Traditional sewing relies on hand-stitching methods and basic sewing machines, emphasizing craftsmanship and detail in creating pet accessories such as collars and beds. Technical sewing employs advanced machinery and specialized materials, enhancing durability and functionality for pet products like waterproof coats and reinforced harnesses. This blend of tradition and technology ensures both aesthetic appeal and practical performance in pet sewing projects.
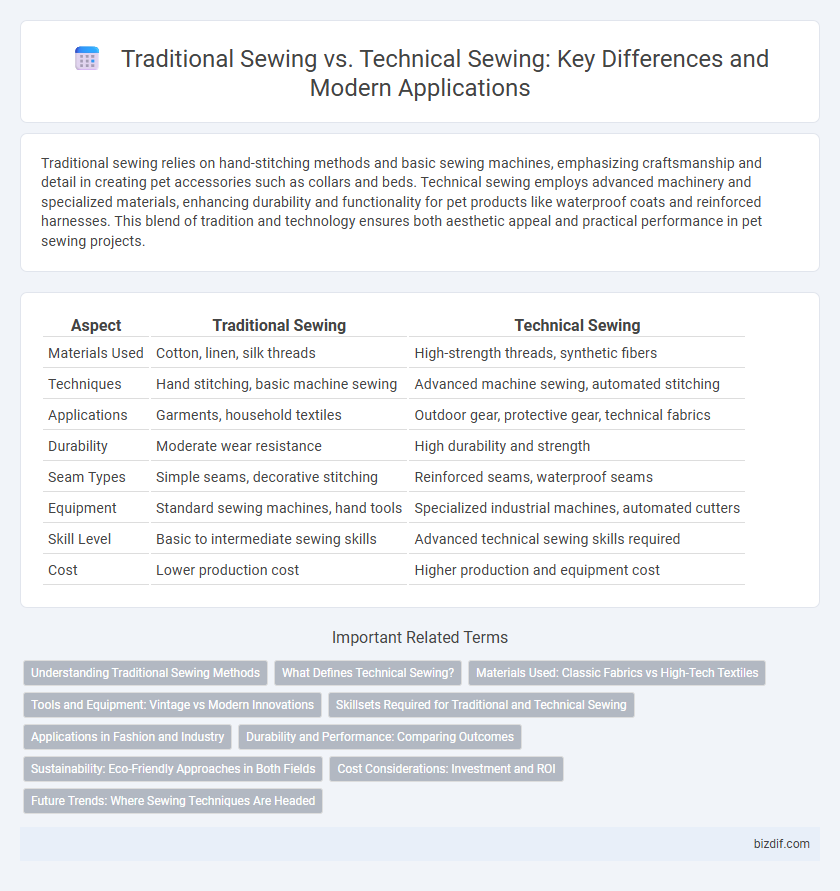
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Sewing | Technical Sewing |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Used | Cotton, linen, silk threads | High-strength threads, synthetic fibers |
| Techniques | Hand stitching, basic machine sewing | Advanced machine sewing, automated stitching |
| Applications | Garments, household textiles | Outdoor gear, protective gear, technical fabrics |
| Durability | Moderate wear resistance | High durability and strength |
| Seam Types | Simple seams, decorative stitching | Reinforced seams, waterproof seams |
| Equipment | Standard sewing machines, hand tools | Specialized industrial machines, automated cutters |
| Skill Level | Basic to intermediate sewing skills | Advanced technical sewing skills required |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher production and equipment cost |
Understanding Traditional Sewing Methods
Traditional sewing methods emphasize hand stitching techniques such as backstitch, running stitch, and slip stitch that have been passed down through generations. These methods prioritize precision, craftsmanship, and attention to detail, often using natural fibers like cotton and silk for authentic textile creation. Understanding traditional sewing lays a foundational skill set that enhances fabric manipulation and garment construction before integrating modern technical sewing innovations.
What Defines Technical Sewing?
Technical sewing is defined by its focus on precision, durability, and functionality, often involving advanced materials like Kevlar, Gore-Tex, and heavy-duty threads. It requires specialized machinery and techniques tailored for industrial applications, such as outdoor gear, automotive upholstery, and protective clothing. Unlike traditional sewing, technical sewing prioritizes performance standards and seam reinforcements to withstand extreme conditions and rigorous use.
Materials Used: Classic Fabrics vs High-Tech Textiles
Traditional sewing primarily uses classic fabrics such as cotton, wool, silk, and linen, prized for their natural fibers and comfort. Technical sewing incorporates high-tech textiles like Kevlar, Gore-Tex, and moisture-wicking synthetics designed for durability, flexibility, and specialized performance. The distinct materials influence the sewing techniques and end-use applications, ranging from everyday garments to protective and functional apparel.
Tools and Equipment: Vintage vs Modern Innovations
Traditional sewing relies on vintage tools such as manual sewing machines, wooden spools, and hand-sewing needles that emphasize craftsmanship and tactile control. Technical sewing integrates modern innovations like computerized embroidery machines, laser-cut fabrics, and advanced synthetic threads designed for precision and durability. The evolution from manual to digital equipment reflects a shift towards efficiency and complexity in garment construction within the sewing industry.
Skillsets Required for Traditional and Technical Sewing
Traditional sewing requires strong hand-eye coordination, manual dexterity, and knowledge of basic stitching techniques, often focusing on intricate handwork such as embroidery and applique. Technical sewing demands proficiency with industrial machines, understanding of material properties, and precision in automated pattern handling for mass production. Both skillsets emphasize attention to detail, but technical sewing integrates mechanical skills and software competency alongside manual craftsmanship.
Applications in Fashion and Industry
Traditional sewing techniques, often used in fashion design, emphasize hand-stitched details and intricate embroidery for bespoke garments and haute couture. Technical sewing incorporates advanced machinery and specialized threads, enabling durable seams essential in industrial applications such as automotive upholstery, protective gear, and sportswear manufacturing. Fashion relies on craftsmanship and aesthetic appeal, while industrial sewing prioritizes strength, precision, and functional performance.
Durability and Performance: Comparing Outcomes
Traditional sewing techniques often emphasize hand-stitched details that provide aesthetic value but may lack the reinforced strength found in technical sewing methods. Technical sewing utilizes advanced machinery and specialized threads to enhance durability, ensuring garments withstand rigorous use and frequent washing. Performance outcomes favor technical sewing in industries requiring high resilience, such as outdoor gear and sportswear, where longevity and structural integrity are critical.
Sustainability: Eco-Friendly Approaches in Both Fields
Traditional sewing utilizes natural fibers such as organic cotton and linen, minimizing environmental impact through biodegradable materials and low-energy handcrafting techniques. Technical sewing incorporates advanced sustainable textiles like recycled polyester and bio-based polymers, enhancing durability while reducing carbon footprints in industrial production. Both fields emphasize reducing waste by employing precise cutting methods and repairing garments, promoting longevity and eco-friendly practices in the fashion industry.
Cost Considerations: Investment and ROI
Traditional sewing often requires lower initial investment in tools and equipment, making it accessible for small-scale or hobbyist projects, but may result in slower production and higher labor costs over time. Technical sewing demands advanced machinery and specialized training, leading to higher upfront expenses, yet it offers greater efficiency, precision, and scalability, improving return on investment (ROI) for large-scale or industrial applications. Evaluating cost considerations between traditional and technical sewing depends on project volume, complexity, and long-term financial goals.
Future Trends: Where Sewing Techniques Are Headed
Emerging future trends in sewing emphasize the integration of smart textiles and automated machinery, revolutionizing both traditional and technical sewing methods. Advanced techniques incorporating nanotechnology and AI-driven precision promise enhanced durability and customization in garment production. Sustainable practices are increasingly prioritized, blending eco-friendly materials with cutting-edge technical sewing innovations to meet evolving consumer demands.
Traditional Sewing vs Technical Sewing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com