The Chart of Accounts organizes an entire business's financial transactions into categories such as assets, liabilities, income, and expenses, providing a comprehensive framework for bookkeeping. Account Codes are unique identifiers within this chart, enabling precise tracking and categorization of each transaction for efficient financial reporting. This system enhances accuracy and simplifies the reconciliation process in pet-related bookkeeping.
Table of Comparison
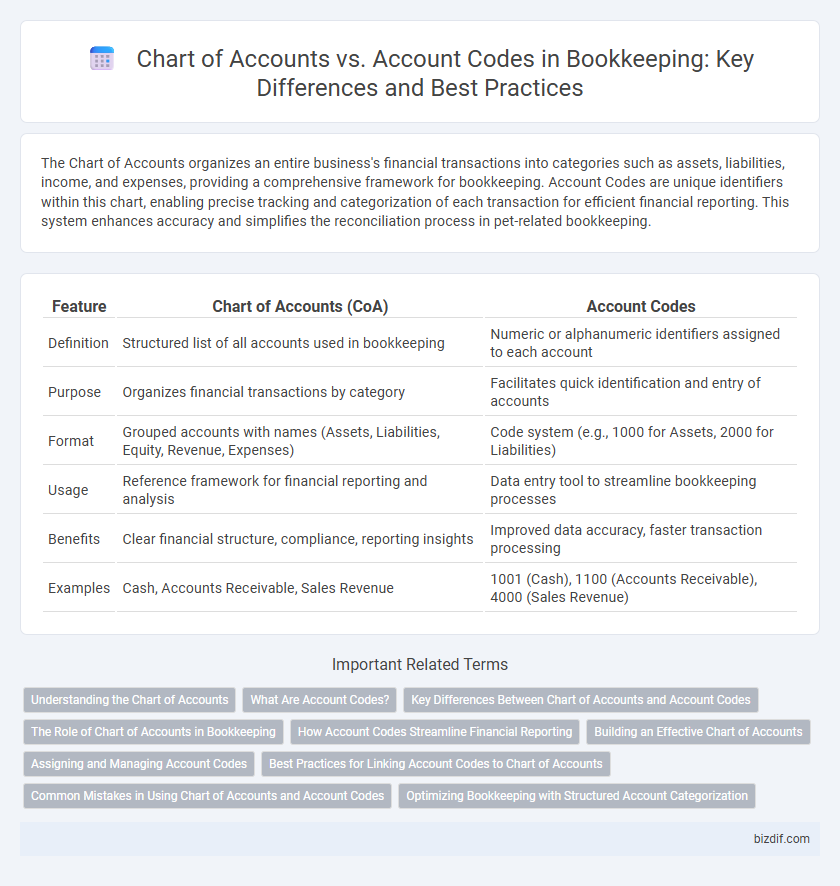
| Feature | Chart of Accounts (CoA) | Account Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured list of all accounts used in bookkeeping | Numeric or alphanumeric identifiers assigned to each account |
| Purpose | Organizes financial transactions by category | Facilitates quick identification and entry of accounts |
| Format | Grouped accounts with names (Assets, Liabilities, Equity, Revenue, Expenses) | Code system (e.g., 1000 for Assets, 2000 for Liabilities) |
| Usage | Reference framework for financial reporting and analysis | Data entry tool to streamline bookkeeping processes |
| Benefits | Clear financial structure, compliance, reporting insights | Improved data accuracy, faster transaction processing |
| Examples | Cash, Accounts Receivable, Sales Revenue | 1001 (Cash), 1100 (Accounts Receivable), 4000 (Sales Revenue) |
Understanding the Chart of Accounts
The Chart of Accounts is a comprehensive listing of all financial accounts used by a business to categorize transactions and organize financial reporting, enabling clear tracking of assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses. Account Codes, typically numeric or alphanumeric, serve as unique identifiers within the Chart of Accounts to streamline data entry and ensure consistency across accounting software. Understanding the structure and purpose of the Chart of Accounts is essential for accurate bookkeeping and financial analysis, as it forms the foundation for recording and summarizing all financial activities.
What Are Account Codes?
Account codes are unique numerical or alphanumeric identifiers assigned to each account within a chart of accounts, enabling precise classification and tracking of financial transactions. These codes streamline bookkeeping by facilitating faster data entry, accurate reporting, and easier reconciliation of accounts. Proper use of account codes enhances financial analysis by allowing clear categorization of revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
Key Differences Between Chart of Accounts and Account Codes
The Chart of Accounts organizes all financial accounts in a structured list, categorized by assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses, providing a comprehensive overview of an organization's financial structure. Account Codes are unique identifiers assigned to each account within the Chart of Accounts, enabling precise tracking and reporting of financial transactions. Key differences between the two lie in function and granularity: the Chart of Accounts defines the account categories and hierarchy, while Account Codes facilitate detailed data entry and system integration for bookkeeping accuracy.
The Role of Chart of Accounts in Bookkeeping
The Chart of Accounts serves as the foundational framework in bookkeeping, categorizing all financial transactions into organized, specific accounts to ensure accurate record-keeping. It provides a systematic structure that facilitates the classification, tracking, and reporting of assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses. By using the Chart of Accounts, businesses enhance financial analysis and compliance, promoting clear visibility into financial health and operational efficiency.
How Account Codes Streamline Financial Reporting
Account codes enhance the Chart of Accounts by assigning unique identifiers to each financial category, enabling faster data retrieval and error reduction. Streamlined account coding improves accuracy in transaction classification, facilitating real-time financial reporting and comprehensive analysis. Businesses benefit from increased efficiency in budgeting, auditing, and regulatory compliance through standardized account codes.
Building an Effective Chart of Accounts
Building an effective Chart of Accounts involves organizing financial data into clear, distinct categories that align with business operations. Account codes streamline this process by providing a systematic numbering system, improving accuracy and ease of tracking transactions. A well-structured Chart of Accounts ensures consistent financial reporting and simplifies bookkeeping tasks.
Assigning and Managing Account Codes
Assigning and managing account codes in bookkeeping involves systematically categorizing financial transactions within the chart of accounts to ensure accurate tracking and reporting. Account codes provide a numerical or alphanumeric system that links each transaction to specific accounts, facilitating efficient data entry and retrieval. Proper management of these codes enhances financial clarity, simplifies audits, and supports compliance with accounting standards.
Best Practices for Linking Account Codes to Chart of Accounts
Linking account codes to the chart of accounts ensures precise financial categorization and streamlines reporting accuracy in bookkeeping. Best practices include maintaining a consistent and hierarchical coding structure aligned with the chart of accounts to facilitate quick identification and minimize errors. Regular audits and updates to both the chart of accounts and account codes promote data integrity and adaptability to evolving business needs.
Common Mistakes in Using Chart of Accounts and Account Codes
Common mistakes in using Chart of Accounts and Account Codes include inconsistent naming conventions, which complicate financial reporting and analysis. Overloading account codes with excessive detail can lead to confusion and errors in transaction categorization. Neglecting regular updates to the chart fails to reflect organizational changes, resulting in inaccurate financial statements and compliance issues.
Optimizing Bookkeeping with Structured Account Categorization
A well-structured Chart of Accounts (COA) organizes financial transactions into clear categories, enabling precise tracking of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Account Codes within the COA assign specific numerical identifiers to each category, streamlining data entry and enhancing reporting accuracy. Optimizing bookkeeping through structured account categorization improves financial analysis, reduces errors, and supports compliance with accounting standards.
Chart of Accounts vs Account Codes Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com