The Periodic Inventory System updates inventory records at specific intervals, requiring physical counts to determine stock levels and cost of goods sold, which can delay accurate financial reporting. In contrast, the Perpetual Inventory System continuously records inventory transactions in real time, providing up-to-date stock information and improving accuracy in bookkeeping. Understanding the differences between these systems helps businesses choose the best method for efficient inventory management and financial oversight.
Table of Comparison
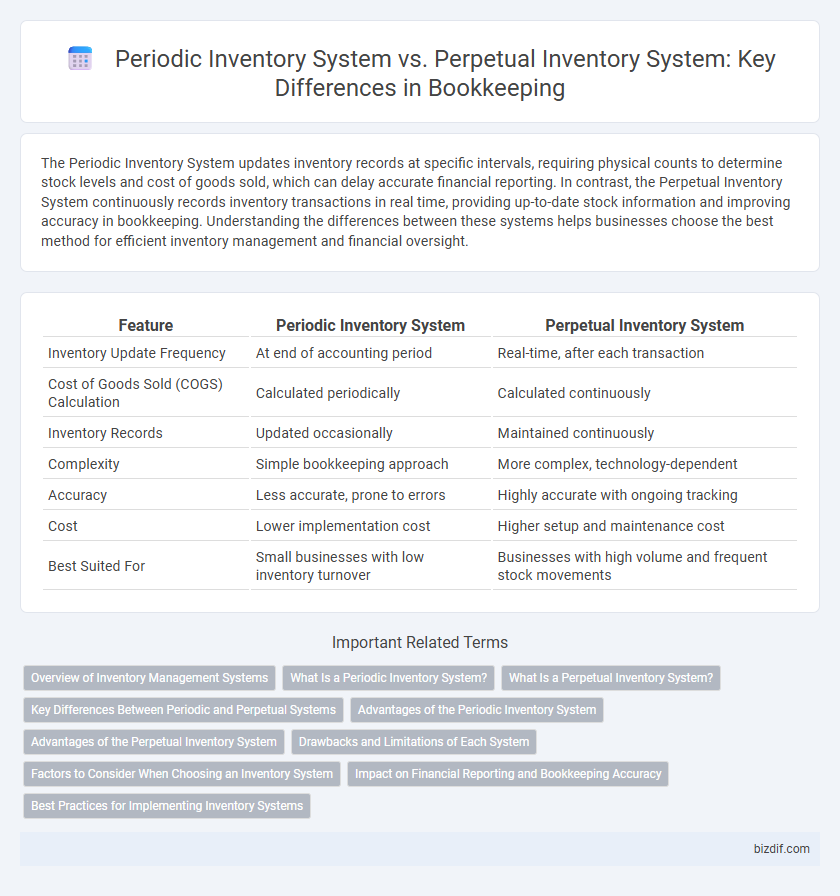
| Feature | Periodic Inventory System | Perpetual Inventory System |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Update Frequency | At end of accounting period | Real-time, after each transaction |
| Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Calculation | Calculated periodically | Calculated continuously |
| Inventory Records | Updated occasionally | Maintained continuously |
| Complexity | Simple bookkeeping approach | More complex, technology-dependent |
| Accuracy | Less accurate, prone to errors | Highly accurate with ongoing tracking |
| Cost | Lower implementation cost | Higher setup and maintenance cost |
| Best Suited For | Small businesses with low inventory turnover | Businesses with high volume and frequent stock movements |
Overview of Inventory Management Systems
Periodic Inventory System updates inventory records at specific intervals, requiring physical counts to determine stock levels and cost of goods sold. Perpetual Inventory System continuously tracks inventory in real-time using software and barcode scanning, providing accurate and immediate data for better stock control. Businesses choose between these systems based on transaction volume, accuracy needs, and resource availability for inventory management.
What Is a Periodic Inventory System?
A Periodic Inventory System records inventory balances and cost of goods sold at specific intervals, typically at the end of an accounting period, rather than tracking real-time inventory changes. This method involves manual counts and updates, making it less accurate for day-to-day inventory monitoring compared to a Perpetual Inventory System. Businesses with low transaction volumes or cost concerns often prefer the Periodic Inventory System due to its simplicity and lower immediate record-keeping costs.
What Is a Perpetual Inventory System?
A Perpetual Inventory System continuously updates inventory records in real-time with each purchase and sale, providing accurate and immediate stock levels. This system integrates with point-of-sale technology and accounting software, reducing errors and improving inventory management efficiency. Businesses benefit from enhanced tracking, better demand forecasting, and timely decision-making using the perpetual inventory method.
Key Differences Between Periodic and Perpetual Systems
The Periodic Inventory System updates inventory records and cost of goods sold at specific intervals, typically requiring physical counts, while the Perpetual Inventory System continuously tracks inventory levels and sales in real-time through computerized systems. Key differences include accuracy, as perpetual systems provide immediate data on stock movement, whereas periodic systems may lag, affecting decision-making and financial reporting. The perpetual system is better suited for businesses needing up-to-date inventory control, while the periodic system is simpler and more cost-effective for smaller operations with less frequent inventory transactions.
Advantages of the Periodic Inventory System
The Periodic Inventory System offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness by eliminating the need for continuous tracking of inventory transactions, making it ideal for small businesses with low inventory turnover. It reduces the complexity of record-keeping since inventory quantities and costs are updated only at the end of an accounting period through physical counts. This system also minimizes the use of sophisticated software, lowering operational expenses while providing sufficient accuracy for businesses with less frequent inventory movements.
Advantages of the Perpetual Inventory System
The perpetual inventory system offers real-time inventory tracking, allowing businesses to immediately update stock levels after each transaction, which enhances accuracy and reduces stockouts. This system improves financial reporting by providing up-to-date cost of goods sold and inventory balances, facilitating better decision-making. Integration with point-of-sale systems and automated inventory management reduces manual errors and labor costs compared to the periodic inventory system.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Each System
The Periodic Inventory System faces drawbacks such as less real-time inventory accuracy and potential stockouts due to infrequent updates, complicating timely decision-making. The Perpetual Inventory System, while providing continuous tracking, requires significant investment in technology and can be prone to errors from constant data entry and system malfunctions. Both systems present challenges with inventory valuation accuracy during high transaction volumes or theft, impacting financial reporting reliability.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Inventory System
Choosing between a periodic inventory system and a perpetual inventory system depends on factors such as the size of the business, transaction volume, and the need for real-time inventory tracking. Small businesses with limited transactions may benefit from the periodic system's simplicity and lower cost, while larger businesses or those requiring detailed inventory control and timely data should consider the perpetual system. The choice also hinges on technology availability, budget constraints, and the desired accuracy of financial reporting in bookkeeping.
Impact on Financial Reporting and Bookkeeping Accuracy
The Perpetual Inventory System enhances bookkeeping accuracy by continuously updating inventory records after each transaction, providing real-time financial data essential for precise financial reporting. In contrast, the Periodic Inventory System relies on physical counts at specific intervals, which may delay recognition of inventory fluctuations and introduce discrepancies in financial statements. Businesses using the perpetual method benefit from improved inventory control and timely detection of discrepancies, whereas the periodic system can result in less detailed financial reports and potential errors in inventory valuation.
Best Practices for Implementing Inventory Systems
Implementing inventory systems requires tailored approaches for both Periodic and Perpetual Inventory Systems to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Best practices include regular reconciliation schedules for Periodic Systems to prevent stock discrepancies and leveraging real-time data tracking technologies in Perpetual Systems for continuous inventory updates. Maintaining staff training on system operations and integrating inventory management software can significantly enhance accuracy and streamline bookkeeping processes.
Periodic Inventory System vs Perpetual Inventory System Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com