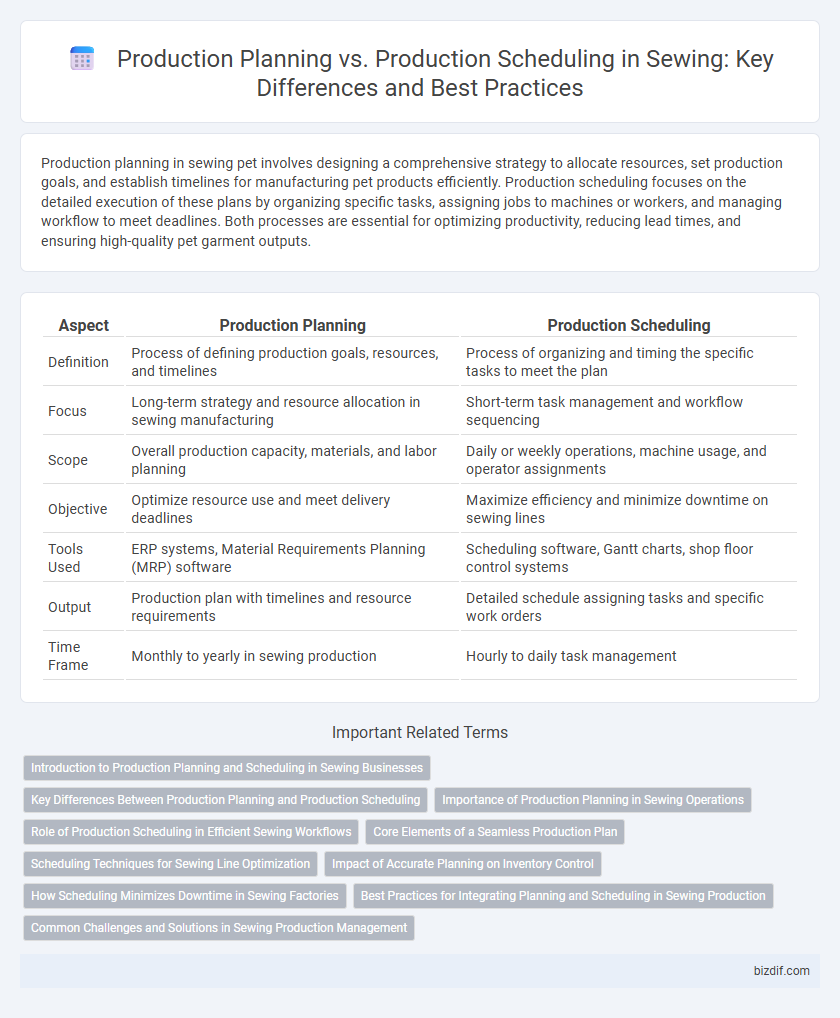
Production planning in sewing pet involves designing a comprehensive strategy to allocate resources, set production goals, and establish timelines for manufacturing pet products efficiently. Production scheduling focuses on the detailed execution of these plans by organizing specific tasks, assigning jobs to machines or workers, and managing workflow to meet deadlines. Both processes are essential for optimizing productivity, reducing lead times, and ensuring high-quality pet garment outputs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Production Planning | Production Scheduling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of defining production goals, resources, and timelines | Process of organizing and timing the specific tasks to meet the plan |
| Focus | Long-term strategy and resource allocation in sewing manufacturing | Short-term task management and workflow sequencing |
| Scope | Overall production capacity, materials, and labor planning | Daily or weekly operations, machine usage, and operator assignments |
| Objective | Optimize resource use and meet delivery deadlines | Maximize efficiency and minimize downtime on sewing lines |
| Tools Used | ERP systems, Material Requirements Planning (MRP) software | Scheduling software, Gantt charts, shop floor control systems |
| Output | Production plan with timelines and resource requirements | Detailed schedule assigning tasks and specific work orders |
| Time Frame | Monthly to yearly in sewing production | Hourly to daily task management |
Introduction to Production Planning and Scheduling in Sewing Businesses
Production planning in sewing businesses involves allocating resources, estimating fabric requirements, and setting production targets to ensure efficient workflow and meet customer deadlines. Production scheduling breaks down the plan into specific tasks, assigning workstations and timelines to optimize machine usage and labor performance. Effective integration of both processes enhances productivity, reduces lead times, and maintains quality standards in garment manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Production Planning and Production Scheduling
Production planning in sewing involves designing the overall workflow, defining resource requirements, and setting timelines for fabric cutting, stitching, and finishing processes, while production scheduling focuses on allocating specific tasks to workstations and operators, optimizing the sequence and timing of garment assembly operations. Planning determines the what, how, and when at a macro level to ensure fabric availability, machinery capacity, and labor allocation, whereas scheduling breaks down these plans into detailed daily or hourly tasks to maximize efficiency and meet delivery deadlines. Key differences lie in scope and granularity: planning establishes strategic objectives and resource allocation, while scheduling implements tactical execution and real-time workflow adjustments in garment manufacturing.
Importance of Production Planning in Sewing Operations
Effective production planning in sewing operations ensures optimal resource allocation, reduces material waste, and enhances workflow efficiency. It establishes a strategic framework that guides inventory management, machine availability, and labor scheduling before actual production begins. Prioritizing production planning minimizes downtime, improves order fulfillment accuracy, and boosts overall garment manufacturing productivity.
Role of Production Scheduling in Efficient Sewing Workflows
Production scheduling plays a crucial role in efficient sewing workflows by allocating specific tasks and timelines to ensure timely garment assembly and minimize bottlenecks. It coordinates labor, machinery, and materials, optimizing machine utilization and reducing idle time in production lines. Effective production scheduling enhances workflow synchronization, leading to increased productivity and consistent product quality in sewing operations.
Core Elements of a Seamless Production Plan
Production planning in sewing focuses on the strategic allocation of resources, including fabric types, machine capacities, and skilled labor, to meet order deadlines. Production scheduling optimizes the sequencing and timing of garment assembly lines, ensuring each phase from cutting to stitching aligns with capacity limits and quality standards. Core elements such as accurate demand forecasting, inventory control, and workflow synchronization enable a seamless production plan that minimizes delays and maximizes efficiency in garment manufacturing.
Scheduling Techniques for Sewing Line Optimization
Production scheduling in sewing involves allocating tasks and sequencing operations to maximize efficiency on the sewing line. Advanced scheduling techniques such as Gantt charts, finite capacity scheduling, and just-in-time (JIT) methods enable dynamic adjustment of workloads, reduce idle time, and balance operator skills with machine availability. Implementing these techniques enhances workflow synchronization, minimizes bottlenecks, and improves overall production output in garment manufacturing.
Impact of Accurate Planning on Inventory Control
Accurate production planning in sewing directly influences inventory control by optimizing material requirements and reducing excess stock. Detailed planning forecasts demand precisely, preventing overproduction and minimizing storage costs. Effective synchronization between production planning and scheduling ensures timely availability of fabrics and accessories, enhancing overall inventory efficiency.
How Scheduling Minimizes Downtime in Sewing Factories
Production scheduling in sewing factories optimizes machine and labor allocation to reduce idle time and ensure continuous workflow. By sequencing tasks based on fabric availability, machine capability, and worker skill sets, scheduling minimizes bottlenecks and downtime during production runs. Effective scheduling leads to higher productivity and timely order fulfillment by aligning resources with peak demand periods.
Best Practices for Integrating Planning and Scheduling in Sewing Production
Effective integration of production planning and scheduling in sewing production involves aligning resource allocation with real-time workflow management to minimize downtime and enhance productivity. Best practices include implementing robust software systems for accurate demand forecasting and capacity planning, combined with dynamic scheduling tools that adapt to order priorities and machine availability. Continuous communication between planning and shop floor teams ensures timely adjustments, reducing bottlenecks and maintaining optimal output quality.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Sewing Production Management
Production planning and production scheduling in sewing involve coordinating resources and timelines to meet garment manufacturing targets efficiently, yet common challenges include inaccurate demand forecasting, resource constraints, and workflow bottlenecks. Solutions emphasize implementing advanced ERP systems tailored for sewing production, real-time data tracking with IoT devices, and adopting lean manufacturing principles to improve flexibility and reduce waste. Effective integration of these strategies enhances production accuracy, minimizes lead times, and ensures timely delivery in the competitive apparel industry.
Production Planning vs Production Scheduling Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com