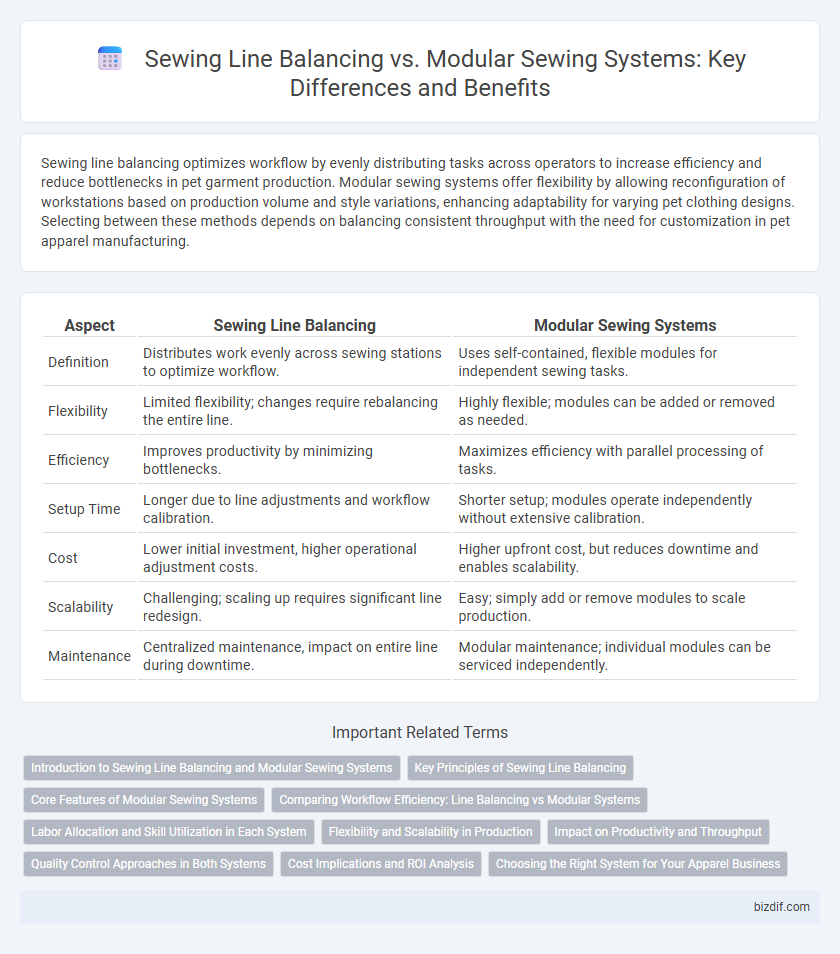
Sewing line balancing optimizes workflow by evenly distributing tasks across operators to increase efficiency and reduce bottlenecks in pet garment production. Modular sewing systems offer flexibility by allowing reconfiguration of workstations based on production volume and style variations, enhancing adaptability for varying pet clothing designs. Selecting between these methods depends on balancing consistent throughput with the need for customization in pet apparel manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sewing Line Balancing | Modular Sewing Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributes work evenly across sewing stations to optimize workflow. | Uses self-contained, flexible modules for independent sewing tasks. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility; changes require rebalancing the entire line. | Highly flexible; modules can be added or removed as needed. |
| Efficiency | Improves productivity by minimizing bottlenecks. | Maximizes efficiency with parallel processing of tasks. |
| Setup Time | Longer due to line adjustments and workflow calibration. | Shorter setup; modules operate independently without extensive calibration. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, higher operational adjustment costs. | Higher upfront cost, but reduces downtime and enables scalability. |
| Scalability | Challenging; scaling up requires significant line redesign. | Easy; simply add or remove modules to scale production. |
| Maintenance | Centralized maintenance, impact on entire line during downtime. | Modular maintenance; individual modules can be serviced independently. |
Introduction to Sewing Line Balancing and Modular Sewing Systems
Sewing line balancing optimizes workflow by evenly distributing tasks across operators to minimize bottlenecks and improve productivity, crucial in traditional straight assembly lines. Modular sewing systems divide production into self-contained units or modules, enhancing flexibility and allowing teams to focus on complete garment sections, which reduces idle time and increases quality control. Both approaches aim to maximize efficiency, but modular systems offer greater adaptability for variable production demands.
Key Principles of Sewing Line Balancing
Sewing line balancing optimizes workflow by evenly distributing tasks to minimize idle time and maximize machine efficiency, improving overall production rates. Key principles include task time measurement, workload analysis, and station assignment to ensure smooth fabric flow and technician productivity. Modular sewing systems offer flexibility by grouping operations into self-contained units but require precise line balancing for seamless integration and reduced bottlenecks.
Core Features of Modular Sewing Systems
Modular sewing systems feature flexible workstations designed to optimize ergonomic placement of tools and materials, reducing operator movement and increasing efficiency. These systems enable easy reconfiguration and scalability, supporting diverse garment styles and varying production volumes without extensive downtime. Integrated automation and real-time data monitoring further enhance productivity by streamlining workflow and minimizing bottlenecks in the sewing process.
Comparing Workflow Efficiency: Line Balancing vs Modular Systems
Line balancing in sewing optimizes workflow by evenly distributing tasks across workstations to minimize idle time and bottlenecks. Modular sewing systems enhance workflow flexibility by grouping specialized operations into compact units, allowing simultaneous processing and quicker adjustments to production changes. Comparing the two, line balancing offers streamlined, steady throughput, while modular systems provide adaptability and faster response times for variable demand.
Labor Allocation and Skill Utilization in Each System
Sewing line balancing allocates labor based on task times to ensure consistent workflow and minimize bottlenecks, optimizing skill utilization by matching operators to specific, often repetitive tasks. Modular sewing systems leverage multi-skilled workers assigned to versatile modules, enhancing flexibility and allowing dynamic labor shifts to meet fluctuating production demands. This approach improves overall skill utilization by encouraging cross-training and enabling rapid reallocation of labor to balance workloads efficiently.
Flexibility and Scalability in Production
Sewing line balancing optimizes workload distribution across sequential workstations, enhancing efficiency but limiting flexibility when product styles or volumes change. Modular sewing systems offer greater adaptability by enabling rapid reconfiguration of sewing modules to accommodate diverse garment designs and fluctuating production demands. This scalability supports agile manufacturing, reducing downtime and improving responsiveness in dynamic production environments.
Impact on Productivity and Throughput
Sewing line balancing optimizes workflow by evenly distributing tasks among operators, reducing bottlenecks and ensuring consistent throughput, which directly enhances productivity in apparel manufacturing. Modular sewing systems offer flexibility by grouping related operations into compact units, allowing rapid adjustments to production volumes and styles, thus improving responsiveness and overall throughput. Integrating both approaches can maximize efficiency, with line balancing ensuring steady flow and modular systems providing adaptability for fluctuating demands.
Quality Control Approaches in Both Systems
Sewing line balancing emphasizes evenly distributing tasks to maintain consistent quality by minimizing bottlenecks and ensuring steady workflow, which aids in immediate defect detection and standardized inspection checkpoints. Modular sewing systems incorporate specialized modules with integrated quality control mechanisms, enabling real-time monitoring and prompt isolation of defects within specific modules for enhanced accuracy. Both approaches prioritize quality control but differ in their operational focus: line balancing optimizes task flow across workers, while modular systems leverage compartmentalization for targeted quality assurance.
Cost Implications and ROI Analysis
Sewing line balancing optimizes workflow by evenly distributing tasks, reducing labor costs and minimizing idle time, which enhances overall production efficiency and shortens ROI timelines. Modular sewing systems offer greater flexibility and scalability but may incur higher initial investment and maintenance expenses, affecting upfront cost implications. Analyzing ROI requires comparing improved throughput and reduced operational bottlenecks in line balancing against the adaptability and long-term cost savings of modular setups.
Choosing the Right System for Your Apparel Business
Selecting the right sewing system for your apparel business depends on production volume, labor skills, and product complexity. Sewing line balancing optimizes workflow by evenly distributing tasks to minimize bottlenecks, ideal for high-volume, standardized garment manufacturing. Modular sewing systems offer flexibility and adaptability, allowing quick changes between styles and sizes, making them suitable for small to medium operations with diverse product lines.
Sewing line balancing vs Modular sewing systems Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com