Contract sewing offers pet product businesses cost-effective scalability and access to specialized skills without the overhead of maintaining an in-house team. In-house manufacturing provides greater control over quality, customization, and production timelines, essential for maintaining consistent brand standards. Choosing between contract sewing and in-house manufacturing depends on balancing flexibility, budget, and the need for hands-on oversight in pet product production.
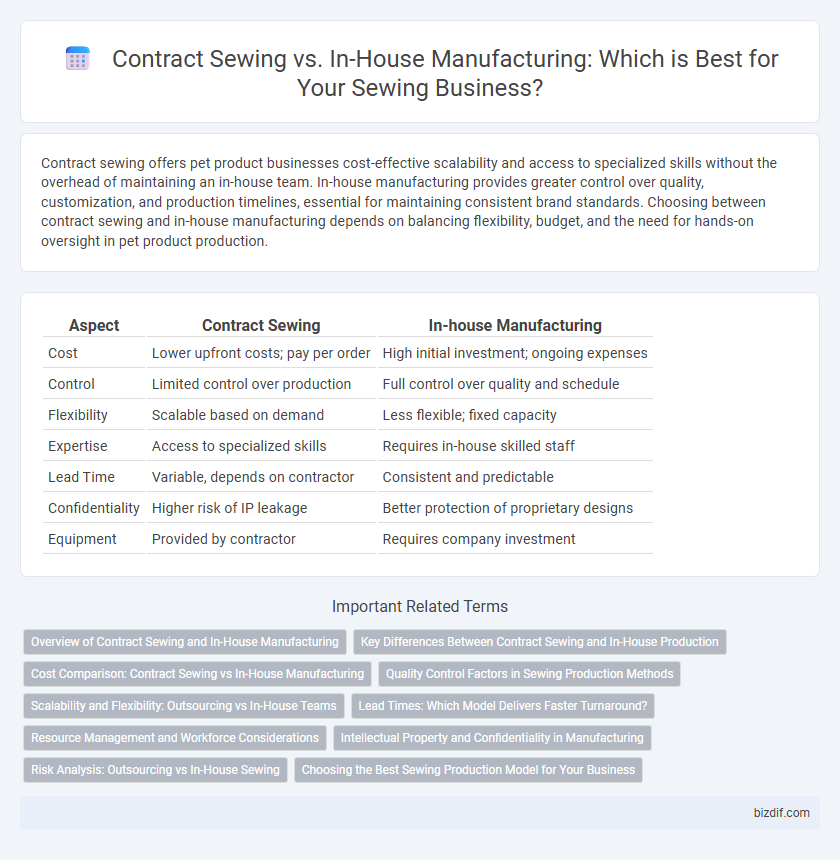
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Contract Sewing | In-house Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront costs; pay per order | High initial investment; ongoing expenses |
| Control | Limited control over production | Full control over quality and schedule |
| Flexibility | Scalable based on demand | Less flexible; fixed capacity |
| Expertise | Access to specialized skills | Requires in-house skilled staff |
| Lead Time | Variable, depends on contractor | Consistent and predictable |
| Confidentiality | Higher risk of IP leakage | Better protection of proprietary designs |
| Equipment | Provided by contractor | Requires company investment |
Overview of Contract Sewing and In-House Manufacturing
Contract sewing involves outsourcing garment production to specialized manufacturers, offering scalability, expertise, and cost efficiency without the need for heavy capital investment. In-house manufacturing provides complete control over the production process, quality assurance, and customization but requires higher upfront costs and workforce management. Brands choose contract sewing for flexibility and speed, while in-house manufacturing supports brand integrity and detailed oversight.
Key Differences Between Contract Sewing and In-House Production
Contract sewing involves outsourcing garment production to specialized manufacturers, which can reduce labor costs and increase scalability, while in-house manufacturing offers greater control over quality and production timelines. Contract sewing typically allows for flexibility in handling large or fluctuating order volumes, whereas in-house production requires fixed investments in equipment and skilled labor. Key differences also include varying lead times, intellectual property considerations, and the ability to customize production processes closely aligned with brand standards.
Cost Comparison: Contract Sewing vs In-House Manufacturing
Contract sewing often reduces upfront costs by eliminating expenses related to equipment, labor, and facility maintenance, making it a cost-effective option for businesses with fluctuating production volumes. In-house manufacturing requires significant capital investment in machinery, skilled labor, and ongoing overhead, but offers greater control over quality and production schedules, potentially lowering per-unit costs in high-volume runs. Evaluating contract sewing against in-house options depends on production scale, cost flexibility, and long-term financial strategy.
Quality Control Factors in Sewing Production Methods
Contract sewing offers specialized expertise and access to advanced machinery, which can enhance garment quality through stringent quality control protocols. In-house manufacturing allows for direct oversight of production processes, enabling immediate identification and resolution of defects, thus maintaining consistent quality standards. Both methods require robust quality control factors such as precise stitch evaluation, fabric inspection, and adherence to production specifications to ensure superior sewing outcomes.
Scalability and Flexibility: Outsourcing vs In-House Teams
Contract sewing offers greater scalability by allowing businesses to adjust production volumes quickly based on demand, minimizing overhead costs associated with staffing and equipment. In-house manufacturing provides more control and customization but often lacks the flexibility to scale operations rapidly due to fixed labor and facility constraints. Choosing contract sewing supports dynamic market responsiveness, while in-house teams excel in maintaining consistent quality and proprietary processes.
Lead Times: Which Model Delivers Faster Turnaround?
Contract sewing often provides faster turnaround times due to specialized production facilities and streamlined workflows focused on high-volume orders, reducing lead times significantly compared to in-house manufacturing. In-house manufacturing may face longer lead times because of limited resources, production capacity, and multitasking across multiple projects. When lead time is critical, industries such as fashion or retail typically prefer contract sewing to ensure rapid order fulfillment and timely market entry.
Resource Management and Workforce Considerations
Contract sewing allows businesses to optimize resource management by leveraging external expertise and specialized labor without investing in costly equipment or hiring full-time staff. In-house manufacturing requires significant workforce planning to maintain consistent production, including training, scheduling, and compliance with labor regulations. Efficient management of human capital in both approaches directly impacts production quality, lead times, and overall operational costs in the sewing industry.
Intellectual Property and Confidentiality in Manufacturing
Contract sewing poses significant challenges to maintaining intellectual property and confidentiality, as sensitive designs and proprietary techniques are shared with external manufacturers. In-house manufacturing offers tighter control over trade secrets and reduces the risk of unauthorized replication or leaks of confidential information. Ensuring robust non-disclosure agreements and security protocols is critical when outsourcing to protect proprietary patterns and innovation in garment production.
Risk Analysis: Outsourcing vs In-House Sewing
Contract sewing reduces upfront capital investment and labor management risks but increases dependency on third-party quality control and delivery timelines. In-house manufacturing offers greater oversight, proprietary process confidentiality, and faster response to production changes but requires significant investment in equipment, skilled labor, and ongoing operational expenses. Risk analysis must weigh supply chain stability, quality assurance, and cost variability to determine the optimal sewing production approach.
Choosing the Best Sewing Production Model for Your Business
Contract sewing offers scalability and access to specialized expertise, making it ideal for businesses aiming to reduce overhead and focus on core competencies. In-house manufacturing provides greater control over quality, production timelines, and customization, beneficial for brands prioritizing proprietary designs and rapid iteration. Evaluating factors like cost-efficiency, production volume, and flexibility will help determine the best sewing production model tailored to your business goals.
Contract sewing vs In-house manufacturing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com