Overlock stitching creates strong, flexible seams by trimming fabric edges while stitching, making it ideal for sewing stretchy or knit pet clothing. Lockstitch sewing produces durable, precise seams with a balanced stitch formed by interlocking threads, perfect for structured pet accessories and garments. Choosing between overlock and lockstitch stitching depends on the desired stretch and finish of the pet item being sewn.
Table of Comparison
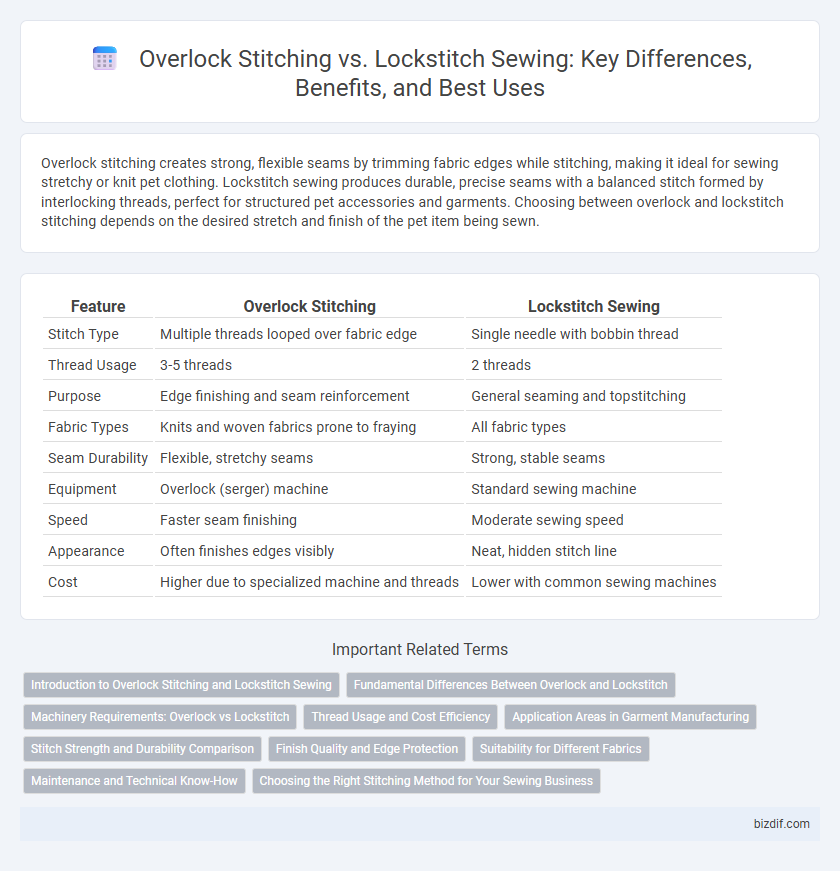
| Feature | Overlock Stitching | Lockstitch Sewing |
|---|---|---|
| Stitch Type | Multiple threads looped over fabric edge | Single needle with bobbin thread |
| Thread Usage | 3-5 threads | 2 threads |
| Purpose | Edge finishing and seam reinforcement | General seaming and topstitching |
| Fabric Types | Knits and woven fabrics prone to fraying | All fabric types |
| Seam Durability | Flexible, stretchy seams | Strong, stable seams |
| Equipment | Overlock (serger) machine | Standard sewing machine |
| Speed | Faster seam finishing | Moderate sewing speed |
| Appearance | Often finishes edges visibly | Neat, hidden stitch line |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized machine and threads | Lower with common sewing machines |
Introduction to Overlock Stitching and Lockstitch Sewing
Overlock stitching uses multiple threads to sew, trim, and finish fabric edges simultaneously, creating durable seams ideal for stretch and knit materials. Lockstitch sewing employs a single needle with a bobbin thread to form strong, precise stitches commonly used in garment construction and quilting. Overlock machines typically produce faster, flexible seams, while lockstitch machines deliver neat, secure stitches essential for everyday sewing projects.
Fundamental Differences Between Overlock and Lockstitch
Overlock stitching uses multiple threads and a loopers system to simultaneously trim fabric edges and sew, creating stretchable seams ideal for knit fabrics and preventing fraying. Lockstitch sewing employs two threads--the needle thread and bobbin thread--that interlock within the fabric layers, producing a strong, straight stitch suitable for most general sewing applications but without edge finishing capabilities. The fundamental difference lies in overlock's edge finishing and stretch adaptability versus lockstitch's strength and versatility in seam construction.
Machinery Requirements: Overlock vs Lockstitch
Overlock stitching machines require multiple threads and loopers to create strong, flexible seams while trimming fabric edges simultaneously, making them ideal for stretch fabrics and finishing raw edges efficiently. Lockstitch machines use a single needle thread and a bobbin thread, producing a tight, durable stitch ideal for straight seams and general garment construction. Overlock machines tend to have more complex mechanisms and require specialized threading skills, whereas lockstitch machines are simpler and more versatile for various sewing tasks.
Thread Usage and Cost Efficiency
Overlock stitching uses multiple threads, often three to five, providing strong seam durability and preventing fabric fraying, but it consumes more thread than lockstitch sewing, which typically uses two threads. Lockstitch sewing is more thread-efficient, resulting in lower thread costs, making it ideal for production runs where cost control is critical. The higher thread expenditure in overlock stitching is offset by its superior edge finishing and faster sewing speeds, enhancing overall production efficiency despite increased material use.
Application Areas in Garment Manufacturing
Overlock stitching excels in finishing edges and preventing fabric fraying, making it ideal for knitwear, activewear, and stretch fabrics where seam flexibility is crucial. Lockstitch sewing is preferred for constructing durable seams in woven fabrics, such as denim, formal wear, and tailored garments, offering strength and a clean, professional finish. Combining both techniques optimizes garment durability and aesthetics across diverse apparel categories.
Stitch Strength and Durability Comparison
Overlock stitching features multiple threads looping around fabric edges, enhancing edge strength and preventing fraying, making it ideal for stretch fabrics and seams under tension. Lockstitch sewing uses a single needle and bobbin thread interlocked within the fabric, providing superior tensile strength and long-lasting durability for flat seams on woven fabrics. Overlock excels in seam flexibility and edge finishing, while lockstitch delivers higher overall stitch strength and resistance to seam burst during wear.
Finish Quality and Edge Protection
Overlock stitching offers superior edge protection by encasing fabric edges with multiple threads, preventing fraying and ensuring durability, which is ideal for knit and stretch fabrics. Lockstitch sewing produces a clean, precise finish with strong, tight stitches suitable for seams but lacks the edge-wrapping capability that overlock provides, making it less effective in preventing fraying. The finish quality of overlock stitching is generally smoother and more elastic, enhancing garment longevity compared to the more rigid and less flexible lockstitch seams.
Suitability for Different Fabrics
Overlock stitching excels in finishing stretch fabrics and knits by providing flexible, durable seams that prevent fraying, making it ideal for activewear and casual garments. Lockstitch sewing offers strong, precise stitches suited for woven fabrics and tailored pieces, such as dress shirts and suits, where a clean and polished appearance is essential. Choosing between overlock and lockstitch depends on fabric type; overlock suits stretchy, delicate materials while lockstitch is preferred for stable, structured textiles.
Maintenance and Technical Know-How
Overlock stitching requires regular maintenance of the loopers and differential feed to prevent thread tension issues and fabric puckering, demanding intermediate technical skills for timely adjustments and troubleshooting. Lockstitch sewing machines need frequent needle and bobbin case care, with precise timing alignment to avoid skipped stitches or thread breakage, typically requiring a higher level of mechanical expertise. Understanding the specific maintenance routines and technical know-how is essential for optimizing machine performance and extending the lifespan of both overlock and lockstitch equipment.
Choosing the Right Stitching Method for Your Sewing Business
Choosing Overlock stitching enhances efficiency for sewing businesses by simultaneously trimming, stitching, and finishing fabric edges, ideal for stretch and knit materials demanding durability. Lockstitch sewing offers precise, strong seams suitable for a wide range of fabrics, making it the preferred choice for detail-oriented, high-quality garment construction. Evaluating product type, fabric flexibility, and desired seam strength helps determine the optimal stitching method to maximize production quality and customer satisfaction.
Overlock stitching vs Lockstitch sewing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com