Payroll processing involves managing employee salaries, tax withholdings, benefits, and compliance with labor laws, ensuring accurate and timely payment. Contractor payments, on the other hand, require tracking invoices, issuing 1099 forms, and handling variable payment schedules without withholding taxes. Both processes demand meticulous record-keeping but differ significantly in regulatory requirements and tax treatment.
Table of Comparison
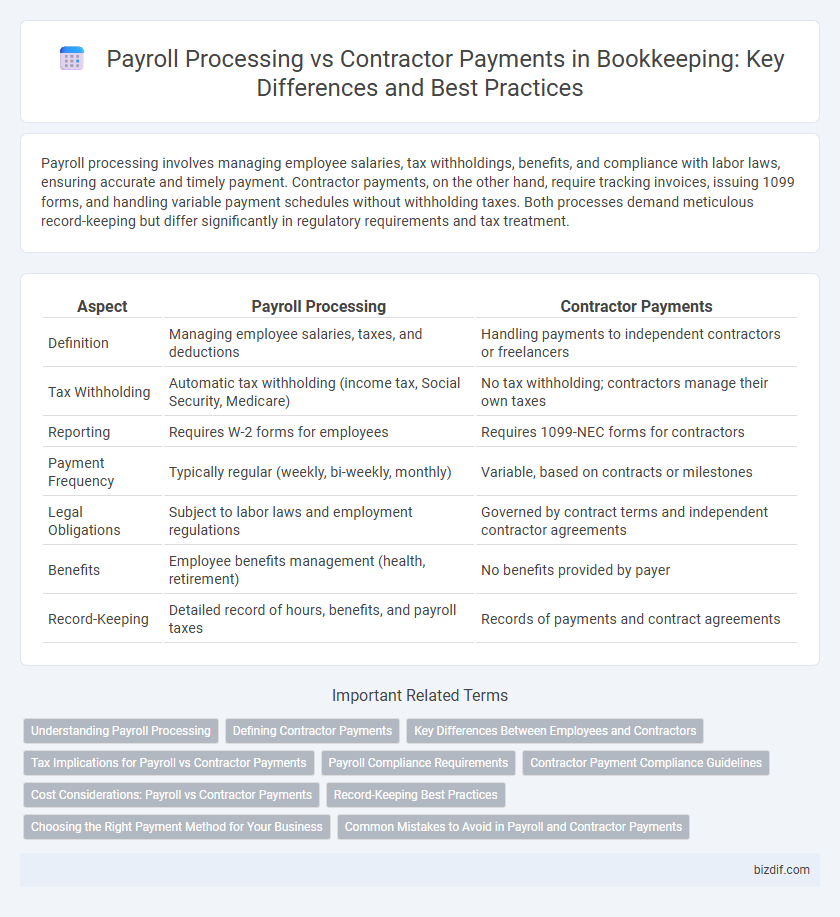
| Aspect | Payroll Processing | Contractor Payments |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Managing employee salaries, taxes, and deductions | Handling payments to independent contractors or freelancers |
| Tax Withholding | Automatic tax withholding (income tax, Social Security, Medicare) | No tax withholding; contractors manage their own taxes |
| Reporting | Requires W-2 forms for employees | Requires 1099-NEC forms for contractors |
| Payment Frequency | Typically regular (weekly, bi-weekly, monthly) | Variable, based on contracts or milestones |
| Legal Obligations | Subject to labor laws and employment regulations | Governed by contract terms and independent contractor agreements |
| Benefits | Employee benefits management (health, retirement) | No benefits provided by payer |
| Record-Keeping | Detailed record of hours, benefits, and payroll taxes | Records of payments and contract agreements |
Understanding Payroll Processing
Payroll processing involves calculating employee wages, withholding taxes, and ensuring compliance with labor laws to maintain accurate financial records. It requires managing benefits, deductions, and timely payment schedules for salaried and hourly employees. Proper payroll processing reduces errors, prevents legal issues, and streamlines employee compensation within a business's bookkeeping system.
Defining Contractor Payments
Contractor payments refer to the compensation made to independent contractors or freelancers for services rendered, typically documented through invoices rather than payroll systems. These payments are subject to different tax regulations compared to payroll wages, requiring careful tracking for tax reporting purposes such as issuing 1099 forms in the U.S. Proper classification and accounting of contractor payments help maintain compliance with labor laws and ensure accurate financial records in bookkeeping.
Key Differences Between Employees and Contractors
Payroll processing involves managing wages, tax withholdings, and benefits for employees, who typically work under a company's direction and receive regular paychecks with deductions. Contractor payments are treated as business expenses without tax withholdings, as contractors operate independently, invoice for services rendered, and are responsible for their own taxes. Key differences include employee eligibility for benefits, tax treatment, and legal obligations such as wage laws and reporting requirements.
Tax Implications for Payroll vs Contractor Payments
Payroll processing involves withholding income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes from employee wages, with employers responsible for matching payroll taxes and filing regular tax reports. Contractor payments are generally treated as non-employee compensation, requiring businesses to issue Form 1099-NEC without withholding taxes, shifting tax payment responsibility to the contractor. Misclassifying employees as contractors can result in significant tax penalties, interest, and back payments for unpaid payroll taxes.
Payroll Compliance Requirements
Payroll processing requires strict adherence to payroll compliance standards including tax withholdings, Social Security contributions, and accurate employee classification under IRS regulations. Contractor payments bypass traditional payroll tax withholdings but mandate proper issuance of Form 1099-MISC or 1099-NEC for non-employee compensation reporting. Ensuring compliance in payroll processing minimizes legal risks and promotes accurate tax reporting for both employers and employees.
Contractor Payment Compliance Guidelines
Contractor payment compliance guidelines require strict adherence to tax regulations, including accurate classification of workers as independent contractors to avoid misclassification penalties. Documentation such as W-9 forms and timely 1099 filings ensure transparency and legal compliance in contractor payments. Maintaining detailed records of payments and contracts supports audit readiness and minimizes risks associated with payroll processing errors.
Cost Considerations: Payroll vs Contractor Payments
Payroll processing involves fixed costs such as payroll software, tax withholding, and employee benefits management, which can increase overall expenses for businesses with many employees. Contractor payments reduce costs by eliminating benefits and tax withholdings, but contractors typically charge higher hourly rates to cover their own taxes and insurance. Choosing between payroll and contractor payments requires evaluating the trade-off between predictable payroll expenses and the potential cost-efficiency of variable contractor fees.
Record-Keeping Best Practices
Accurate payroll processing requires detailed record-keeping of employee hours, wages, tax withholdings, and benefits to comply with labor laws and tax regulations. Contractor payments demand meticulous tracking of invoices, payment dates, contract terms, and IRS Form 1099-MISC submissions to ensure proper documentation and tax reporting. Implementing dedicated ledgers or digital accounting systems enhances transparency, minimizes errors, and supports IRS audits for both payroll and contractor payment records.
Choosing the Right Payment Method for Your Business
Choosing the appropriate payment method between payroll processing and contractor payments hinges on your business structure and compliance needs. Payroll processing includes tax withholding, benefits, and employee protections, aligning with W-2 employee classifications, while contractor payments require issuing 1099 forms with no tax withholding, ideal for freelancers or independent contractors. Proper classification ensures adherence to IRS regulations, minimizes legal risks, and optimizes your bookkeeping accuracy for tax reporting.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Payroll and Contractor Payments
Common mistakes in payroll processing include misclassifying employees as contractors, resulting in tax and compliance issues. Overlooking proper documentation for contractor payments can lead to audit risks and inaccurate financial records. Ensuring timely and accurate tax withholdings and reporting for both employees and contractors is essential to avoid penalties and legal complications.
Payroll processing vs Contractor payments Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com