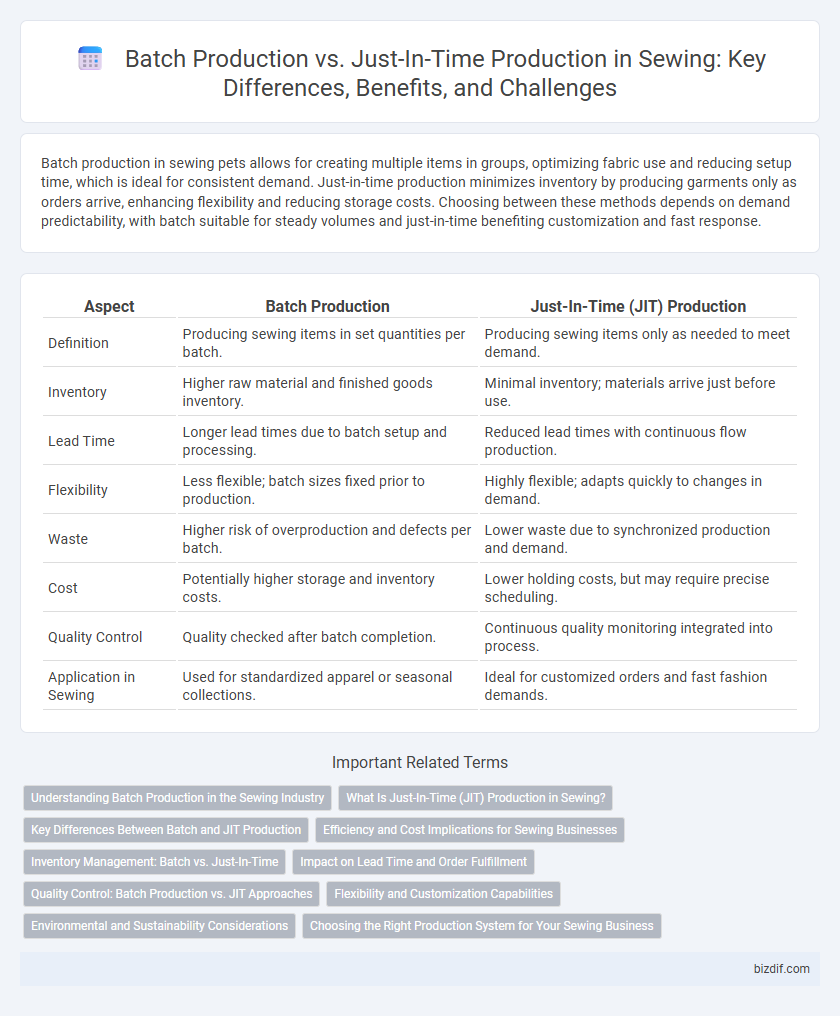
Batch production in sewing pets allows for creating multiple items in groups, optimizing fabric use and reducing setup time, which is ideal for consistent demand. Just-in-time production minimizes inventory by producing garments only as orders arrive, enhancing flexibility and reducing storage costs. Choosing between these methods depends on demand predictability, with batch suitable for steady volumes and just-in-time benefiting customization and fast response.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Batch Production | Just-In-Time (JIT) Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Producing sewing items in set quantities per batch. | Producing sewing items only as needed to meet demand. |
| Inventory | Higher raw material and finished goods inventory. | Minimal inventory; materials arrive just before use. |
| Lead Time | Longer lead times due to batch setup and processing. | Reduced lead times with continuous flow production. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; batch sizes fixed prior to production. | Highly flexible; adapts quickly to changes in demand. |
| Waste | Higher risk of overproduction and defects per batch. | Lower waste due to synchronized production and demand. |
| Cost | Potentially higher storage and inventory costs. | Lower holding costs, but may require precise scheduling. |
| Quality Control | Quality checked after batch completion. | Continuous quality monitoring integrated into process. |
| Application in Sewing | Used for standardized apparel or seasonal collections. | Ideal for customized orders and fast fashion demands. |
Understanding Batch Production in the Sewing Industry
Batch production in the sewing industry involves manufacturing a specific quantity of garments in groups, allowing for efficient use of machinery and labor while reducing setup times. This method enhances quality control by enabling consistent inspection throughout the production cycle and is ideal for meeting moderate demand levels without overproducing inventory. Batch production supports flexibility in design changes, making it suitable for seasonal collections and varied fashion trends.
What Is Just-In-Time (JIT) Production in Sewing?
Just-In-Time (JIT) production in sewing is a manufacturing strategy that minimizes inventory by producing garments only as they are needed, reducing waste and storage costs. This method relies on precise demand forecasting and efficient workflow to ensure fabric, thread, and components arrive exactly when required. JIT enhances flexibility, allowing sewing units to quickly adapt to changing fashion trends and order volumes without overproduction.
Key Differences Between Batch and JIT Production
Batch production in sewing involves creating a set number of garments at once, allowing for efficient use of equipment and skilled labor but requiring larger inventory storage. Just-In-Time (JIT) production minimizes inventory by producing garments only as needed, reducing holding costs and waste but demanding precise demand forecasting and supply chain coordination. The key differences lie in inventory levels, production scheduling, and flexibility, with batch production suited for standardized products and JIT ideal for customized or rapidly changing designs.
Efficiency and Cost Implications for Sewing Businesses
Batch production in sewing allows for efficient use of materials and labor by producing large quantities at once, reducing setup times and per-unit costs. Just-in-time production minimizes inventory holding costs and waste by producing garments only as needed, enhancing cash flow but requiring precise demand forecasting. Balancing these methods helps sewing businesses optimize efficiency and control operational expenses based on order volume and market fluctuations.
Inventory Management: Batch vs. Just-In-Time
Batch production involves creating large quantities of sewn products, resulting in higher inventory levels that require substantial storage space and increase carrying costs. Just-In-Time (JIT) production minimizes inventory by producing garments only as orders are received, reducing waste and improving cash flow efficiency. Effective inventory management in sewing depends on balancing batch production's stock availability with JIT's lean principles to optimize fabric usage and meet customer demand promptly.
Impact on Lead Time and Order Fulfillment
Batch production in sewing typically results in longer lead times due to the processing of large quantities before moving to the next stage, which can delay order fulfillment but allows for economies of scale. Just-In-Time (JIT) production reduces lead time by producing garments only as orders are received, improving responsiveness and minimizing inventory costs. However, JIT requires precise demand forecasting and efficient supply chain coordination to maintain timely order fulfillment without stockouts.
Quality Control: Batch Production vs. JIT Approaches
Batch production allows for comprehensive quality control checks at the end of each batch, enabling the identification and correction of fabric defects or stitching errors before the next batch begins. Just-In-Time (JIT) production emphasizes continuous quality monitoring throughout the sewing process, reducing waste by addressing defects immediately and minimizing inventory holding costs. Both methods impact overall garment quality, but JIT's real-time quality control often leads to faster detection of inconsistencies and improved responsiveness to production issues.
Flexibility and Customization Capabilities
Batch production in sewing allows for greater flexibility in handling varied fabric types and garment styles within a single production run, enabling customization for niche markets. Just-In-Time (JIT) production emphasizes minimizing inventory and quickly responding to real-time demand, but may limit customization due to streamlined processes and shorter setup times. Choosing batch production supports diverse design modifications, while JIT prioritizes efficiency and rapid order fulfillment.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Batch production in sewing generates higher fabric waste and increased energy consumption due to bulk processing and storage, impacting environmental sustainability negatively. Just-in-time production minimizes excess inventory and reduces material waste by aligning sewing schedules closely with demand, promoting resource efficiency and lowering carbon footprint. Sustainable sewing operations benefit from just-in-time approaches that decrease overproduction and support eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Choosing the Right Production System for Your Sewing Business
Batch production in sewing offers efficiency for moderate order volumes by allowing the creation of multiple garments simultaneously, reducing setup time and material waste. Just-In-time production minimizes inventory costs and enhances flexibility by producing garments only as orders are received, making it ideal for customized or rapidly changing fashion trends. Selecting the right system depends on factors like order size, lead time, product variety, and capital investment, ensuring optimal resource utilization and customer satisfaction in a sewing business.
Batch Production vs Just-In-Time Production Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com