Cost accounting primarily focuses on analyzing and controlling internal costs to improve operational efficiency, while financial accounting emphasizes recording and reporting financial transactions for external stakeholders. Cost accounting provides detailed insights for budgeting and cost management, whereas financial accounting ensures compliance with regulatory standards and prepares financial statements. Both disciplines are essential for informed decision-making and overall business performance evaluation.
Table of Comparison
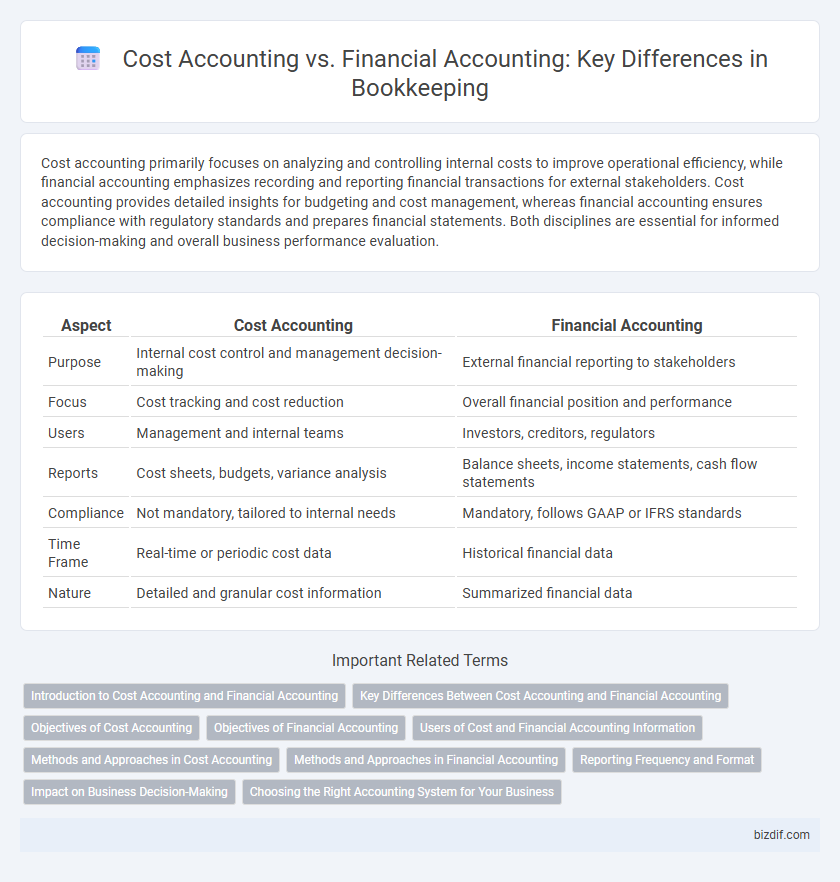
| Aspect | Cost Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Internal cost control and management decision-making | External financial reporting to stakeholders |
| Focus | Cost tracking and cost reduction | Overall financial position and performance |
| Users | Management and internal teams | Investors, creditors, regulators |
| Reports | Cost sheets, budgets, variance analysis | Balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements |
| Compliance | Not mandatory, tailored to internal needs | Mandatory, follows GAAP or IFRS standards |
| Time Frame | Real-time or periodic cost data | Historical financial data |
| Nature | Detailed and granular cost information | Summarized financial data |
Introduction to Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting
Cost accounting tracks, analyzes, and controls costs related to production, focusing on internal financial management. Financial accounting records, summarizes, and reports overall financial transactions to external stakeholders, following regulatory standards. Understanding cost accounting helps improve operational efficiency, while financial accounting ensures compliance and provides a clear financial position of the business.
Key Differences Between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting
Cost accounting focuses on tracking, recording, and analyzing production costs to aid internal management in budgeting and controlling expenses, while financial accounting centers on summarizing overall financial performance for external stakeholders like investors and regulators. Cost accounting provides detailed cost information related to processes, departments, or products, enabling managerial decision-making, whereas financial accounting aggregates financial data into statements such as the balance sheet and income statement for compliance and reporting. The primary distinction lies in cost accounting's emphasis on internal cost control and operational efficiency compared to financial accounting's role in presenting historical financial results and financial position.
Objectives of Cost Accounting
Cost accounting aims to determine the actual cost of production by analyzing direct and indirect expenses, enabling businesses to control costs and improve efficiency. It provides detailed cost information for internal management decisions, budgeting, and performance evaluation. Unlike financial accounting, which focuses on reporting financial position to external stakeholders, cost accounting prioritizes optimizing operational processes and cost management.
Objectives of Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting aims to provide accurate and comprehensive financial statements that reflect an organization's overall financial health, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulations. It focuses on delivering information for external stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and regulatory agencies to facilitate informed decision-making. The primary objective is to present a clear, consistent, and transparent financial picture that supports accountability and financial performance assessment.
Users of Cost and Financial Accounting Information
Cost accounting primarily serves internal stakeholders such as managers, production supervisors, and company executives by providing detailed cost data to aid in budgeting, performance evaluation, and decision-making. Financial accounting is designed for external users including investors, creditors, regulatory agencies, and tax authorities, offering standardized financial statements that reflect the overall financial position and performance of the organization. The differing user needs drive cost accounting's focus on operational efficiency and financial accounting's emphasis on regulatory compliance and transparency.
Methods and Approaches in Cost Accounting
Cost accounting employs specific methods such as job order costing, process costing, and activity-based costing to analyze and allocate production costs accurately. These approaches enable businesses to track direct and indirect expenses, optimize resource usage, and set appropriate product pricing. In contrast, financial accounting focuses on preparing standardized financial statements following GAAP or IFRS for external reporting and regulatory compliance.
Methods and Approaches in Financial Accounting
Financial accounting primarily employs standardized methods such as accrual accounting and double-entry bookkeeping to systematically record and report a company's financial transactions. It integrates Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to ensure consistency, transparency, and accuracy in financial statements. This approach focuses on the aggregation and presentation of historical financial data for external stakeholders, contrasting with the more detailed and internal cost-tracking methods used in cost accounting.
Reporting Frequency and Format
Cost accounting reports are typically generated frequently, such as daily or monthly, and presented in detailed formats tailored for internal management to assist in decision-making and cost control. Financial accounting reports, by contrast, are prepared less often, usually quarterly or annually, following standardized formats like balance sheets and income statements to comply with regulatory and external stakeholder requirements. The difference in reporting frequency and format reflects their distinct purposes: cost accounting serves internal operational needs, while financial accounting addresses external financial disclosure.
Impact on Business Decision-Making
Cost accounting provides detailed insights into internal cost control and efficiency, enabling managers to make informed decisions about budgeting, pricing, and operational improvements. Financial accounting focuses on producing standardized financial statements for external stakeholders, ensuring compliance and transparency but offering less granularity on internal cost dynamics. The distinct roles of cost and financial accounting collectively enhance strategic decision-making by balancing internal resource management with external reporting requirements.
Choosing the Right Accounting System for Your Business
Cost accounting focuses on capturing detailed expenses related to production processes, providing businesses with actionable insights to optimize operational efficiency and control costs. Financial accounting records overall financial transactions and presents an accurate picture of a company's financial health to external stakeholders like investors and regulators. Selecting the right accounting system hinges on the business's need for internal cost management versus external financial reporting, ensuring both compliance and strategic decision-making.
Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com