Internal controls are the processes and procedures implemented within a business to safeguard assets, ensure accurate financial reporting, and promote operational efficiency. External audits involve independent evaluations of a company's financial statements and internal controls to provide assurance of their accuracy and compliance with regulations. Effective bookkeeping pet services help maintain strong internal controls, making external audits smoother and more reliable.
Table of Comparison
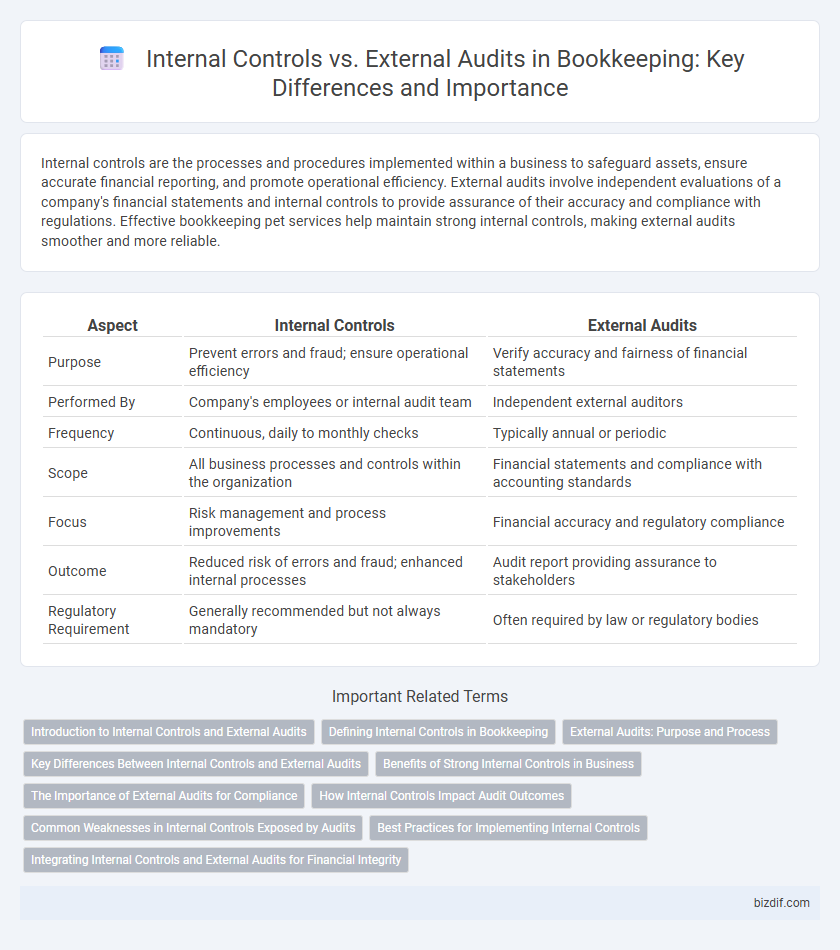
| Aspect | Internal Controls | External Audits |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevent errors and fraud; ensure operational efficiency | Verify accuracy and fairness of financial statements |
| Performed By | Company's employees or internal audit team | Independent external auditors |
| Frequency | Continuous, daily to monthly checks | Typically annual or periodic |
| Scope | All business processes and controls within the organization | Financial statements and compliance with accounting standards |
| Focus | Risk management and process improvements | Financial accuracy and regulatory compliance |
| Outcome | Reduced risk of errors and fraud; enhanced internal processes | Audit report providing assurance to stakeholders |
| Regulatory Requirement | Generally recommended but not always mandatory | Often required by law or regulatory bodies |
Introduction to Internal Controls and External Audits
Internal controls consist of processes and procedures implemented by a company to safeguard assets, ensure accurate financial reporting, and promote operational efficiency. External audits involve independent evaluations by certified auditors who assess the fairness and accuracy of financial statements. Both practices are essential for maintaining financial integrity and compliance with regulatory standards.
Defining Internal Controls in Bookkeeping
Internal controls in bookkeeping refer to the policies and procedures implemented within an organization to ensure accuracy, reliability, and integrity of financial data. These controls help prevent errors, detect fraud, and safeguard assets by regulating the authorization, recording, and reconciliation of transactions. Strong internal controls are essential for maintaining compliance with accounting standards and supporting effective financial reporting.
External Audits: Purpose and Process
External audits provide an independent evaluation of a company's financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. The audit process involves systematic examination of financial records, internal controls, and transactions by certified auditors to detect errors or fraud. These audits enhance stakeholder confidence by verifying the integrity of financial reporting and safeguarding against misstatements.
Key Differences Between Internal Controls and External Audits
Internal controls are processes and procedures implemented by an organization to ensure accuracy and reliability in financial reporting, safeguard assets, and prevent fraud. External audits are independent evaluations conducted by external auditors to verify the accuracy and fairness of financial statements and compliance with regulatory standards. Key differences include that internal controls are ongoing, managed internally, and focus on prevention, while external audits are periodic, performed by external parties, and emphasize verification and assurance.
Benefits of Strong Internal Controls in Business
Strong internal controls enhance accuracy and reliability in financial reporting, reducing the risk of errors and fraud within a business. Effective internal controls improve operational efficiency by streamlining processes and ensuring compliance with regulations, which minimizes costly penalties. Robust internal control systems build stakeholder confidence and facilitate smoother external audits by providing transparent and well-documented financial data.
The Importance of External Audits for Compliance
External audits play a crucial role in ensuring compliance by providing an independent assessment of a company's financial statements and internal controls. They help identify discrepancies and risks that internal controls might overlook, promoting transparency and accuracy in financial reporting. Regulatory bodies often require external audits to verify adherence to legal and industry standards, safeguarding stakeholders' interests.
How Internal Controls Impact Audit Outcomes
Internal controls establish a framework for accurate financial reporting and risk mitigation, directly influencing the scope and findings of external audits. Effective internal controls reduce the likelihood of material misstatements, allowing auditors to streamline testing and focus on high-risk areas. Consequently, strong internal control systems enhance audit reliability and can lower audit costs by minimizing errors and discrepancies.
Common Weaknesses in Internal Controls Exposed by Audits
Internal audits frequently reveal common weaknesses in internal controls such as inadequate segregation of duties, insufficient documentation, and lack of regular reconciliations. External audits often expose these deficiencies by identifying discrepancies in financial reporting and compliance failures. Addressing these vulnerabilities is critical to enhancing accuracy, preventing fraud, and ensuring regulatory adherence within bookkeeping systems.
Best Practices for Implementing Internal Controls
Effective internal controls in bookkeeping involve establishing clear authorization protocols, segregation of duties, and regular reconciliation of accounts to prevent errors and fraud. Best practices prioritize continuous monitoring, employee training, and using automated accounting software to enhance accuracy and accountability. Regular internal reviews combined with well-documented procedures create a robust framework that supports external audit processes and financial integrity.
Integrating Internal Controls and External Audits for Financial Integrity
Integrating internal controls and external audits strengthens financial integrity by creating a comprehensive framework for risk management and accuracy in financial reporting. Internal controls proactively identify and mitigate potential errors or fraud, while external audits provide independent verification and assurance of the organization's financial statements. This synergy enhances transparency, regulatory compliance, and stakeholder confidence in the company's financial health.
Internal Controls vs External Audits Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com