantee traceability and uphold consumer trust through verified product integrity.
What Is Self-Certification for Soaps?
Self-certification for soaps involves manufacturers declaring that their products meet specific safety, quality, and regulatory standards without third-party testing. This process allows soap makers to verify compliance with ingredient safety, labeling accuracy, and manufacturing practices internally. Self-certification streamlines market entry but requires rigorous documentation and adherence to local cosmetic and soap regulations to ensure consumer trust and legal conformity.
Key Differences Between Batch and Self-Certification
Batch certification requires each soap batch to undergo independent third-party testing for quality and safety, ensuring consistent compliance with regulatory standards. Self-certification relies on the manufacturer's internal quality controls and documentation without external verification, offering faster production but potentially less oversight. Key differences include the level of regulatory assurance, cost implications, and the degree of process transparency required for market acceptance.
Legal Requirements for Soap Certification
Batch certification mandates independent laboratory testing and official approval for each soap batch before market release, ensuring compliance with strict regulatory standards. Self-certification allows manufacturers to declare compliance based on internal quality control but still requires adherence to legal labeling and safety regulations under agencies like the FDA or EU Cosmetic Regulation. Legal requirements for soap certification vary by region, but both methods demand accurate documentation, ingredient transparency, and conformity to health and safety laws to prevent consumer harm and ensure product reliability.
Costs Involved: Batch vs Self-Certification
Batch certification incurs higher costs due to third-party laboratory testing, documentation, and regulatory fees that ensure each batch meets stringent quality standards. In contrast, self-certification reduces expenses by allowing manufacturers to verify compliance internally, minimizing external testing and administrative overhead. Choosing self-certification can significantly lower overall production costs but may increase legal and quality risks if compliance is not rigorously maintained.
Quality Assurance: Which Method Is More Reliable?
Batch certification ensures rigorous quality assurance by requiring independent laboratory testing for each production batch, guaranteeing consistency and compliance with regulatory standards. Self-certification relies on in-house quality control measures, which can vary in accuracy and may risk overlooking contamination or formulation errors. For manufacturers prioritizing product safety and consumer trust, batch certification provides a more reliable and verifiable quality assurance method in soap making.
Impact on Time-to-Market for New Soap Products
Batch certification requires thorough laboratory testing and regulatory approval for each soap batch, significantly extending the time-to-market for new products. Self-certification allows manufacturers to internally verify product compliance, enabling faster market entry by bypassing lengthy external validation processes. This streamlined approach accelerates product launches but demands rigorous internal quality controls to ensure safety and regulatory adherence.
Consumer Trust: Certification and Brand Reputation
Batch certification ensures each soap production batch meets stringent quality standards verified by an external authority, significantly enhancing consumer trust and brand reputation. Self-certification relies on internal quality checks, which may lack the perceived rigor and transparency, potentially impacting consumer confidence. Brands that invest in batch certification often experience stronger market credibility and customer loyalty.
Challenges and Risks of Each Certification Approach
Batch certification in soap making ensures rigorous quality control through third-party verification but presents challenges such as higher costs, longer processing times, and dependency on external labs, increasing operational delays. Self-certification offers faster market entry and reduced expenses but carries risks including potential non-compliance with regulatory standards, liability for product defects, and diminished consumer trust due to lack of independent verification. Manufacturers must carefully assess trade-offs between thorough validation versus speed and cost-efficiency to minimize legal risks and maintain brand integrity.
Choosing the Best Certification Method for Your Soap Business
Batch Certification provides verified safety and quality assurance for each soap batch, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and fostering consumer trust. Self-Certification offers greater flexibility and cost savings by allowing soap makers to internalize quality control processes but requires thorough documentation and risk management. Choosing the best certification method depends on business scale, target market requirements, and the importance placed on third-party validation versus operational autonomy.
Batch Certification vs Self-Certification Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com