Mass customization in sewing pets allows for personalized designs tailored to individual preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction through unique features and perfect fit. In contrast, mass production prioritizes efficiency and uniformity, producing large quantities of identical items at lower costs but with limited variety. Balancing customization and production volume is essential for meeting diverse market demands while maintaining profitability in the pet sewing industry.
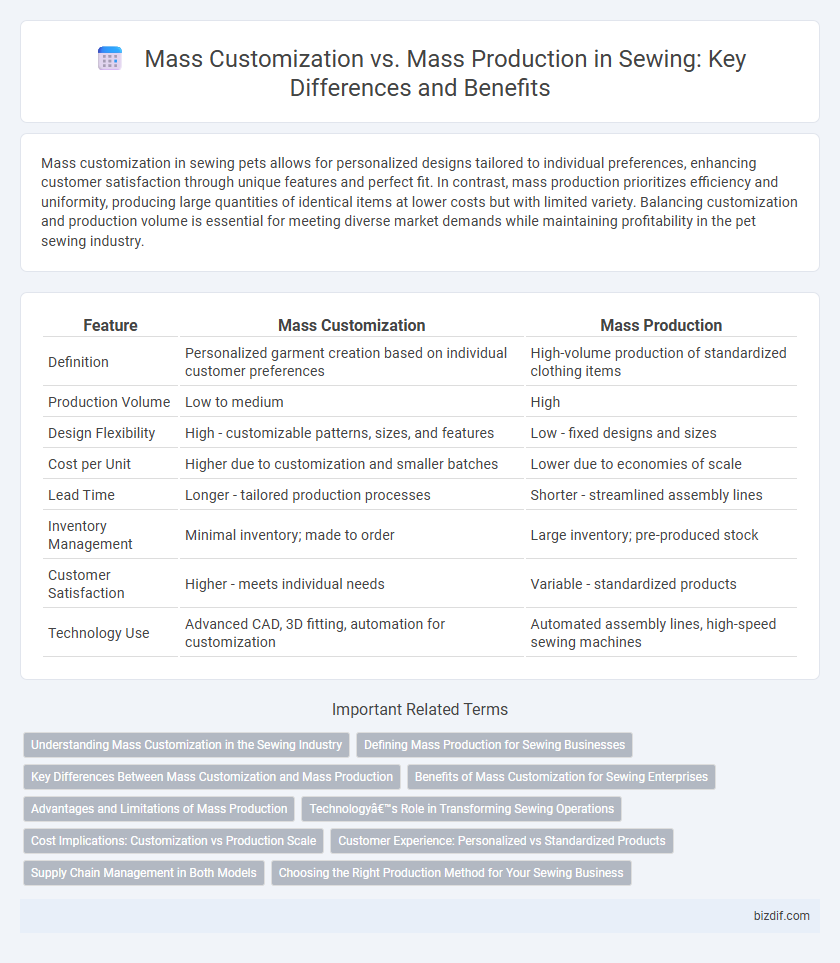
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mass Customization | Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personalized garment creation based on individual customer preferences | High-volume production of standardized clothing items |
| Production Volume | Low to medium | High |
| Design Flexibility | High - customizable patterns, sizes, and features | Low - fixed designs and sizes |
| Cost per Unit | Higher due to customization and smaller batches | Lower due to economies of scale |
| Lead Time | Longer - tailored production processes | Shorter - streamlined assembly lines |
| Inventory Management | Minimal inventory; made to order | Large inventory; pre-produced stock |
| Customer Satisfaction | Higher - meets individual needs | Variable - standardized products |
| Technology Use | Advanced CAD, 3D fitting, automation for customization | Automated assembly lines, high-speed sewing machines |
Understanding Mass Customization in the Sewing Industry
Mass customization in the sewing industry combines the efficiency of mass production with personalized garment options, using advanced technologies like automated cutting and digital pattern making to tailor products to individual customer preferences. This approach enables manufacturers to offer unique designs and precise fits without sacrificing large-scale output, reducing waste and improving customer satisfaction. Unlike traditional mass production, mass customization leverages real-time data and flexible manufacturing systems to respond swiftly to market trends and specific consumer demands.
Defining Mass Production for Sewing Businesses
Mass production in sewing businesses involves producing large quantities of identical garments using standardized processes and machinery to achieve efficiency and cost reduction. This approach emphasizes high-volume output with minimal variation, streamlining fabric cutting, stitching, and assembly to meet consistent quality standards. Mass production relies heavily on automation and skilled labor to maintain speed and uniformity across product lines.
Key Differences Between Mass Customization and Mass Production
Mass customization involves producing personalized clothing tailored to individual measurements and preferences, while mass production focuses on manufacturing large quantities of standardized garments. Key differences include the flexibility of design options in mass customization versus predefined patterns in mass production, as well as the typically higher production cost and longer lead time associated with customized sewing. Mass production benefits from economies of scale and faster turnaround, whereas mass customization emphasizes customer satisfaction through unique, made-to-order apparel.
Benefits of Mass Customization for Sewing Enterprises
Mass customization in sewing enterprises offers significant benefits including increased customer satisfaction through personalized garment design and fit, which leads to higher brand loyalty and repeat business. It reduces inventory costs and waste by producing items on demand rather than in large batches, enhancing sustainability and cost efficiency. Advanced digital technologies and automated sewing machines enable faster turnaround times and flexibility in production, allowing these businesses to rapidly respond to market trends and customer preferences.
Advantages and Limitations of Mass Production
Mass production in sewing enables high-volume garment manufacturing with consistent quality and reduced unit costs, making it ideal for meeting large market demands efficiently. It benefits from streamlined processes and economies of scale but struggles with limited customization options and slower response to fashion trends or individual customer preferences. The rigidity of production lines can hinder flexibility, resulting in potential overstock and challenges in adapting to niche or seasonal variations.
Technology’s Role in Transforming Sewing Operations
Technology's integration in sewing operations drives a shift from traditional mass production to mass customization, enabling personalized garment creation at scale. Advanced automation tools, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and programmable sewing machines, streamline precise production processes while accommodating unique customer specifications. Digital fabric cutting and real-time data analytics enhance efficiency and reduce waste, reshaping the apparel manufacturing landscape toward flexible, demand-driven output.
Cost Implications: Customization vs Production Scale
Mass customization in sewing often incurs higher per-unit costs due to individualized designs and smaller batch sizes, increasing labor and material expenses. In contrast, mass production benefits from economies of scale, significantly lowering costs through bulk purchasing, standardized processes, and automated machinery. Balancing customization demands with cost efficiency requires strategic investment in flexible manufacturing technologies and optimized workflow management.
Customer Experience: Personalized vs Standardized Products
Mass customization in sewing enhances customer experience by offering personalized garments tailored to individual measurements, styles, and preferences, resulting in higher satisfaction and a unique fit. In contrast, mass production focuses on standardized products with uniform sizing and design, prioritizing efficiency but often leading to generic fits and limited personalization. Personalized sewing solutions utilize technology such as 3D body scanning and on-demand manufacturing to meet specific customer needs, elevating the overall buying experience.
Supply Chain Management in Both Models
Mass customization in sewing requires a flexible supply chain capable of rapid adaptation to individual customer demands, leveraging just-in-time inventory and digital integration for real-time order processing. In contrast, mass production relies on a linear, standardized supply chain focused on economies of scale, bulk material procurement, and long production runs to minimize costs and maximize efficiency. Effective supply chain management in mass customization emphasizes agility, decentralized sourcing, and advanced demand forecasting, while mass production prioritizes process optimization and supplier consistency.
Choosing the Right Production Method for Your Sewing Business
Mass customization in sewing enables businesses to offer personalized garments tailored to individual customer measurements and preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction through flexibility and uniqueness. Mass production emphasizes large-scale efficiency, delivering consistent quality and lower costs per unit by using standardized patterns and automated machinery. Selecting the appropriate production method depends on factors like target market demand, production volume, lead time, and the level of customization required by the sewing business.
Mass Customization vs Mass Production Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com