Debits increase asset or expense accounts and decrease liability, revenue, or equity accounts, while credits do the opposite by increasing liability, revenue, or equity accounts and decreasing asset or expense accounts. Understanding the roles of debits and credits is essential for accurate financial statement preparation and maintaining balanced accounts. Correct application of these principles ensures precise tracking of business transactions and financial health.
Table of Comparison
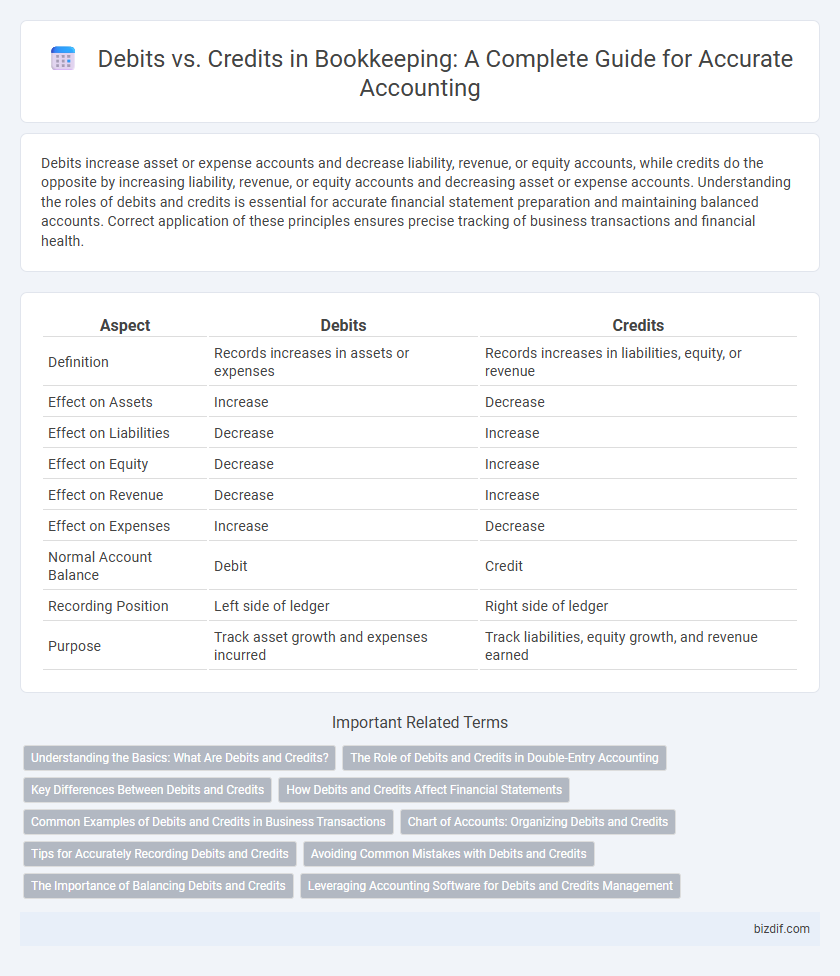
| Aspect | Debits | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Records increases in assets or expenses | Records increases in liabilities, equity, or revenue |
| Effect on Assets | Increase | Decrease |
| Effect on Liabilities | Decrease | Increase |
| Effect on Equity | Decrease | Increase |
| Effect on Revenue | Decrease | Increase |
| Effect on Expenses | Increase | Decrease |
| Normal Account Balance | Debit | Credit |
| Recording Position | Left side of ledger | Right side of ledger |
| Purpose | Track asset growth and expenses incurred | Track liabilities, equity growth, and revenue earned |
Understanding the Basics: What Are Debits and Credits?
Debits and credits are fundamental accounting entries that record increases or decreases in financial accounts based on double-entry bookkeeping principles. A debit typically increases asset or expense accounts while decreasing liability, equity, or revenue accounts; conversely, a credit increases liability, equity, or revenue accounts and decreases asset or expense accounts. Mastering the impact of debits and credits on the accounting equation ensures accurate financial statements and effective bookkeeping.
The Role of Debits and Credits in Double-Entry Accounting
Debits and credits form the foundation of double-entry accounting by ensuring every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, maintaining the accounting equation's balance. Debits increase asset and expense accounts, while credits increase liabilities, equity, and revenue accounts, providing a precise method to record and track financial activities. This dual-entry system enhances accuracy and fraud detection by requiring equal debit and credit entries for each transaction.
Key Differences Between Debits and Credits
Debits increase asset and expense accounts while decreasing liabilities and equity, whereas credits increase liabilities, equity, and revenue accounts and reduce assets and expenses. In double-entry bookkeeping, every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, with debits recorded on the left side and credits on the right. Understanding the opposite impact of debits and credits is essential for accurate financial reporting and maintaining balanced accounting records.
How Debits and Credits Affect Financial Statements
Debits increase asset and expense accounts while decreasing liabilities, equity, and revenue accounts, directly influencing the balance sheet and income statement. Credits have the opposite effect, increasing liabilities, equity, and revenue but decreasing assets and expenses. Understanding how debits and credits impact financial statements ensures accurate recording of transactions and proper financial reporting.
Common Examples of Debits and Credits in Business Transactions
In bookkeeping, common examples of debits include asset increases such as cash, inventory, and accounts receivable, reflecting resources owned by the business. Credits typically represent liabilities and equity changes, including accounts payable, loans, and owner's capital contributions, indicating sources of financing or obligations. Understanding these typical debit and credit entries is essential for maintaining balanced accounting records in business transactions.
Chart of Accounts: Organizing Debits and Credits
The Chart of Accounts categorizes debits and credits to maintain clear and organized financial records, grouping accounts into assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. Debits increase asset and expense accounts while decreasing liabilities, equity, and revenue accounts; credits operate inversely. Proper classification within the Chart of Accounts ensures accurate tracking of financial transactions and improves the reliability of financial statements.
Tips for Accurately Recording Debits and Credits
Accurately recording debits and credits requires understanding that debits increase asset and expense accounts while credits increase liability, equity, and revenue accounts. Consistently applying the double-entry bookkeeping principle ensures each transaction has equal debits and credits, maintaining balanced accounts. Utilizing accounting software with built-in validation features can reduce errors and improve accuracy in financial records.
Avoiding Common Mistakes with Debits and Credits
Misclassifying debits and credits often leads to unbalanced accounts and inaccurate financial statements in bookkeeping. Maintaining a clear understanding that debits increase asset and expense accounts while credits increase liability, equity, and revenue accounts prevents common errors. Implementing consistent double-entry bookkeeping and regularly reconciling accounts ensures accurate transaction recording and reduces discrepancies.
The Importance of Balancing Debits and Credits
Balancing debits and credits is crucial in bookkeeping to ensure the accuracy of financial statements and maintain the integrity of the double-entry accounting system. Every transaction affects at least two accounts, requiring equal debits and credits to prevent discrepancies and errors in the ledger. Consistent balance verification supports reliable financial reporting, regulatory compliance, and effective decision-making for businesses.
Leveraging Accounting Software for Debits and Credits Management
Leveraging accounting software enhances the accuracy and efficiency of managing debits and credits by automating transaction recording and real-time account reconciliation. Advanced bookkeeping tools provide clear visualization of debit and credit flows, reducing errors and ensuring compliance with accounting standards. Cloud-based solutions enable seamless integration and data access, streamlining financial audits and reporting processes.
Debits vs Credits Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com