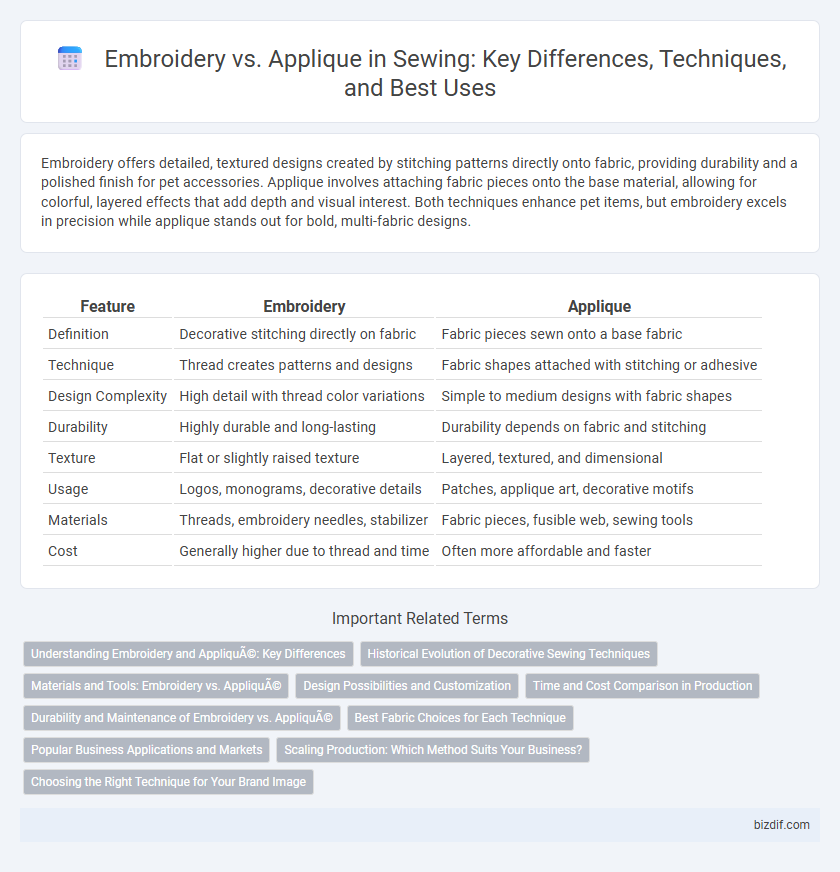
Embroidery offers detailed, textured designs created by stitching patterns directly onto fabric, providing durability and a polished finish for pet accessories. Applique involves attaching fabric pieces onto the base material, allowing for colorful, layered effects that add depth and visual interest. Both techniques enhance pet items, but embroidery excels in precision while applique stands out for bold, multi-fabric designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Embroidery | Applique |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decorative stitching directly on fabric | Fabric pieces sewn onto a base fabric |
| Technique | Thread creates patterns and designs | Fabric shapes attached with stitching or adhesive |
| Design Complexity | High detail with thread color variations | Simple to medium designs with fabric shapes |
| Durability | Highly durable and long-lasting | Durability depends on fabric and stitching |
| Texture | Flat or slightly raised texture | Layered, textured, and dimensional |
| Usage | Logos, monograms, decorative details | Patches, applique art, decorative motifs |
| Materials | Threads, embroidery needles, stabilizer | Fabric pieces, fusible web, sewing tools |
| Cost | Generally higher due to thread and time | Often more affordable and faster |
Understanding Embroidery and Appliqué: Key Differences
Embroidery involves stitching patterns directly onto fabric using threads to create intricate and durable designs, while applique entails sewing fabric pieces onto a base fabric to form decorative shapes or pictures. Key differences include embroidery's focus on thread-based detailing versus applique's reliance on layering fabrics, often enhanced by stitching, to add texture and dimension. Understanding these techniques allows sewers to select the appropriate method for durability, design complexity, and fabric type.
Historical Evolution of Decorative Sewing Techniques
Embroidery and applique both trace their origins to ancient civilizations, with embroidery dating back over 30,000 years as a method of embellishing fabrics through needle and thread patterns. Applique, emerging prominently in ancient Egypt and later flourishing in medieval Europe, involves layering fabric pieces to create intricate designs and textures. These decorative sewing techniques evolved alongside cultural expressions, with embroidery often reflecting intricate stitching skills while applique emphasized bold visual impact through fabric layering.
Materials and Tools: Embroidery vs. Appliqué
Embroidery requires threads like cotton, silk, or metallic, along with needles, embroidery hoops, and stabilizers to create detailed stitched patterns directly on fabric. Applique involves fabric pieces, fusible web, and sewing machines or hand stitching tools to adhere and secure shapes onto a base fabric, often complemented by scissors, rotary cutters, and pressing tools. Both techniques demand precision, but embroidery emphasizes thread selection and stitch variety, while applique focuses on fabric texture and adhesion methods.
Design Possibilities and Customization
Embroidery offers intricate, detailed designs with fine threadwork that enhances texture and depth, making it ideal for delicate patterns and personalized monograms. Applique allows for bold, multi-layered fabric shapes sewn onto the base material, enabling vibrant color contrasts and larger, more graphic motifs. Combining both techniques expands customization options, allowing creators to blend detailed stitching with eye-catching fabric patches for unique, multidimensional designs.
Time and Cost Comparison in Production
Embroidery typically requires more time and higher production costs due to intricate stitching techniques and specialized machinery, making it ideal for detailed designs. Applique tends to be faster to produce and more cost-effective, involving fabric pieces stitched onto a base material, which reduces labor intensity and thread consumption. Choosing between embroidery and applique depends on balancing design complexity with budget constraints and production timelines.
Durability and Maintenance of Embroidery vs. Appliqué
Embroidery offers superior durability due to its stitched patterns that tightly bind directly to the fabric, resisting wear and washing better than applique, which relies on fabric pieces sewn or glued onto the base material. Maintenance of embroidery is generally easier because it withstands frequent laundering without fraying or peeling, whereas applique may require gentle handling to prevent edges from loosening or fabric from fraying. Choosing embroidery over applique enhances longevity and reduces the need for delicate care, making it ideal for high-use garments and items.
Best Fabric Choices for Each Technique
Embroidery works best on stable, tightly woven fabrics such as cotton, linen, and denim, which provide a strong base to support the stitches and prevent puckering. Applique thrives on medium-weight fabrics like felt, canvas, and twill, allowing the decorative fabric pieces to hold their shape while being securely stitched onto a contrasting base material. Selecting the right fabric based on technique enhances durability and visual appeal in sewing projects.
Popular Business Applications and Markets
Embroidery is widely favored in corporate branding, uniform customization, and promotional merchandise due to its durability and professional appearance. Applique excels in fashion design, home decor, and personalized gifts, offering vibrant, textured patterns that attract niche markets. Both techniques thrive in the custom apparel industry, driving demand in sportswear, children's clothing, and handcrafted product markets.
Scaling Production: Which Method Suits Your Business?
Embroidery offers precise, durable designs ideal for high-volume production, making it suitable for businesses seeking consistent quality and scalability. Applique involves layering fabric pieces to create patterns, often requiring more manual labor and time, which can slow down large-scale output but adds texture and complexity. For rapid scaling, embroidery machinery automates stitching, while applique may be better for smaller batches or custom, intricate designs needing artisanal detail.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Brand Image
Embroidery offers a refined, durable finish with intricate thread designs ideal for luxury or professional brands seeking a polished look, while applique provides bold, textured patterns perfect for casual or artistic brands aiming to showcase creativity and vibrant visuals. Selecting the right technique depends on your brand's identity, budget, and the fabric type, as embroidery suits heavier materials and frequent washing, whereas applique works well on lighter fabrics with a more playful or handcrafted appeal. Understanding the visual impact and longevity requirements of each method ensures your products align seamlessly with your brand image and customer expectations.
Embroidery vs applique Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com