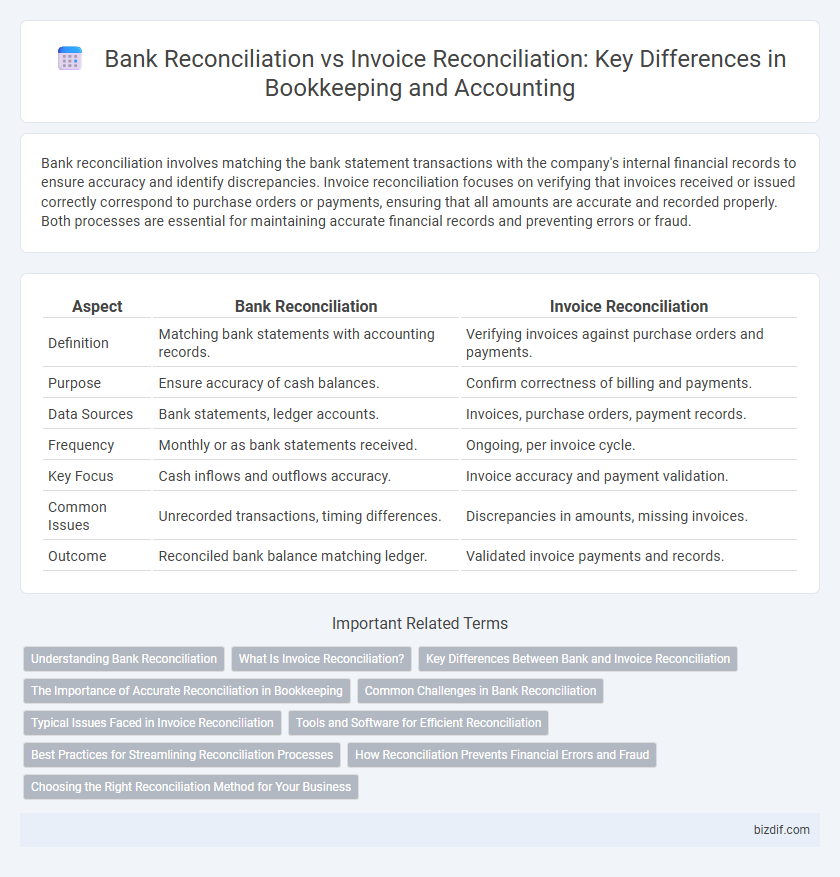
Bank reconciliation involves matching the bank statement transactions with the company's internal financial records to ensure accuracy and identify discrepancies. Invoice reconciliation focuses on verifying that invoices received or issued correctly correspond to purchase orders or payments, ensuring that all amounts are accurate and recorded properly. Both processes are essential for maintaining accurate financial records and preventing errors or fraud.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bank Reconciliation | Invoice Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Matching bank statements with accounting records. | Verifying invoices against purchase orders and payments. |
| Purpose | Ensure accuracy of cash balances. | Confirm correctness of billing and payments. |
| Data Sources | Bank statements, ledger accounts. | Invoices, purchase orders, payment records. |
| Frequency | Monthly or as bank statements received. | Ongoing, per invoice cycle. |
| Key Focus | Cash inflows and outflows accuracy. | Invoice accuracy and payment validation. |
| Common Issues | Unrecorded transactions, timing differences. | Discrepancies in amounts, missing invoices. |
| Outcome | Reconciled bank balance matching ledger. | Validated invoice payments and records. |
Understanding Bank Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation involves comparing the company's internal financial records with the bank statement to identify discrepancies such as outstanding checks or deposits in transit. This process ensures the accuracy of cash balances by verifying that all transactions recorded by the business are reflected correctly in the bank's records. Understanding bank reconciliation is crucial for maintaining financial integrity and detecting potential errors or fraud.
What Is Invoice Reconciliation?
Invoice reconciliation involves comparing and verifying invoices against purchase orders and payment records to ensure accuracy and prevent discrepancies. This process helps detect errors such as overcharges, duplicates, or missing invoices, improving financial accuracy. Effective invoice reconciliation aids in maintaining correct accounts payable balances and supports timely payment processing.
Key Differences Between Bank and Invoice Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation involves comparing the company's bank statements with its internal financial records to identify discrepancies and ensure accurate cash balances. Invoice reconciliation focuses on matching invoices received or issued against purchase orders or payment records to verify the accuracy of billed amounts and transaction details. Key differences include the source documents used--bank statements versus invoices--and the primary purpose: bank reconciliation ensures cash account accuracy, while invoice reconciliation validates payable and receivable transactions.
The Importance of Accurate Reconciliation in Bookkeeping
Accurate reconciliation in bookkeeping ensures that bank statements match internal financial records, preventing discrepancies that could lead to financial misstatements or fraud. Bank reconciliation validates cash flow by comparing company records to bank transactions, while invoice reconciliation verifies that invoices correspond with purchase orders and payments. Maintaining precise reconciliation processes enhances financial reporting accuracy, supports audit readiness, and strengthens overall financial management.
Common Challenges in Bank Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation often faces common challenges such as timing differences between bank statements and company records, missing or duplicate transactions, and discrepancies caused by bank fees or errors. In contrast, invoice reconciliation primarily deals with matching invoices to purchase orders and verifying payment status, focusing on document accuracy rather than transaction timing. Effective bank reconciliation requires meticulous cross-checking of ledger entries against bank statements to prevent financial discrepancies and ensure accurate cash flow management.
Typical Issues Faced in Invoice Reconciliation
Typical issues faced in invoice reconciliation include discrepancies between purchase orders and invoices, missing or duplicate invoices, and incorrect payment terms. Errors in quantity, pricing, or tax rates often cause delays in matching invoices to corresponding transactions. Manual data entry mistakes and lack of proper documentation further complicate the reconciliation process, hindering accurate financial reporting.
Tools and Software for Efficient Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation and invoice reconciliation both benefit significantly from specialized tools like QuickBooks, Xero, and Zoho Books, which automate transaction matching and error detection to streamline financial accuracy. Advanced software integrates bank feeds and invoice data, reducing manual entry and speeding up discrepancy resolution through features like real-time syncing and AI-powered anomaly detection. Utilizing these tools enhances reconciliation efficiency, minimizes human error, and ensures compliance with accounting standards.
Best Practices for Streamlining Reconciliation Processes
Bank reconciliation requires matching the company's bank statements with internal cash records to identify discrepancies and ensure accuracy. Invoice reconciliation focuses on verifying invoices against purchase orders and payment records to confirm the validity of transactions. Best practices include automating data entry, regularly scheduling reconciliations, and using integrated accounting software to reduce errors and streamline the reconciliation process.
How Reconciliation Prevents Financial Errors and Fraud
Bank reconciliation and invoice reconciliation both serve as critical controls in detecting discrepancies and ensuring the accuracy of financial records by matching bank statements with internal ledgers and verifying invoice amounts against payments, respectively. These reconciliation processes help identify errors such as double payments, missing deposits, or unauthorized transactions, effectively minimizing the risk of financial misstatements. Rigorous reconciliation also acts as a preventive measure against fraud by revealing irregular patterns that could indicate fraudulent activities, thereby safeguarding the business's financial integrity.
Choosing the Right Reconciliation Method for Your Business
Bank reconciliation compares your business's cash records with bank statements to identify discrepancies and ensure accuracy. Invoice reconciliation verifies payments and outstanding balances by matching invoices with corresponding payment records. Select bank reconciliation for cash flow accuracy and fraud detection, while invoice reconciliation suits accounts receivable management and customer payment tracking.
Bank Reconciliation vs Invoice Reconciliation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com