Book balance refers to the balance of an account as recorded in a company's accounting records, while bank balance is the amount shown on the bank statement. Discrepancies between these balances often arise due to outstanding checks, deposits in transit, or bank fees not yet recorded in the books. Regular reconciliation of book balance and bank balance ensures accurate financial reporting and helps identify errors or fraudulent transactions.
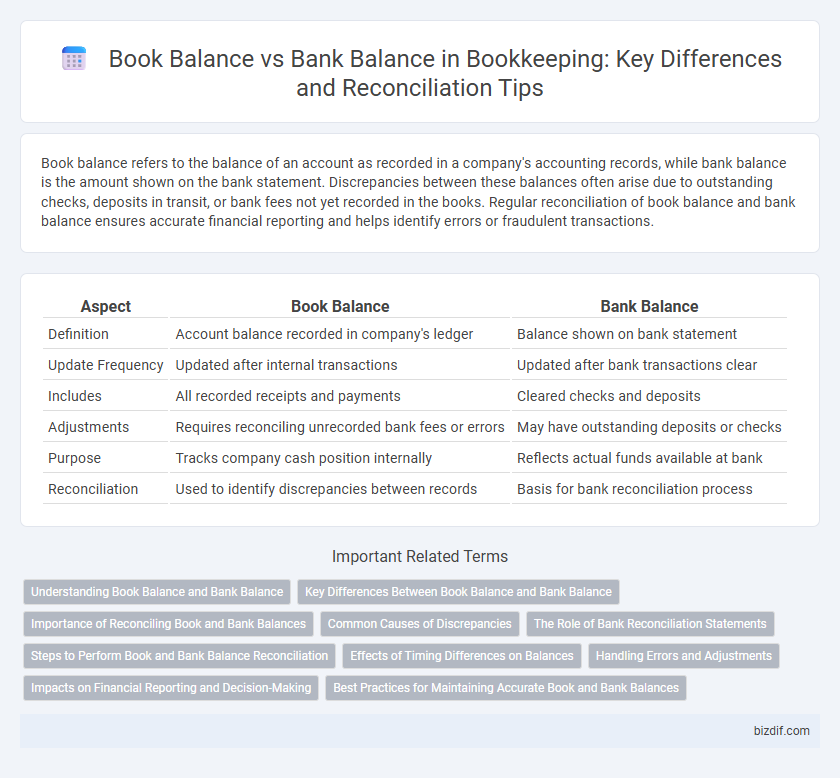
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Book Balance | Bank Balance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Account balance recorded in company's ledger | Balance shown on bank statement |
| Update Frequency | Updated after internal transactions | Updated after bank transactions clear |
| Includes | All recorded receipts and payments | Cleared checks and deposits |
| Adjustments | Requires reconciling unrecorded bank fees or errors | May have outstanding deposits or checks |
| Purpose | Tracks company cash position internally | Reflects actual funds available at bank |
| Reconciliation | Used to identify discrepancies between records | Basis for bank reconciliation process |
Understanding Book Balance and Bank Balance
Book balance refers to the amount recorded in the company's accounting records, including all outstanding checks and deposits in transit, while bank balance represents the amount available in the bank account at a given moment. Differences between book balance and bank balance arise due to timing differences, errors, bank service charges, or unrecorded transactions. Accurate reconciliation of book balance and bank balance ensures reliable financial reporting and helps identify discrepancies promptly.
Key Differences Between Book Balance and Bank Balance
Book balance refers to the amount recorded in a company's accounting records, reflecting transactions recorded by the business, while bank balance is the actual amount available in the bank account as shown on the bank statement. Differences arise due to timing issues such as outstanding checks, deposits in transit, and bank fees or errors not yet captured in the book records. Reconciling these balances is essential for accurate financial management and detecting discrepancies or fraud.
Importance of Reconciling Book and Bank Balances
Reconciling book balance and bank balance is crucial for accurate financial management and fraud detection. It ensures that all transactions are recorded correctly, highlighting discrepancies such as outstanding checks or bank fees. Regular reconciliation prevents errors, maintains cash flow accuracy, and supports reliable financial reporting.
Common Causes of Discrepancies
Discrepancies between book balance and bank balance often arise from outstanding checks, deposits in transit, and bank fees not yet recorded in the books. Timing differences occur when transactions are recorded by the bank after the company has updated its ledgers. Errors such as double posting, omission, or incorrect amounts in either the bank statement or accounting records also contribute to these variances.
The Role of Bank Reconciliation Statements
Bank reconciliation statements play a critical role in identifying discrepancies between the book balance and the bank balance by systematically comparing the company's ledger records with the bank statement. This process highlights timing differences, unrecorded transactions, errors, and fraudulent activities, ensuring accurate financial reporting and cash flow management. Regular bank reconciliation enhances internal controls, supports effective decision-making, and maintains the integrity of accounting records.
Steps to Perform Book and Bank Balance Reconciliation
Performing book and bank balance reconciliation requires collecting bank statements and internal ledger records to compare transaction details for accuracy. Identify discrepancies such as outstanding checks, deposits in transit, or bank fees by cross-referencing each entry between the book balance and bank balance. Adjust the company's books accordingly to reflect any unrecorded transactions, ensuring both balances match for accurate financial reporting.
Effects of Timing Differences on Balances
Timing differences between book balance and bank balance often arise from transactions recorded in one ledger but not yet reflected in the other. Outstanding checks, deposits in transit, and bank fees cause temporary discrepancies, impacting cash flow analysis and reconciliation processes. Accurate adjustment for these timing differences ensures reliable financial reporting and effective cash management.
Handling Errors and Adjustments
Discrepancies between book balance and bank balance often arise from timing differences, unrecorded transactions, or data entry errors. Handling errors involves identifying and correcting mistakes such as duplicate entries, omissions, or incorrect amounts in the ledger. Adjustments like bank fees, interest income, or outstanding checks must be reconciled promptly to ensure accurate financial reporting and maintain trust in bookkeeping records.
Impacts on Financial Reporting and Decision-Making
Differences between book balance and bank balance can create discrepancies that significantly impact financial reporting accuracy and decision-making processes. Reconciling these balances ensures that financial statements reflect the true cash position, preventing errors in income calculations and misstatements of assets. Accurate alignment supports informed decisions regarding cash flow management, budgeting, and investment strategies.
Best Practices for Maintaining Accurate Book and Bank Balances
Maintaining accurate book and bank balances requires regular reconciliation to identify and correct discrepancies caused by timing differences or errors. Implementing systematic record-keeping practices, such as promptly recording all transactions and verifying bank statements against internal records monthly, enhances accuracy. Utilizing accounting software with automated reconciliation features further reduces human errors and improves financial data integrity.
Book balance vs Bank balance Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com