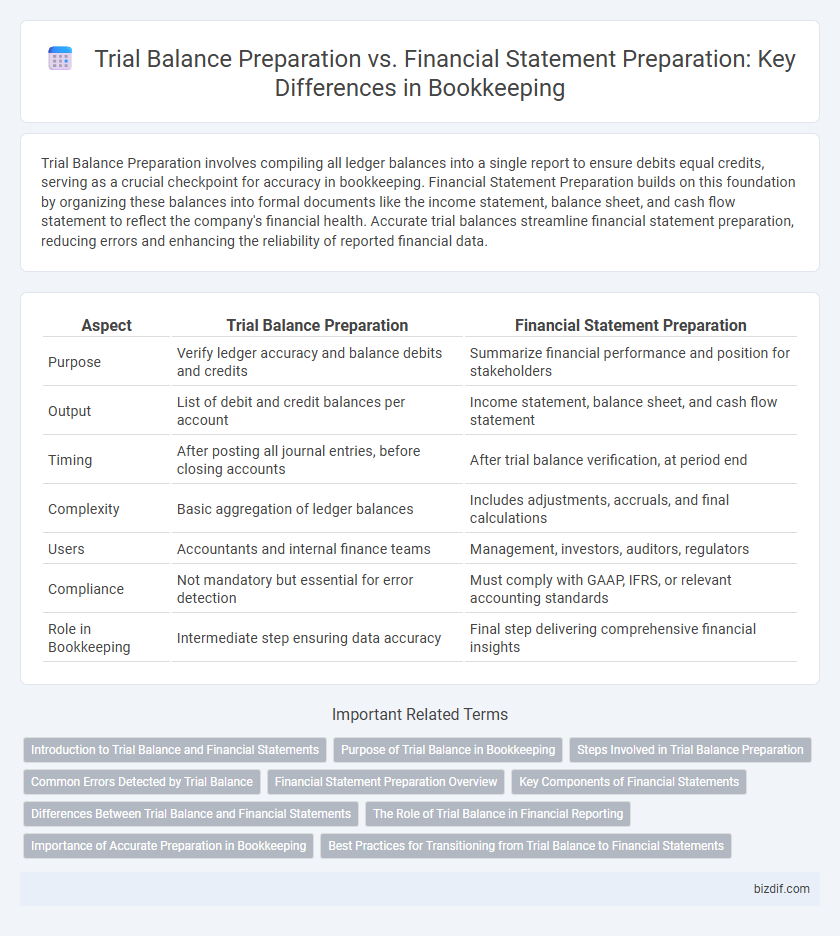
Trial Balance Preparation involves compiling all ledger balances into a single report to ensure debits equal credits, serving as a crucial checkpoint for accuracy in bookkeeping. Financial Statement Preparation builds on this foundation by organizing these balances into formal documents like the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to reflect the company's financial health. Accurate trial balances streamline financial statement preparation, reducing errors and enhancing the reliability of reported financial data.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Trial Balance Preparation | Financial Statement Preparation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify ledger accuracy and balance debits and credits | Summarize financial performance and position for stakeholders |
| Output | List of debit and credit balances per account | Income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement |
| Timing | After posting all journal entries, before closing accounts | After trial balance verification, at period end |
| Complexity | Basic aggregation of ledger balances | Includes adjustments, accruals, and final calculations |
| Users | Accountants and internal finance teams | Management, investors, auditors, regulators |
| Compliance | Not mandatory but essential for error detection | Must comply with GAAP, IFRS, or relevant accounting standards |
| Role in Bookkeeping | Intermediate step ensuring data accuracy | Final step delivering comprehensive financial insights |
Introduction to Trial Balance and Financial Statements
Trial balance preparation involves compiling all ledger account balances to verify the equality of total debits and credits, serving as a preliminary step to detect errors in bookkeeping. Financial statements preparation uses the verified trial balance to create formal reports, including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, which provide a comprehensive view of a company's financial health. Accurate trial balance ensures reliability in financial statements, facilitating informed decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Purpose of Trial Balance in Bookkeeping
The primary purpose of a trial balance in bookkeeping is to verify the accuracy of ledger accounts by ensuring that total debits equal total credits. This process helps detect any mathematical errors in the accounting records before preparing financial statements. Accurate trial balances form the foundation for generating reliable financial statements, which provide stakeholders with a comprehensive view of a company's financial position.
Steps Involved in Trial Balance Preparation
Trial balance preparation involves recording all ledger account balances to ensure debits equal credits, which is essential for accurate financial reporting. The steps include listing all accounts with their debit or credit balances, totaling both columns, and verifying that the totals match to detect any discrepancies. This process provides a foundational check before proceeding to financial statement preparation, ensuring accuracy in the accounting records.
Common Errors Detected by Trial Balance
Trial balance preparation often identifies common errors such as ledger posting mistakes, transposition errors, and misclassified accounts, which are crucial to rectify before financial statement preparation. These discrepancies include unmatched debit and credit totals, omission of ledger entries, and incorrect account balances that skew overall financial reporting. Ensuring accuracy with trial balance checks prevents misstatements in profit and loss accounts and balance sheets during financial statement preparation.
Financial Statement Preparation Overview
Financial statement preparation involves compiling and presenting key financial data, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, to provide a comprehensive overview of a company's financial performance and position. Accurate financial statements are essential for stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and management, to make informed decisions based on reliable and standardized financial information. This process requires adherence to accounting principles and standards, ensuring transparency and comparability across reporting periods.
Key Components of Financial Statements
Financial statement preparation centers on key components such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which collectively summarize an entity's financial position and performance. Trial balance preparation involves listing all ledger accounts with debit or credit balances to ensure total debits equal total credits, serving as a preliminary step before compiling financial statements. Accurate trial balances facilitate the creation of financial statements by validating account balances and revealing any discrepancies in bookkeeping records.
Differences Between Trial Balance and Financial Statements
Trial balance preparation involves listing all ledger account balances to ensure debits equal credits, serving as the first step in the accounting process. Financial statement preparation compiles these verified balances into structured reports like the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to provide a comprehensive view of a company's financial performance and position. The key difference lies in their purpose: trial balance acts as an internal verification tool, while financial statements are formal reports used for decision-making by stakeholders.
The Role of Trial Balance in Financial Reporting
The trial balance plays a critical role in financial reporting by ensuring that all ledger accounts are accurately balanced before the preparation of financial statements. It serves as an internal check to identify discrepancies and errors in the double-entry bookkeeping system, facilitating the adjustment process. Accurate trial balance preparation directly supports the reliability and integrity of financial statements such as the balance sheet and income statement.
Importance of Accurate Preparation in Bookkeeping
Accurate trial balance preparation ensures all ledger accounts are correctly balanced, providing a reliable foundation for financial statement preparation. Precise financial statements derived from accurate trial balances enable businesses to present trustworthy financial health to stakeholders and comply with regulatory standards. Errors in either stage can lead to misinformed decisions, impacting cash flow management, tax filings, and investor confidence.
Best Practices for Transitioning from Trial Balance to Financial Statements
Ensure accuracy by thoroughly verifying all ledger entries during trial balance preparation before moving to financial statement creation. Utilize standardized templates and software to maintain consistency and reduce errors in recording adjustments and classifications. Regularly reconcile trial balances with supporting documentation to facilitate a seamless and reliable transition to comprehensive financial statements.
Trial Balance Preparation vs Financial Statement Preparation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com