Batch production allows for the creation of sewing pets in specific quantities, offering flexibility and customization to meet diverse customer preferences. Mass production focuses on high-volume output, reducing costs per unit but limiting variety and personalization. Choosing between these methods depends on balancing quality, demand, and production efficiency.
Table of Comparison
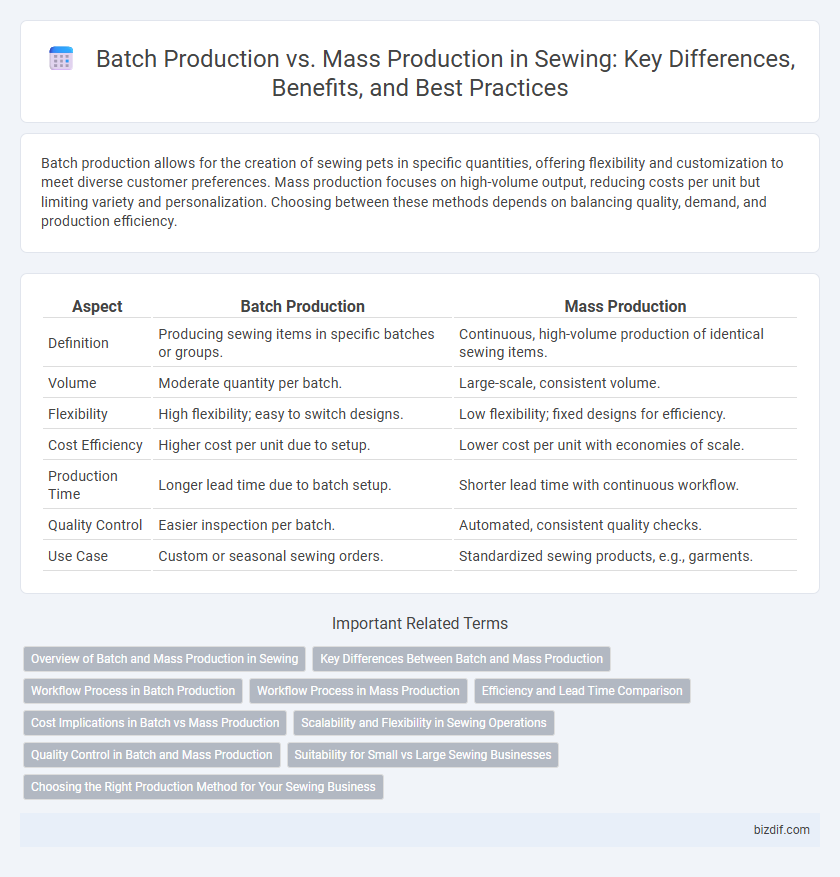
| Aspect | Batch Production | Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Producing sewing items in specific batches or groups. | Continuous, high-volume production of identical sewing items. |
| Volume | Moderate quantity per batch. | Large-scale, consistent volume. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; easy to switch designs. | Low flexibility; fixed designs for efficiency. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost per unit due to setup. | Lower cost per unit with economies of scale. |
| Production Time | Longer lead time due to batch setup. | Shorter lead time with continuous workflow. |
| Quality Control | Easier inspection per batch. | Automated, consistent quality checks. |
| Use Case | Custom or seasonal sewing orders. | Standardized sewing products, e.g., garments. |
Overview of Batch and Mass Production in Sewing
Batch production in sewing involves creating limited quantities of garments with a focus on flexibility and customization, allowing for variations in design and fabric choices. Mass production emphasizes high-volume output through standardized processes and automated machinery, optimizing efficiency and reducing unit costs. Both methods play crucial roles in the apparel industry, with batch production suited for niche markets and mass production targeting large-scale distribution.
Key Differences Between Batch and Mass Production
Batch production involves manufacturing goods in groups or sets, allowing for greater flexibility and customization, which is ideal for limited sewing runs or diverse product lines. Mass production focuses on continuous, high-volume output with standardized designs, optimizing efficiency and reducing costs per unit in large-scale garment manufacturing. Key differences include scalability, cost per unit, production speed, and the ability to accommodate variations in design and fabric types.
Workflow Process in Batch Production
Batch production in sewing involves completing a specific quantity of garments through sequential stages, allowing quality control at each step before moving to the next batch. This workflow process enhances flexibility and reduces downtime by enabling adjustments between batches, catering to varied designs and sizes. Operators focus on one stage at a time, which streamlines resource allocation and minimizes errors compared to continuous mass production lines.
Workflow Process in Mass Production
Mass production in sewing relies on a highly streamlined workflow process characterized by assembly line techniques where each worker or machine performs a specific, repetitive task to enhance efficiency and consistency. This process minimizes production time per garment and reduces labor costs by dividing the sewing job into distinct, easily manageable steps. The integration of specialized equipment and standardized procedures ensures high output rates and uniform quality across large quantities of apparel.
Efficiency and Lead Time Comparison
Batch production in sewing allows for flexibility and customization, optimizing efficiency for small to medium order sizes by reducing setup times between different styles. Mass production achieves higher overall efficiency through continuous, high-volume runs, significantly minimizing lead time per unit by standardizing processes and utilizing automated machinery. While batch production offers shorter lead times for diverse products, mass production excels in economies of scale and consistent quality for large-volume orders.
Cost Implications in Batch vs Mass Production
Batch production in sewing typically incurs higher per-unit costs due to setup times and frequent machine adjustments, while mass production benefits from economies of scale, reducing the cost per garment through continuous, large-volume output. Inventory carrying costs can be higher in batch production because of smaller, more frequent runs, whereas mass production optimizes raw material usage and minimizes waste, contributing to lower overall expenses. Labor costs vary as batch production demands skilled workers for diverse tasks, whereas mass production often relies on repetitive, streamlined processes allowing for lower labor costs per unit.
Scalability and Flexibility in Sewing Operations
Batch production in sewing offers greater flexibility by allowing adjustments in design and fabric choices between batches, making it ideal for customized or seasonal clothing lines. Mass production prioritizes scalability, enabling the efficient manufacture of large quantities with standardized processes, significantly reducing per-unit costs. Choosing between batch and mass production depends on the balance of scalability needs and the flexibility required for product variety in sewing operations.
Quality Control in Batch and Mass Production
Batch production in sewing allows for more precise quality control due to smaller quantities and focused inspection at each stage, reducing defects and ensuring consistency. Mass production relies heavily on automated quality control systems and statistical process control to maintain standards across large volumes, though it may face higher risks of widespread defects if issues go undetected. Effective quality management in both methods is crucial to minimize rework costs and maintain brand reputation in garment manufacturing.
Suitability for Small vs Large Sewing Businesses
Batch production is ideal for small sewing businesses that require flexibility and customization, producing limited quantities of garments with varied designs. Mass production suits large sewing enterprises focused on high-volume output and cost efficiency, utilizing automated processes for uniformity. Small businesses benefit from reduced inventory risks, while large firms achieve economies of scale with mass production techniques.
Choosing the Right Production Method for Your Sewing Business
Batch production allows sewing businesses to create limited quantities with higher customization and flexibility, ideal for niche markets or seasonal collections. Mass production suits high-volume orders with standardized designs, maximizing efficiency and reducing per-unit costs in large-scale manufacturing. Selecting the right method depends on order size, product variety, turnaround time, and cost considerations to optimize workflow and profitability in a sewing operation.
Batch Production vs Mass Production Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com