Overlocking creates strong, stretchable seams that prevent fabric edges from fraying, making it ideal for durable pet clothing and accessories. Coverstitching provides a professional, flexible finish on hems and seams, enhancing comfort and aesthetic appeal for pet garments. Choosing between overlocking and coverstitching depends on whether seam strength or garment finish is the primary concern in sewing your pet's attire.
Table of Comparison
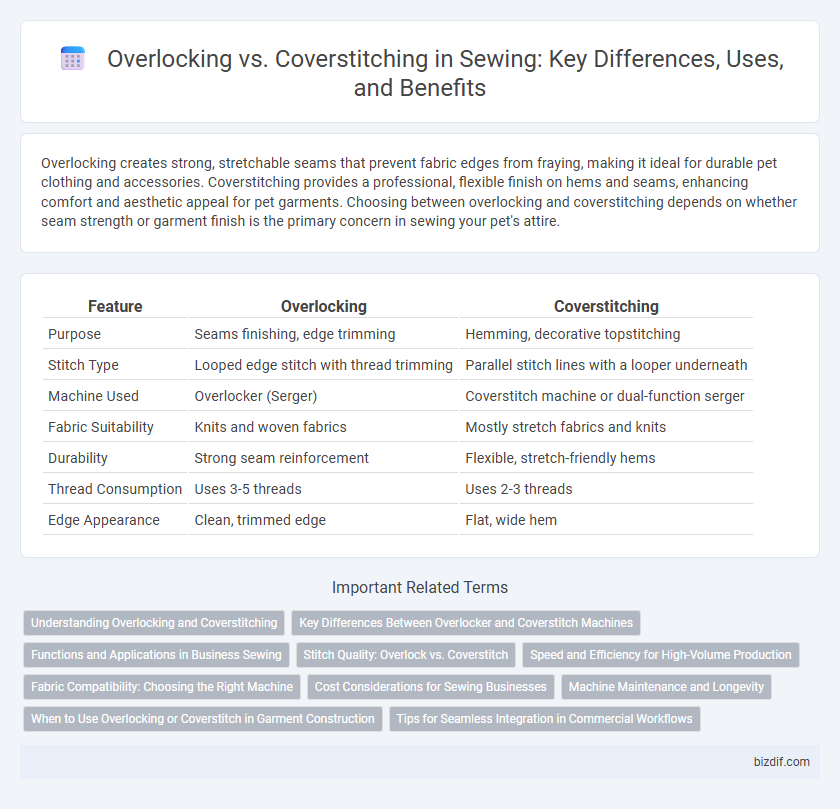
| Feature | Overlocking | Coverstitching |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Seams finishing, edge trimming | Hemming, decorative topstitching |
| Stitch Type | Looped edge stitch with thread trimming | Parallel stitch lines with a looper underneath |
| Machine Used | Overlocker (Serger) | Coverstitch machine or dual-function serger |
| Fabric Suitability | Knits and woven fabrics | Mostly stretch fabrics and knits |
| Durability | Strong seam reinforcement | Flexible, stretch-friendly hems |
| Thread Consumption | Uses 3-5 threads | Uses 2-3 threads |
| Edge Appearance | Clean, trimmed edge | Flat, wide hem |
Understanding Overlocking and Coverstitching
Overlocking involves stitching the edges of fabric to prevent fraying while creating a clean, finished seam, commonly used in garment construction for durability and stretch. Coverstitching, on the other hand, is designed to sew hems and topstitch knit fabrics, providing a professional finish with a stretchy, durable seam ideal for activewear and casual clothing. Both techniques are essential in sewing for different purposes: overlocking secures raw edges, while coverstitching offers decorative and functional hemming.
Key Differences Between Overlocker and Coverstitch Machines
Overlocker machines specialize in trimming fabric edges while simultaneously sewing over them to prevent fraying, making them essential for seam finishing with multiple thread loops. Coverstitch machines focus on creating professional-looking hems, topstitching, and twin-needle finishes, using parallel rows of stitching that stretch with knit fabrics. While overlockers work primarily on seam edges to join fabric pieces, coverstitch machines reinforce hems and decorative stitching on garment exteriors.
Functions and Applications in Business Sewing
Overlocking primarily functions to finish garment edges by trimming and enclosing fabric seams with thread, preventing fraying and enhancing durability in mass production. Coverstitching is used to create professional hems and decorative topstitching, offering stretchable seams ideal for knitwear and activewear businesses. Both techniques improve product quality and efficiency but target different sewing applications essential in apparel manufacturing.
Stitch Quality: Overlock vs. Coverstitch
Overlock stitches offer superior seam strength and edge finishing, preventing fabric fraying with multiple thread loops that create a clean, durable edge. Coverstitching provides a flat, stretchy seam ideal for hemming knit fabrics, maintaining elasticity without compromising stitch integrity. Both techniques ensure high-quality stitching, but overlocking excels in edge durability while coverstitching optimizes stretch and appearance on garment edges.
Speed and Efficiency for High-Volume Production
Overlocking machines excel in speed, completing seams faster by trimming fabric edges and stitching simultaneously, making them ideal for high-volume production. Coverstitch machines, while slower, specialize in finishing hems with strong, flexible seams that enhance garment durability. For maximum efficiency, overlocking is preferred for rapid assembly, whereas coverstitching is used selectively for professional finishing.
Fabric Compatibility: Choosing the Right Machine
Overlocking machines excel with knit fabrics, providing stretch-friendly, durable seam finishes, while coverstitch machines are better suited for hemming and topstitching knit garments for a clean, professional look. Fabrics like jersey, interlock, and ribbed knits benefit from overlocking for edge stability, whereas coverstitching enhances stretch and recovery in hems and seams of similar knit materials. Selecting the right machine depends on fabric type and desired finish, ensuring optimal stitch flexibility and fabric compatibility.
Cost Considerations for Sewing Businesses
Overlocking machines typically cost less than coverstitch machines, making them a more budget-friendly option for small sewing businesses focused on seam finishing. Coverstitch machines, essential for hemming and professional-looking knitwear hems, tend to be pricier but add value through specialized stitching capabilities. Investing in both machines can elevate product quality but requires balancing upfront costs with the anticipated return on investment in garment durability and appearance.
Machine Maintenance and Longevity
Regular maintenance of overlock and coverstitch machines, including thorough cleaning and timely lubrication, significantly extends their operational lifespan and ensures optimal stitch quality. Proper tension adjustment and blade replacement prevent fabric damage and mechanical wear, reducing the need for costly repairs. Investing in routine servicing tailored to each machine type maximizes durability and consistent performance in professional sewing projects.
When to Use Overlocking or Coverstitch in Garment Construction
Overlocking is ideal for finishing raw edges and preventing fabric fraying, making it perfect for seams and hems in knitwear and woven garments. Coverstitching is best used for hemming and topstitching, providing a professional, stretchy finish often seen on cuffs, waistbands, and hems of activewear. Choosing overlocking ensures durability and edge neatness, while coverstitching enhances garment flexibility and a polished appearance.
Tips for Seamless Integration in Commercial Workflows
Overlocking and coverstitching serve distinct functions in commercial sewing, with overlocking providing edge finishing and seam reinforcement, while coverstitching offers professional hemming and stretch seam finishes. To seamlessly integrate both techniques, utilize industrial overlock machines with customizable stitch settings alongside dedicated coverstitch machines to streamline production workflows. Standardizing thread types and tension settings across machines ensures consistent fabric handling and reduces downtime in high-volume garment manufacturing.
Overlocking vs Coverstitching Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com