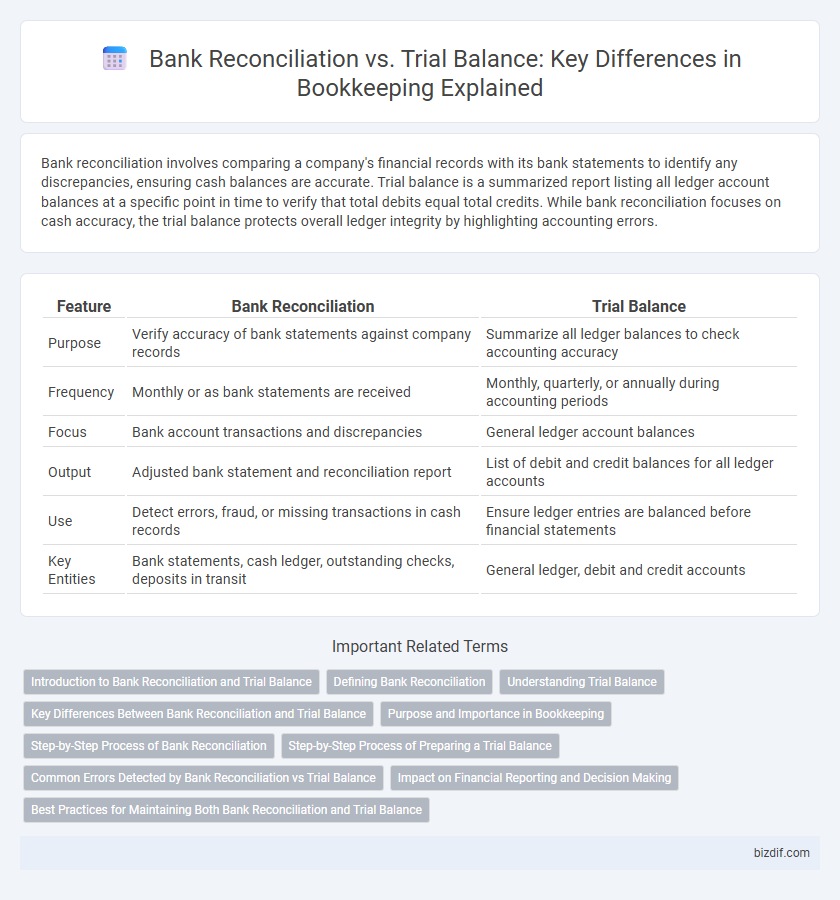
Bank reconciliation involves comparing a company's financial records with its bank statements to identify any discrepancies, ensuring cash balances are accurate. Trial balance is a summarized report listing all ledger account balances at a specific point in time to verify that total debits equal total credits. While bank reconciliation focuses on cash accuracy, the trial balance protects overall ledger integrity by highlighting accounting errors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bank Reconciliation | Trial Balance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify accuracy of bank statements against company records | Summarize all ledger balances to check accounting accuracy |
| Frequency | Monthly or as bank statements are received | Monthly, quarterly, or annually during accounting periods |
| Focus | Bank account transactions and discrepancies | General ledger account balances |
| Output | Adjusted bank statement and reconciliation report | List of debit and credit balances for all ledger accounts |
| Use | Detect errors, fraud, or missing transactions in cash records | Ensure ledger entries are balanced before financial statements |
| Key Entities | Bank statements, cash ledger, outstanding checks, deposits in transit | General ledger, debit and credit accounts |
Introduction to Bank Reconciliation and Trial Balance
Bank reconciliation is the process of comparing and matching the balances in an entity's accounting records to the corresponding information on a bank statement to identify and resolve discrepancies. Trial balance is a financial report listing all ledger accounts and their balances at a specific point in time to verify that total debits equal total credits. Both tools play crucial roles in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial records in bookkeeping.
Defining Bank Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation is the process of comparing and matching a company's internal financial records against its bank statement to ensure accuracy and identify discrepancies. It involves verifying deposits, withdrawals, and balances recorded in the ledger with those reflected by the bank. This adjustment procedure helps detect errors, unrecorded transactions, and potential fraud, maintaining the integrity of financial statements.
Understanding Trial Balance
A Trial Balance is a critical bookkeeping report that lists all ledger accounts and their balances at a specific date, ensuring the total debits equal total credits. It helps identify arithmetic errors in the double-entry accounting system but does not detect all types of discrepancies like bank reconciliation does. Understanding the Trial Balance allows accountants to verify ledger accuracy before preparing financial statements.
Key Differences Between Bank Reconciliation and Trial Balance
Bank reconciliation involves comparing the company's bank statement with its internal financial records to identify discrepancies and ensure accuracy in cash balances. Trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts that verifies total debits equal total credits, serving as a preliminary check for financial statement preparation. The key difference lies in bank reconciliation focusing on cash accuracy through external verification, while trial balance ensures overall ledger balance within internal records.
Purpose and Importance in Bookkeeping
Bank reconciliation ensures that the bank statement aligns with the company's ledger, identifying discrepancies such as outstanding checks or deposits in transit to maintain accurate cash records. Trial balance compiles all ledger accounts' balances at a specific period, verifying that total debits equal total credits, essential for detecting bookkeeping errors. Both play a crucial role in financial accuracy, with bank reconciliation focusing on cash verification and trial balance serving as a checkpoint for overall ledger integrity.
Step-by-Step Process of Bank Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation involves comparing the company's bank statement with its internal ledger to identify discrepancies, starting with collecting both records and matching transactions one by one. The process requires adjusting for outstanding checks, deposits in transit, and bank fees to ensure the book balance aligns with the bank statement. Unlike trial balance, which summarizes account balances to check for ledger accuracy, bank reconciliation focuses on verifying the cash account's correctness through a detailed transaction verification process.
Step-by-Step Process of Preparing a Trial Balance
Preparing a trial balance involves first listing all ledger account balances individually, ensuring every debit and credit amount is captured accurately. Next, sum the total debits and credits separately to verify they are equal, which confirms the books are mathematically balanced. This step-by-step process is pivotal for identifying ledger errors before producing financial statements and differs from bank reconciliation, which specifically matches company records with bank statements to resolve discrepancies.
Common Errors Detected by Bank Reconciliation vs Trial Balance
Bank reconciliation identifies common errors such as unrecorded bank fees, outstanding checks, and deposits in transit, ensuring the cash book aligns with the bank statement. Trial balance detects discrepancies like ledger posting errors, transposition mistakes, and unbalanced debit and credit totals, highlighting inaccuracies within the accounting records. Both tools are essential for maintaining accurate financial statements by pinpointing different types of bookkeeping errors.
Impact on Financial Reporting and Decision Making
Bank reconciliation ensures the accuracy of cash records by matching bank statements with company books, directly affecting the reliability of reported cash balances. Trial balance compiles all ledger account balances, serving as a foundational tool to detect errors before preparing financial statements and supporting comprehensive financial analysis. Accurate bank reconciliations and trial balances together enhance the integrity of financial reporting, enabling informed decision making and effective management of business resources.
Best Practices for Maintaining Both Bank Reconciliation and Trial Balance
Maintaining accurate bank reconciliation involves regularly comparing bank statements with company records to identify discrepancies and ensure cash balances match. Best practices for trial balance include consistently updating ledger accounts and verifying that total debits equal total credits to detect errors early. Combining timely bank reconciliation with systematic trial balance reviews enhances financial accuracy and supports reliable financial reporting.
Bank Reconciliation vs Trial Balance Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com