Accounts Payable refers to the money a business owes to its suppliers or vendors for goods and services received, representing outgoing payments that impact cash flow management. Accounts Receivable, on the other hand, consists of funds owed to the business by customers who have purchased products or services on credit, reflecting incoming payments expected to improve liquidity. Understanding the distinction between these two accounts is crucial for accurate financial reporting and effective cash flow optimization in bookkeeping.
Table of Comparison
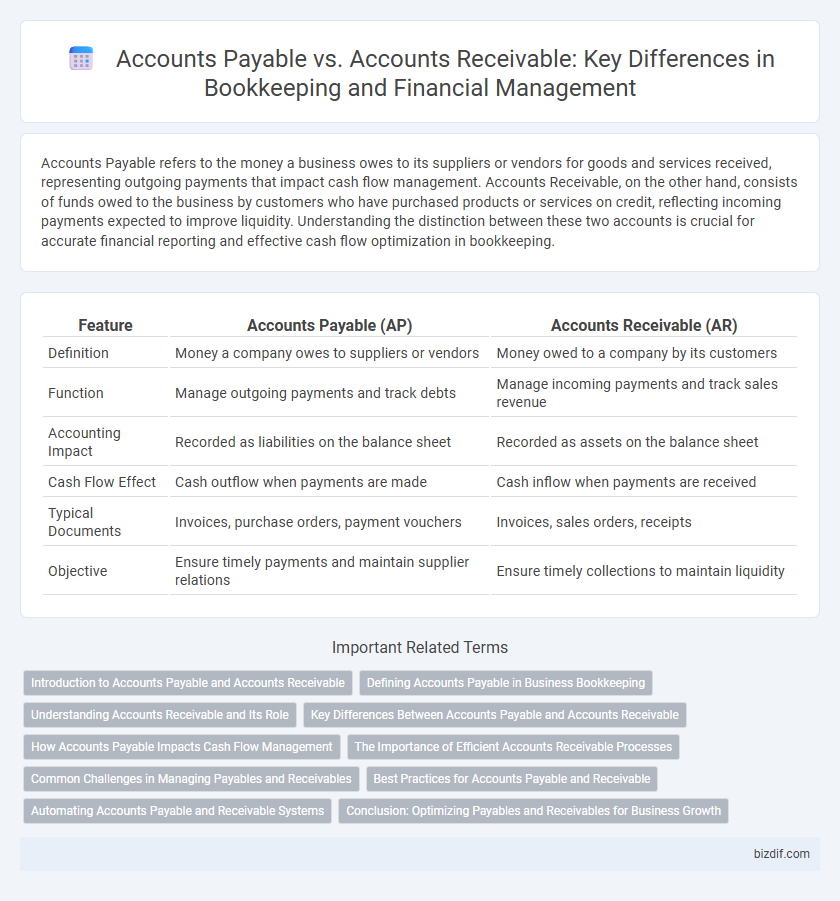
| Feature | Accounts Payable (AP) | Accounts Receivable (AR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Money a company owes to suppliers or vendors | Money owed to a company by its customers |
| Function | Manage outgoing payments and track debts | Manage incoming payments and track sales revenue |
| Accounting Impact | Recorded as liabilities on the balance sheet | Recorded as assets on the balance sheet |
| Cash Flow Effect | Cash outflow when payments are made | Cash inflow when payments are received |
| Typical Documents | Invoices, purchase orders, payment vouchers | Invoices, sales orders, receipts |
| Objective | Ensure timely payments and maintain supplier relations | Ensure timely collections to maintain liquidity |
Introduction to Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable
Accounts Payable represents the outstanding amounts a business owes to its suppliers for goods or services received, reflecting the company's short-term liabilities. Accounts Receivable denotes the amounts owed to the business by customers for products or services delivered, indicating expected incoming cash flow. Both accounts are essential for maintaining accurate financial records and managing cash flow effectively in bookkeeping.
Defining Accounts Payable in Business Bookkeeping
Accounts Payable in business bookkeeping refers to the outstanding debts a company owes to its suppliers or creditors for goods and services received but not yet paid for. It represents a key liability account on the balance sheet, essential for managing cash flow and maintaining accurate financial records. Proper tracking of accounts payable ensures timely payments, prevents late fees, and supports effective budgeting and financial planning.
Understanding Accounts Receivable and Its Role
Accounts receivable represents the outstanding invoices a company expects to collect from its customers for goods or services sold on credit, playing a crucial role in managing cash flow and maintaining liquidity. Efficient tracking and timely collection of accounts receivable enhance working capital and reduce the risk of bad debt, directly impacting financial stability. Accurate accounts receivable records support forecasting, budgeting, and informed decision-making in bookkeeping processes.
Key Differences Between Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable
Accounts Payable represents the company's obligations to pay off short-term debts to suppliers or vendors, while Accounts Receivable denotes the money owed to the company by its customers for goods or services delivered. Key differences include their impact on cash flow--Accounts Payable is a liability affecting outgoing payments, whereas Accounts Receivable is an asset influencing incoming cash. Effective management of both accounts is essential for maintaining liquidity and ensuring accurate financial reporting in bookkeeping.
How Accounts Payable Impacts Cash Flow Management
Accounts Payable directly influences cash flow management by determining the timing and amount of outgoing payments, affecting the company's liquidity. Efficient management of accounts payable allows businesses to maintain optimal cash reserves, avoid late payment penalties, and leverage favorable payment terms with suppliers. Monitoring accounts payable turnover ratios helps identify payment practices that can improve cash flow stability and operational efficiency.
The Importance of Efficient Accounts Receivable Processes
Efficient accounts receivable processes enhance cash flow management by reducing payment delays and minimizing bad debt risks. Streamlined invoicing, timely follow-ups, and accurate record-keeping optimize customer payment cycles and improve financial forecasting. Prioritizing accounts receivable efficiency supports business liquidity and operational stability within overall bookkeeping practices.
Common Challenges in Managing Payables and Receivables
Managing Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable presents common challenges such as maintaining accurate records, ensuring timely payments, and avoiding cash flow disruptions. Errors in invoice processing or delayed collections can lead to financial discrepancies and strained vendor relationships. Implementing automated systems and regular reconciliations helps mitigate risks associated with missed payments and uncollected receivables.
Best Practices for Accounts Payable and Receivable
Implement clear approval workflows and maintain organized documentation to ensure accuracy and prevent payment errors in accounts payable. For accounts receivable, establish timely invoicing schedules and proactive follow-up processes to improve cash flow and reduce outstanding debts. Regular reconciliation and leveraging automated accounting software enhance efficiency and minimize discrepancies in both accounts payable and receivable management.
Automating Accounts Payable and Receivable Systems
Automating accounts payable and receivable systems enhances accuracy and efficiency in financial management by reducing manual entry errors and accelerating transaction processing. Integration with accounting software enables real-time tracking of cash flow, improves invoice management, and streamlines payment schedules for both incoming and outgoing funds. This automation supports better vendor relationships and faster customer payments, contributing to optimized working capital and overall business performance.
Conclusion: Optimizing Payables and Receivables for Business Growth
Efficient management of accounts payable and accounts receivable directly impacts a company's cash flow, profitability, and operational stability. Streamlining payables ensures timely payments that can leverage supplier discounts and maintain strong vendor relationships, while optimizing receivables accelerates cash inflows and reduces outstanding debts. Balancing both functions strategically supports sustainable business growth and financial health.
Accounts Payable vs Accounts Receivable Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com