The Sales Journal records all credit sales transactions, capturing details such as customer names, invoice numbers, and amounts owed, which aids in tracking revenue efficiently. The Purchase Journal, on the other hand, logs all credit purchases, documenting supplier information, invoice dates, and payable amounts to manage expenses effectively. Differentiating these journals streamlines financial record-keeping and improves accuracy in accounts receivable and accounts payable management.
Table of Comparison
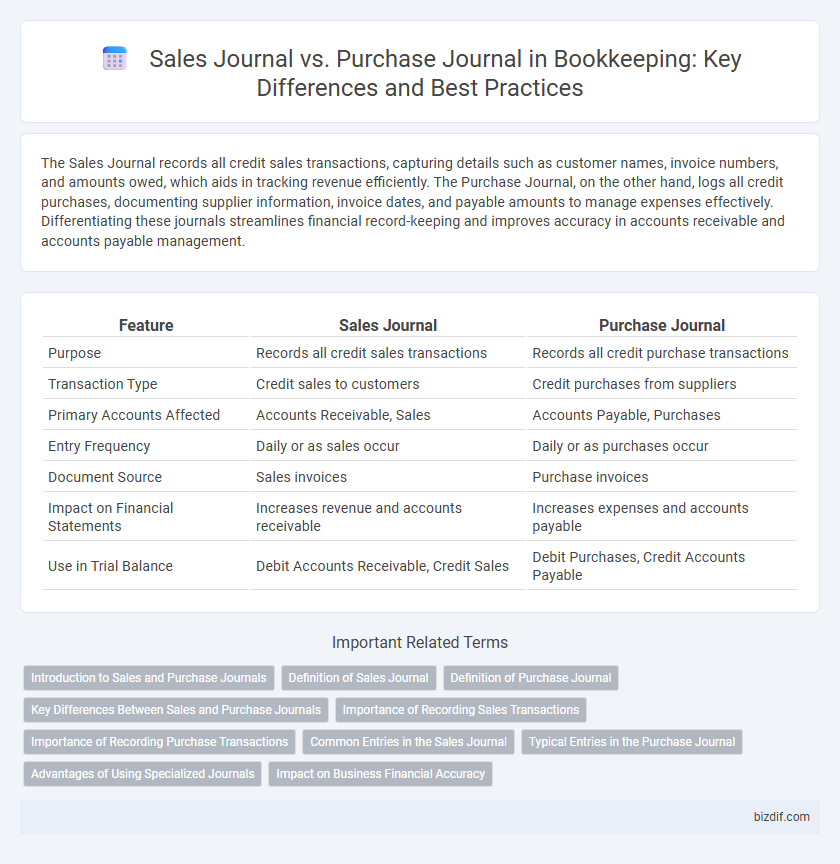
| Feature | Sales Journal | Purchase Journal |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Records all credit sales transactions | Records all credit purchase transactions |
| Transaction Type | Credit sales to customers | Credit purchases from suppliers |
| Primary Accounts Affected | Accounts Receivable, Sales | Accounts Payable, Purchases |
| Entry Frequency | Daily or as sales occur | Daily or as purchases occur |
| Document Source | Sales invoices | Purchase invoices |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Increases revenue and accounts receivable | Increases expenses and accounts payable |
| Use in Trial Balance | Debit Accounts Receivable, Credit Sales | Debit Purchases, Credit Accounts Payable |
Introduction to Sales and Purchase Journals
Sales journals record credit sales transactions, capturing details such as invoice numbers, customer names, and sales amounts to streamline revenue tracking. Purchase journals document credit purchases, logging supplier information, invoice data, and purchase totals for accurate expense management. Both journals serve as specialized subsidiary books that enhance financial accuracy by segregating different types of transactions before posting to the general ledger.
Definition of Sales Journal
The sales journal is a specialized accounting record used to document all credit sales of merchandise made by a business, capturing details such as invoice numbers, customer accounts, and sales amounts. It exclusively tracks sales transactions on credit, separate from cash sales, to streamline revenue recognition and account management. This journal facilitates accurate posting to accounts receivable and revenue accounts, improving financial reporting and audit efficiency.
Definition of Purchase Journal
The Purchase Journal is a specialized accounting ledger used to record all credit purchases of goods and services made by a business. It specifically tracks supplier invoices and purchase transactions, enabling efficient monitoring of payables and accurate financial reporting. Differentiated from the Sales Journal, which records credit sales, the Purchase Journal focuses solely on purchases, ensuring precise data entry and streamlined bookkeeping.
Key Differences Between Sales and Purchase Journals
Sales journals record all credit sales transactions, helping businesses track revenue generated from customers. Purchase journals document credit purchases, focusing on tracking expenses owed to suppliers. The key difference lies in their purpose: sales journals capture income events, while purchase journals detail expenditure events.
Importance of Recording Sales Transactions
Accurate recording of sales transactions in the Sales Journal ensures proper tracking of revenue and customer accounts, which is essential for financial reporting and tax compliance. Maintaining detailed entries in the Sales Journal helps businesses monitor cash flow, manage accounts receivable, and identify sales trends for strategic decision-making. In contrast, the Purchase Journal focuses on recording purchases, which highlights the distinct role each journal plays in organizing financial data efficiently.
Importance of Recording Purchase Transactions
Accurately recording purchase transactions in the purchase journal is essential for maintaining precise accounts payable and inventory levels. This detailed documentation helps businesses track expenses, manage vendor relationships, and prepare financial statements with integrity. Proper purchase journal entries ensure compliance with accounting standards and support effective cash flow management.
Common Entries in the Sales Journal
Common entries in the Sales Journal primarily include credit sales transactions where goods or services are sold on account, recording customer names, invoice dates, and amounts. These entries capture total sales revenue, accounts receivable, and sales tax details for accurate tracking and reporting. Properly maintained Sales Journals enhance financial accuracy and streamline the preparation of financial statements.
Typical Entries in the Purchase Journal
Typical entries in the purchase journal record credit purchases of inventory, supplies, and services, listing details such as date, vendor name, invoice number, and amount. Each entry debits the relevant asset or expense account while crediting Accounts Payable, reflecting the company's obligation to pay the supplier. These detailed entries allow businesses to track outstanding payables and manage cash flow efficiently.
Advantages of Using Specialized Journals
Specialized journals like the Sales Journal and Purchase Journal streamline the bookkeeping process by categorizing transactions, which enhances accuracy and efficiency in recording sales and purchases separately. These journals reduce errors by allowing accountants to focus on specific types of transactions, making reconciliation and auditing more straightforward. Using specialized journals also saves time by speeding up data entry and facilitating better financial analysis through organized transaction records.
Impact on Business Financial Accuracy
Sales journals, which record all credit sales, directly influence revenue recognition and cash flow accuracy, ensuring businesses have precise data on outstanding customer payments. Purchase journals track credit-based vendor transactions, impacting expense recording and payable management, thus maintaining accurate liability statements. Together, these journals enhance overall financial accuracy by providing detailed and organized records crucial for effective financial reporting and decision-making.
Sales Journal vs Purchase Journal Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com